




Introduction of Liberalisation
Liberalisation used to end these cutoff points, and open a few districts of the economy. Anyway, some movement proposals had been presented in the Eighties in areas of item import method, science up-certification, money related approach, and abroad hypothesis, current approving, and financial change strategies sent off in 1991 have been more vital in general.
Liberalisation
What is Liberalisation?
Liberalisation absolutely alludes to the cure of realm limitations inside the areas of social, political, and monetary approaches. Advancement in monetary inclusion centres around the markdown of specialists' lawful rules and limitations in locale to motivate higher support with the guidance of individual elements..These hindrances covered charge guidelines, broad funding impediments, accounting rules, and prison issues. Monetary movement lessened this huge number of cutoff points and conceded two or three impediments to regulating the financial structure of the singular region.
Features of Liberalisation
Some features of liberalisation are:
To further develop obstruction between home associations.
To progress new exchange and change imports and wares.
To work on the mechanical ability and abroad capital.
To push the overall market of a country.
To restrict the commitment weight of a country.
To free the financial sense of the US with the aid of enabling the singular quarter and worldwide associations to make adventures and develop.
To impel the singular district to take an energetic stage in the improvement cycle.
To restrict the spot of the public area in current and future improvement.
Impact of Liberalisation
1. Positive Impact of Liberalisation
Free Movement of Capital: Advancement has redesigned the movement of capital by making it sensible for the associations to show up at the capital from the monetary sponsor and take a useful endeavour.
Assortment for Monetary Sponsor: The monetary supporters will be benefitted by placing a piece of their business into an expanding asset class.
Impact on Cultivating: Around here, the altering plans have experienced a giant change, yet the impact of movement can't be definitively assessed. The government's constraints and interventions ought to be noticeable from the creation to the dissemination of the yields.
2. Negative Impact of Liberalisation
The Crippling of the Economy: An enormous reconstruction of the political power and financial energy will provoke and incapacitate the complete Indian economy.
Mechanical Impact: Fast improvement in science licences many restricted-scope adventures and different social affairs in India to both change to changes or shut their associations.
Combinations and Acquisition: Here, the little social affairs meet with huge associations. The staff of the confidential endeavours may moreover have to embellish their abilities and turn out to be precisely advanced. This bettering off limits and the time it could take could similarly provoke non-effectiveness and can be a load to the association's capital.
Benefits of Liberalisation of FDI
An upgrade in FDI inflows will assemble the dollars helpful in the money-related structure and reasons for monetary intermediation to augment through monetary business areas and banking systems. The affiliations focused on FDI are no question to posting their parts in the neighbourhood securities exchange, which works on the system for monetary new development. Oppositely to this cycle, a well-working. a cash-related market can connect abroad trailblazers, as they recognise such a market as a sign of vitality.
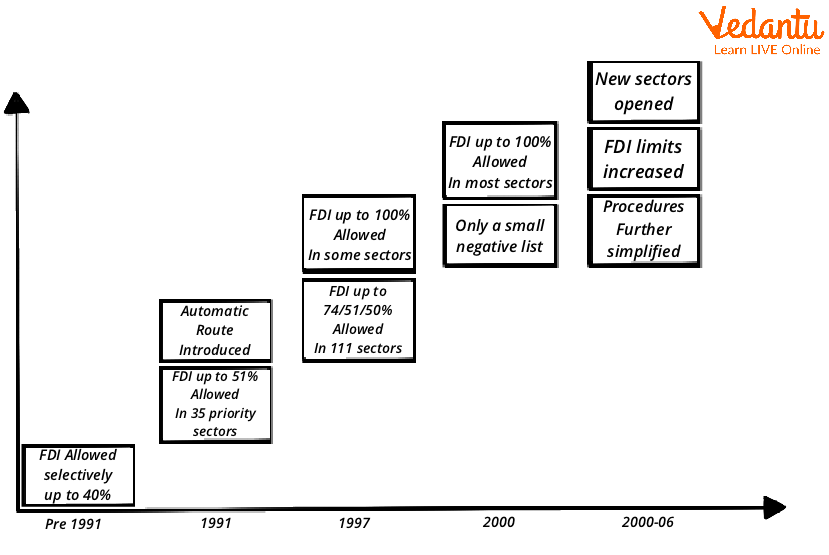
Liberalisation of FDI Policy
Observational investigations have shown that FDI and substitute headway are interlinked. This hyperlink has been created to be more vital in the WTO framework the spot different creating economies have embraced the import headway procedures. The making volumes of the trades of economies and their framework made the procedure makers' principal centre flicker subordinate totally upon the speculation that whether FDI aims to change or change helps FDI inflows. The explicit issue used to be what sort of exchange upholds FDI.
Conclusion
The mark of the union on certainty and nonattendance of sponsoring in went about as limitations to mechanical improvement and accordingly provoked the collecting of unremarkable breathtaking products. There is solid certainty that broad stocks are viable to Indian things notwithstanding predominant in Indian culture. Someone suitably set it up that the circumstance of the state following two centuries of misleading and surprising division should be taken care of in thought sooner than surveying the improvement of the persevering present-day system.
FAQs on Impact of Liberalization on the Economy
1. What does economic liberalisation mean in simple terms?
Economic liberalisation refers to the process of reducing government controls and restrictions on economic activities. In the Indian context, this meant opening up the economy to private and foreign companies, removing trade barriers like high import taxes, and simplifying the rules for businesses to operate. The main goal was to make the economy more market-oriented and globally competitive.
2. What were the main positive impacts of liberalisation on the Indian economy?
Liberalisation brought several significant positive changes to the Indian economy. The most important ones include:
- Increased Foreign Investment (FDI): It became easier for foreign companies to invest in India, bringing in necessary capital, technology, and jobs.
- More Choices for Consumers: The entry of new companies gave consumers a wider variety of goods and services at more competitive prices.
- Growth in Foreign Exchange Reserves: Increased exports and foreign investment helped India build strong reserves of foreign currency.
- Boost to the Service Sector: Sectors like IT, telecommunications, and banking grew rapidly, creating new employment opportunities.
3. Did liberalisation have any negative effects on the economy?
Yes, despite its benefits, liberalisation also had some negative consequences. The main challenges were:
- Threat to Small Industries: Many small, local businesses found it difficult to compete with large multinational corporations that had more resources and advanced technology.
- Unbalanced Development: Economic growth was often concentrated in urban areas and in sectors like services, while the agricultural sector grew much more slowly.
- Increased Dependence: The economy became more dependent on foreign funds and technology, making it vulnerable to global economic shifts.
4. Why was economic liberalisation considered necessary for India in 1991?
By 1991, India was facing a severe economic crisis. Its foreign exchange reserves were dangerously low, almost running out of money to pay for essential imports. Government debt was extremely high, and prices were rising rapidly due to inflation. The old system of government controls, known as the 'Licence Raj', was preventing businesses from growing. Liberalisation was introduced to solve this crisis by encouraging investment, boosting production, and making the Indian economy more efficient.
5. How did liberalisation affect India's industrial sector?
Liberalisation dramatically changed the industrial sector. Before 1991, many industries required a government licence to start or expand production. Liberalisation abolished industrial licensing for most industries. It also reduced the number of industries reserved only for the public sector. This allowed private companies, including foreign ones, to enter new fields, which led to increased competition, modernisation, and greater production.
6. How is liberalisation different from globalisation?
Although they are closely related, they are different concepts. Liberalisation refers to the specific policies a country makes to reduce its own internal government controls and trade barriers. It is an action taken by a country. Globalisation is the broader outcome of such policies, referring to the increasing integration and interdependence of a country's economy with the rest of the world. In short, liberalisation is a key step that helps facilitate globalisation.
7. Did liberalisation only benefit large companies, or did it also affect small-scale industries?
This is a major point of debate. While large companies benefited greatly from the freedom to expand and attract foreign investment, small-scale industries faced a mixed impact. On one hand, they faced intense competition from large firms and imported goods, which forced many to close down. On the other hand, some small businesses adapted by becoming suppliers to larger corporations or found new markets, leading to their growth.
8. What were the key financial sector reforms introduced during liberalisation?
The financial sector saw major reforms to make it more efficient. The role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) shifted from a strict regulator to a facilitator of the financial system. Private sector banks, including foreign banks, were permitted to operate in India. This increased competition, leading to better services and more credit options for both individuals and businesses. Investment rules were also relaxed, allowing more foreign institutional investment in India's stock markets.























