
Among the following, the most reactive towards alcoholic KOH is :
A. \[C{H_2} = CHBr\]
B. \[C{H_3}COC{H_2}C{H_2}Br\]
C. \[C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\]
D. \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}Br\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Halide organic compounds react with alcoholic $KOH$ to undergo nucleophilic elimination reaction of order 2 and it is represented as ${{E}_{2}}$. It is a bimolecular reaction where several atoms either in pairs or groups are removed from the reactant molecule in presence of a strong base.
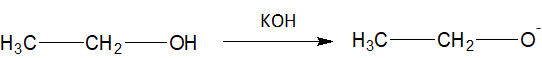
Complete step-by-step answer:Generally ${{E}_{2}}$ is a single-step reaction and in one step carbon-hydrogen bond and carbon-halogen bond mostly break off to form a new double bond. In basic medium, a strong base, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}{{O}^{-}}$ is formed.
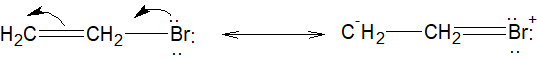
Option A: Br is attached to a \[s{p^2}\] hybridized carbon atom and the carbon-halogen bond gets a double bond character due to the delocalization of lone pairs of bromine atom, hence the bond strength increases. So Bromine ion cannot leave easily, thus the compound does not react with alcoholic $KOH$.
Options B, C, and D have halide attached to \[s{p^3}\]carbon atom and the carbon is a primary carbon as it is attached to further only one carbon.
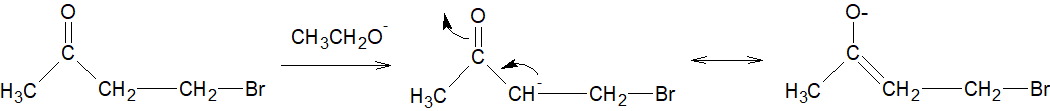
But option B is incorrect because the electronegative oxygen atom in the $C=O$ group pulls the electron density from carbon making it more electrophilic. Thus incoming base abstracts proton and thereby negative charge undergo resonance with the $C=O$ group and the rate of elimination decreases.
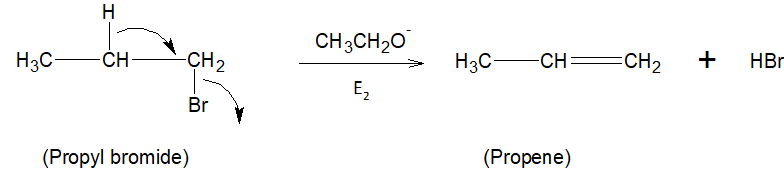
As we know the polarity between carbon-bromine bonds increases by increasing the +I effect which can be increased by increasing the alkyl group. Therefore between options C and D, a higher number of alkyl groups are present in compound D, propyl bromide than compound C. In the presence of strong base ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}{{O}^{-}}$, propyl bromide formed propene by ${{E}_{2}}$ reaction.
Option ‘D’ is correct
Note: In ${{E}_{2}}$ reaction an anti-coplanar orientation of the base and the leaving group must be required since both the electron-rich base and leaving group electrostatically repel each other forcing them to occupy the anti-coplanar position.
Complete step-by-step answer:Generally ${{E}_{2}}$ is a single-step reaction and in one step carbon-hydrogen bond and carbon-halogen bond mostly break off to form a new double bond. In basic medium, a strong base, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}{{O}^{-}}$ is formed.

Option A: Br is attached to a \[s{p^2}\] hybridized carbon atom and the carbon-halogen bond gets a double bond character due to the delocalization of lone pairs of bromine atom, hence the bond strength increases. So Bromine ion cannot leave easily, thus the compound does not react with alcoholic $KOH$.

Options B, C, and D have halide attached to \[s{p^3}\]carbon atom and the carbon is a primary carbon as it is attached to further only one carbon.
But option B is incorrect because the electronegative oxygen atom in the $C=O$ group pulls the electron density from carbon making it more electrophilic. Thus incoming base abstracts proton and thereby negative charge undergo resonance with the $C=O$ group and the rate of elimination decreases.

As we know the polarity between carbon-bromine bonds increases by increasing the +I effect which can be increased by increasing the alkyl group. Therefore between options C and D, a higher number of alkyl groups are present in compound D, propyl bromide than compound C. In the presence of strong base ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}{{O}^{-}}$, propyl bromide formed propene by ${{E}_{2}}$ reaction.

Option ‘D’ is correct
Note: In ${{E}_{2}}$ reaction an anti-coplanar orientation of the base and the leaving group must be required since both the electron-rich base and leaving group electrostatically repel each other forcing them to occupy the anti-coplanar position.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




