
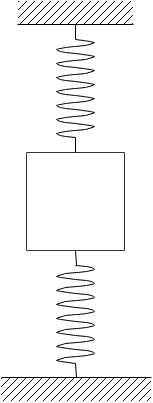
A block tied between two identical springs is in equilibrium. If the upper spring is cut, then the acceleration of the block just after the cut is $5 \mathrm{ms}^{-2}$. Now if instead of upper string lower spring is cut, then the acceleration of the block just after the cut will be (Take $g=10m/{{s}^{2}}$)
A $1.25 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$
B $5 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$
C $10 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$
D $2.5 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: We know that mechanics is the area of physics concerned with the motions of macroscopic objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Keeping this in mind, we can solve the given question.
Complete step by step answer
From the given question,
Let x be the displacement of each spring in equilibrium before any of the spring is cut. For such a situation, the upper spring stretches to exert a force on the body in the upward direction. Similarly, the lower spring compresses to exert a force on the body in the upward direction. Thus $\mathrm{kx}+\mathrm{kx}=\mathrm{mg}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{mg}{2k}$
Now when the upper spring is cut, the forces acting on the body are mg downwards and kx upwards. Thus, the acceleration of body $=\dfrac{\mathrm{mg}-\mathrm{kx}}{\mathrm{m}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{g}}{2}=5 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$ downwards
Now when the lower spring is cut, the forces acting are mg downwards and kx upwards again. Thus, the acceleration is $5 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$ downwards.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We must effectively be able to draw free body diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams.
Complete step by step answer
From the given question,
Let x be the displacement of each spring in equilibrium before any of the spring is cut. For such a situation, the upper spring stretches to exert a force on the body in the upward direction. Similarly, the lower spring compresses to exert a force on the body in the upward direction. Thus $\mathrm{kx}+\mathrm{kx}=\mathrm{mg}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{mg}{2k}$
Now when the upper spring is cut, the forces acting on the body are mg downwards and kx upwards. Thus, the acceleration of body $=\dfrac{\mathrm{mg}-\mathrm{kx}}{\mathrm{m}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{g}}{2}=5 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$ downwards
Now when the lower spring is cut, the forces acting are mg downwards and kx upwards again. Thus, the acceleration is $5 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$ downwards.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We must effectively be able to draw free body diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 - Units And Measurements - 2025-26

Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurement - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26




