NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry - The p-Block Elements - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 - The p-Block Elements solved by expert Chemistry teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 7 - The p-Block Elements Exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your Examinations.
Download the Free PDF covering all the solutions from the Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p- Block Elements from Vedantu to help your understanding go deeper into the subject matter. NCERT Exemplar is a great additional tool that can be very beneficial for students of Class 12 as the book does not only help to solve questions in the final school level Exams but also competitive Exams like JEE, NEET, etc.
Chemistry requires a lot of revision to make sure that students do not forget important formulas. The p-Block Elements is an important Chapter from Inorganic Chemistry that has a massive weightage in most Examinations. What makes this Chapter unique is that it is fairly easy to comprehend and understand and therefore makes it a perfect way for students to score more in their upcoming Exams.
Why Should I study The p-Block Elements from Class 12 NCERT Exemplar?
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
Chapter 7 – p- Block Elements
(Examples, Easy Methods and Step by Step Solutions)
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
1. On addition of conc. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ to a chloride salt, colourless fumes are evolved but in case of iodide salt, violet fumes come out. This is because
(i) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ reduces ${\text{HI}}$ to ${{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$
(ii) ${\text{HI}}$ is of violet colour
(iii) ${\text{HI}}$ gets oxidised to ${{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$
(iv) ${\text{HI}}$ changes to ${\text{H}}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_3}$
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
Hydrogen iodide is a more powerful reducing agent than sulphuric acid, it reduces the amount of iodine in the solution from ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{to S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{and HI to }}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$
When chloride salts are treated with sulfuric acid, ${\text{HCl}}$ gas is formed, which produces a colourless gas.
${\text{NaCl + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} \to {\text{HCl + N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
Violet fumes are produced during the reaction due to the creation of iodine $(I2)$ gas.
${\text{2NaI + }}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + 2HI}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$
2. In qualitative analysis when ${\text{}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with dil. ${\text{HCl}}$, a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with dil. ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives _________.
(i) deep blue precipitate of ${\text{Cu}}{\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}$
(ii) deep blue solution of ${\left[ {{\text{Cu}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{4}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}$
(iii) deep blue solution of ${\text{Cu}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}$
(iv) deep blue solution of ${\text{Cu}}{\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }}{\text{.Cu}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}$
Ans. Correct option (ii)
When ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ is passed through an aqueous solution of salt acidified with dil. ${\text{HCl}}$ in qualitative analysis, a black precipitate is produced. When the precipitate is boiled with dil. ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, a blue solution results. When an excess of ammonia aqueous solution is added to this solution, it produces a deep blue ${{\text{[Cu(N}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{)}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{]}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}$ solution.
3. In a cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid molecule, how many single and double bonds are present?
(i) 3 double bonds; 9 single bonds
(ii) 6 double bonds; 6 single bonds
(iii) 3 double bonds; 12 single bonds
(iv) Zero double bonds; 12 single bonds
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, and other oxoacids are formed by phosphorus. P is tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms in phosphorus oxoacids. At least one P-H bond and an O-H bond are known to form in all of them.
4. Which of the following elements can be involved in ${\text{p\pi --d\pi }}$ bonding?
(i) Carbon
(ii) Nitrogen
(iii) Phosphorus
(iv) Boron
Ans. Correct option (iii)
If an electron pair is donated to a vacant orbital on one atom and a lone pair of electrons on the other, the bonding is designated ${{p\pi --d\pi }}$ depending on the orbital to which the electron pair is donated and the orbital from which the electron pair is donated.
Because their valence shells lack d-orbitals, nitrogen, carbon, and boron cannot form a pi bond. Phosphorus, on the other hand, can produce pi bonds.
5. Which of the following pairs of ions are isoelectronic and isostructural?
(i) ${\text{CO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}{\text{ , NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}$
(ii) ${\text{ClO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ , CO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$
(iii) ${\text{SO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}{\text{, NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}$
(iv) ${\text{ClO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ , SO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$
Ans. Correct option (i)
The compound has the following number of electrons:
${\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ = 32}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
${\text{CO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}{\text{ = 32}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
${\text{ClO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ = 42}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
${\text{SO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ = 42}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
Hence, ${\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{and CO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$ are isoelectronic.
6. Affinity for hydrogen decreases in the group from fluorine to iodine. Which of the halogen acids should have highest bond dissociation enthalpy?
(i) ${\text{HF}}$
(ii) ${\text{HCl}}$
(iii) ${\text{HBr}}$
(iv) ${\text{HI}}$
Ans. Correct option (i)
Fluorine is the most reactive element, forming hydrogen fluoride when it combines with hydrogen gas.
Due to the shorter bond length between the two atoms, it takes a lot of energy to break the link between hydrogen and fluorine.
As a result, as we move down the group, the bond dissociation energy drops.
7. Bond dissociation enthalpy of E—H (E = element) bonds is given below. Which of the compounds will act as the strongest reducing agent?
${\text{Compound N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ As}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ Sb}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }}$
${\Delta _{{\text{diss}}}}\left( {{\text{E---H}}} \right){\text{/kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{{\text{--1}}}}{\text{ 389 322 297 255}}$
(i) ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
(ii) ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
(iii) ${\text{As}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
(iv) ${\text{Sb}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (iv)
The E-H bond dissociation energy of ${\text{Sb}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is the lowest among the aforementioned compounds, it easily releases H, making it a strong reducing agent. The greater the lowering agent, the weaker the E-H bond.
8. On heating with concentrated ${\text{NaOH}}$ solution in an inert atmosphere of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, white phosphorus gives a gas. Which of the following statements is incorrect about the gas?
(i) It is highly poisonous and smells like rotten fish.
(ii) It’s solution in water decomposes in the presence of light.
(iii) It is more basic than ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$.
(iv) It is less basic than ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$.
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
When heated with concentrated ${\text{NaOH}}$ in an inert ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ environment. It forms
${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}$
${\text{P_4}}{\text{ + 3NaOH + 3}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{O}} \to {\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + 3Na}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
As we progress from the top to the bottom in a group, the basic character of hydrides reduces ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}$ is basic than ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}$.
9. Which of the following acids forms three series of salts?
(i) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
(ii) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
(iii) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
(iv) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (iii) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
When it reacts with a metal atom, it can produce three different forms of salts, referred known as the three series of salts.
${{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + Na}} \to {\text{NaH}_{ 2P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}}$
${{\text{Na}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + Na}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{HP}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}}$
${{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{HP}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{ + Na}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{.}}}$
10. Strong reducing behaviour of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is due to
(i) Low oxidation state of phosphorus
(ii) Presence of two –OH groups and one P–H bond
(iii) Presence of one –OH group and two P–H bonds
(iv) High electron gain enthalpy of phosphorus
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has one O-H group and two P-H bonds
The existence of a P-H link gives phosphorus oxyacids their reducing characteristics. It has a strong proclivity for releasing protons. As a result, it demonstrates a decreasing nature.
11. On heating lead nitrate forms oxides of nitrogen and lead. The oxides formed are ______.
(i) ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O, PbO}}$
(ii) ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{, PbO}}$
(iii) ${\text{NO, PbO}}$
(iv) ${\text{NO, Pb}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
On heating, lead nitrate decomposes into lead monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen.
${\text{2Pb(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{2PbO + 4N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{.}}$
12. Which of the following elements does not show allotropy?
(i) Nitrogen
(ii) Bismuth
(iii) Antimony
(iv) Arsenic
Ans. Correct option is (i)
The single N-N bond is weak because of high interelectronic repulsion of the non-bonding electrons, owing to the small bond length. As a result the catenation tendency is weaker in nitrogen that is why it does not show allotropy.
13. Maximum covalency of nitrogen is ______________.
(i) 3
(ii) 5
(iii) 4
(iv) 6
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
The valence electrons of nitrogen are two 2s and three 2p. Nitrogen can make three covalent bonds by sharing its three 2p electrons. Consider the ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule. The nitrogen atom, however, still contains a lone pair of electrons in the 2s orbital. It can make one bond by transferring these two electrons from the lone pair. Consider the NH4+ molecule.
As a result, nitrogen can create four different bonds.
14. Which of the following statements is wrong?
(i) Single N–N bond is stronger than the single P–P bond.
(ii) ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ can act as a ligand in the formation of coordination compound with transition elements.
(iii) ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is paramagnetic in nature.
(iv) Covalency of nitrogen in ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$ is four
Ans. Correct option is (i)
The N-N sigma bond (single bond) is weaker than the P-P sigma bond (single bond) due to the smaller size of nitrogen which increases the interelectronic repulsions and thus making the bond weaker.
15. A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3- ion. It is due to the formation of
(i) ${\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{5}}}\left( {{\text{NO}}} \right)} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}$
(ii) ${\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }}{\text{.N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
(iii) ${\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{4}}}{{\left( {{\text{NO}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}$
(iv) ${\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }}{\text{.HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (i)
The 'Brown Ring Test' is an identification and conformation test of the nitrate ion ${\text{(NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{)}}$ using conc. ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ and newly produced ${\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. Place the ${\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{}}$ containing sample in a test tube. Then, with gentle shaking, add conc ${{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ dropwise, heat it briefly on a Bunsen burner, and add freshly made greenish ${\text{FeS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ Then, due to the creation of brown coloured ${\text{[Fe(}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{(NO)]S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{}}$ complex, a brown ring forms in that test tube.
16. Elements of group-15 form compounds in +5 oxidation state. However, bismuth forms only one well characterised compound in +5 oxidation state. The compound is
(i) ${\text{B}}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$
(ii) ${\text{Bi}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{5}}}$
(iii) ${\text{BiC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$
(iv) ${\text{B}}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{5}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
Bismuth is the sole element that has an inert pair effect. Only generates trihalides and has a +3 oxidation state. Florine, on the other hand, is small and has a high electronegativity.
17. On heating ammonium dichromate and barium azide separately we get
(i) ${{\text{N}}_2}$ in both cases
(ii) ${{\text{N}}_2}$ with ammonium dichromate and ${\text{NO}}$ with barium azide
(iii) ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ with ammonium dichromate and ${{\text{N}}_2}$ with barium azide
(iv) ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ with ammonium dichromate and ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ with barium azide
Ans. Correct option is (i)
We get ${{\text{N}}_2}$ in both situations when we heat ammonium dichromate and barium azide separately.
${{\text{(N}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{{\text{2}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + }}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$
${\text{Ba(}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{Ba + 3}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{.}}$
18. In the preparation of ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$, we get ${\text{NO}}$ gas by catalytic oxidation of ammonia. The moles of ${\text{NO}}$ produced by the oxidation of two moles of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$.
will be ______.
(i) 2
(ii) 3
(iii) 4
(iv) 6
Ans. Correct option is (i)
The catalytic oxidation of ammonia produces ${\text{NO}}$ gas, which is used to make ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}$. 4 moles of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ created 4 moles of ${\text{NO}}$ in the equation below. As a result, the moles of ${\text{NO}}$ produced by oxidising two moles of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ will be two moles.
${\text{4N}}{{\text{H}}}_{\text{3}}{\text{ + 5}}{{\text{O}}}_{\text{2}} \to {\text{4NO + 6H}}{ _{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}{\text{.}}$
19. The oxidation state of central atom in the anion of compound ${\text{Na}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ will be ______.
(i) +3
(ii) +5
(iii) +1
(iv) –3
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
$\mathrm{Na}\left(\mathrm{H}_{2}\right) \mathrm{PO}_{2}$
$=+1+(2 \mathrm{x}+1)+\mathrm{x}+2(-2)=0$
$\mathrm{x}-1=0$
$or \mathrm{x}=1$
20. Which of the following is not tetrahedral in shape?
(i) ${\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ + }}$
(ii) ${\text{SiC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$
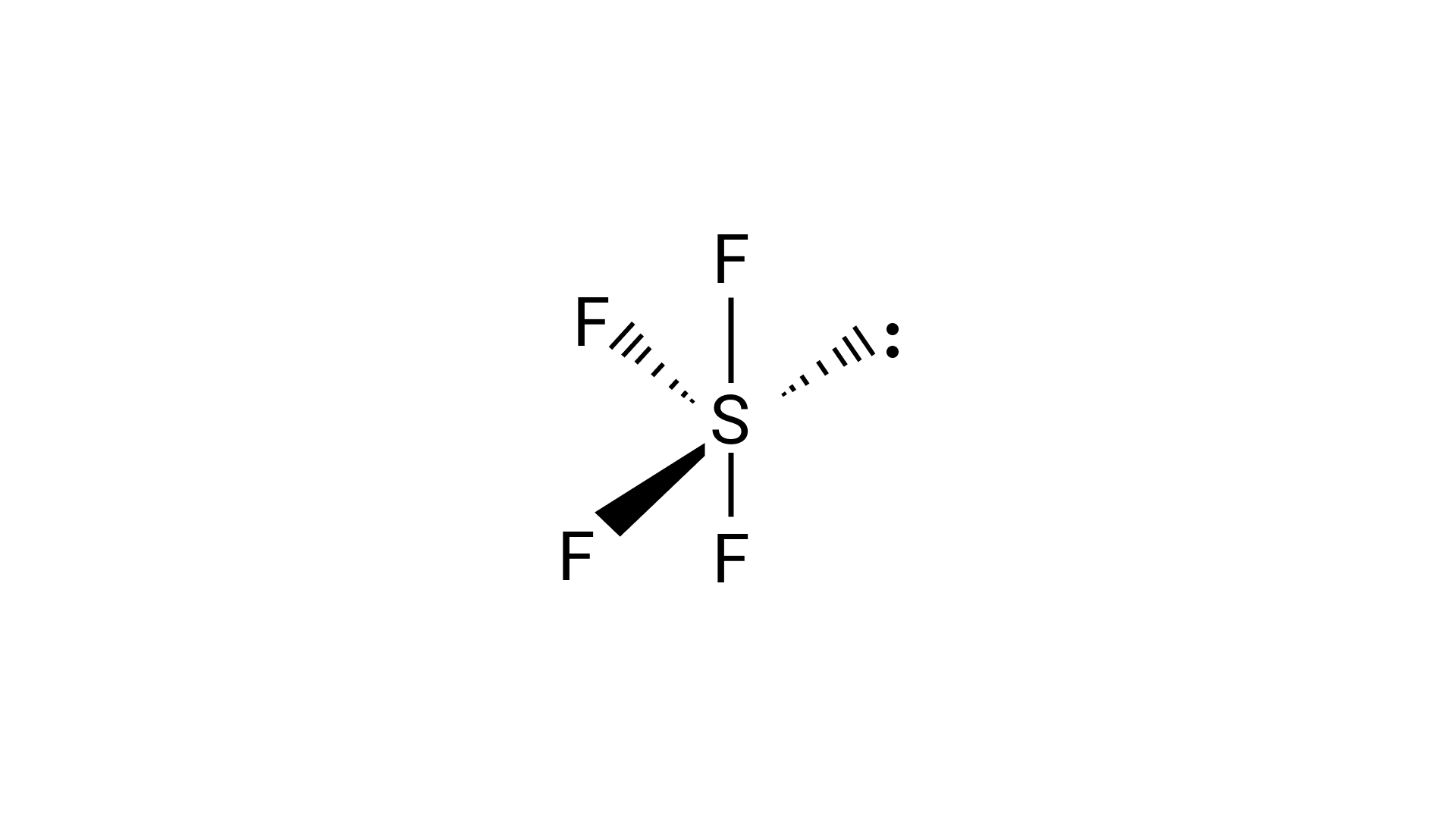
(iii) ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$
(iv) ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
The C-atom in the ${\text{CO}}_{\text{3}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$ ion undergoes ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridization. ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{,NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ + }}{\text{ and SO}}_{\text{4}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$ have a tetrahedral structure, whereas it has a triangular planar structure.
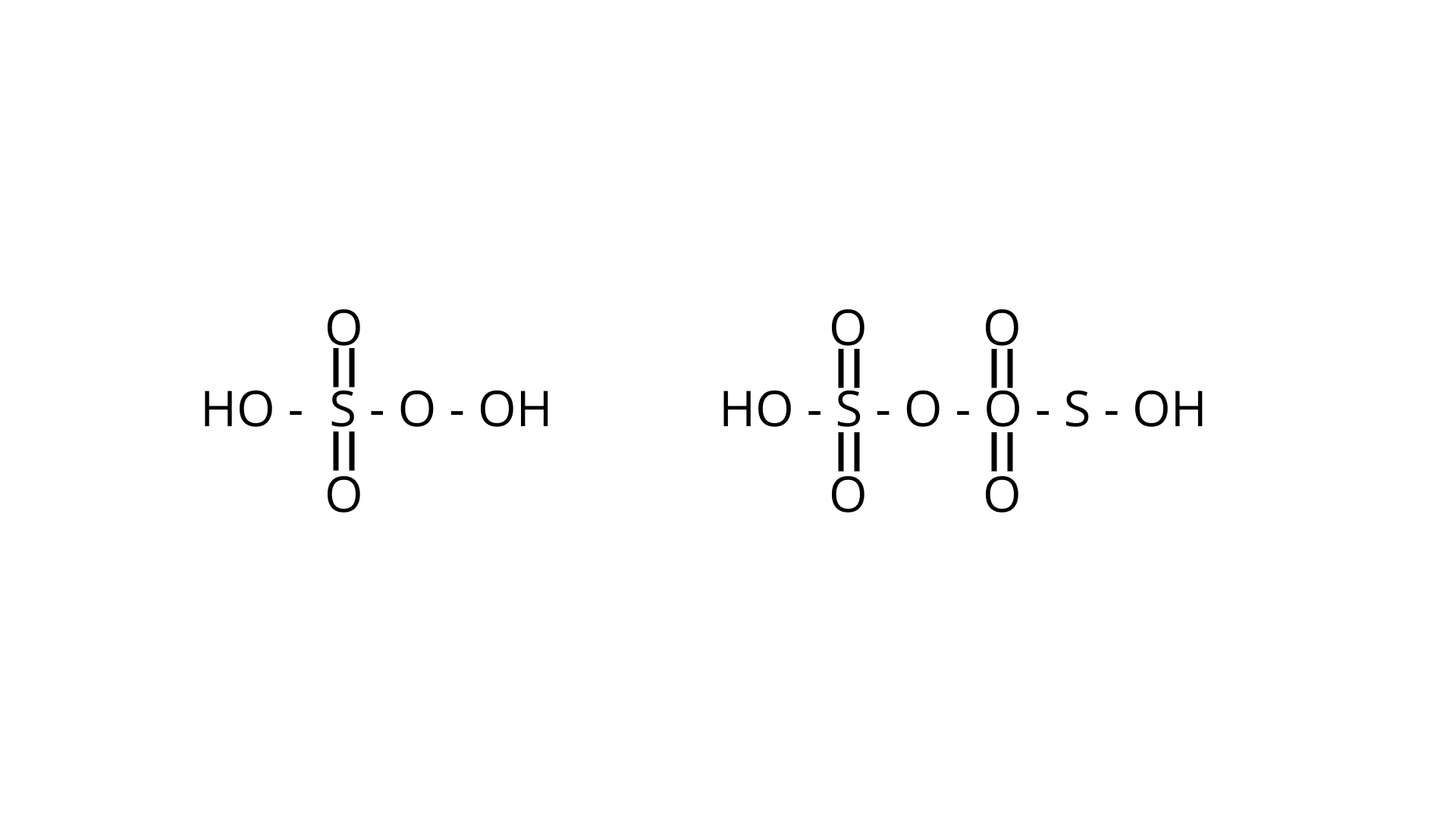
21. Which of the following are peroxoacids of sulphur?
(i) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}}$
(ii) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$
(iii) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{8}}}$
(iv) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (i)
Peroxy linkage refers to the presence of a bond between oxygen and oxygen (O-O) in a molecule.
Only ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$ of the sulphur oxoacids above have a peroxy linkage.
22. Hot conc. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ into two gaseous products?
(i) ${\text{Cu}}$
(ii) ${\text{S}}$
(iii) ${\text{C}}$
(iv) ${\text{Zn}}$
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
$\mathrm{C}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{SO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$
Conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ oxidises C to produce two gaseous products.
23. A black compound of manganese reacts with a halogen acid to give greenish yellow gas. When excess of this gas reacts with ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ an unstable trihalide is formed. In this process the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from _________.
(i) – 3 to +3
(ii) – 3 to 0
(iii) – 3 to +5
(iv) 0 to – 3
Ans. Correct option is (iv)
$\underset{( \text { Black })}{\mathrm{MnO}_{2}}+4 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{MnCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+{\mathrm{Cl}_{2}}$
Greenish yellow color
$\stackrel{-3}{N H_{3}}+3 C l_{2} \rightarrow \stackrel{+3}{N C l_{3}}+3 H C l$
24. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken $O_{2}^{\text{ }+\text{ }}Pt\text{ }F_{6}^{-\text{ }}$ as a base compound. This is because
(i) both ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ and Xe}}$ have the same size.
(ii) both ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ and Xe}}$ have the same electron gain enthalpy.
(iii) both ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ and Xe}}$ have almost the same ionisation enthalpy.
(iv) both ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ and Xe}}$ are gases.
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
Bartlett noticed that Xenon's first ionisation potential is nearly identical to that of oxygen and used Born-Haber calculations to predict the presence of a stable compound: ${\text{X}}{{\text{e}}^ + }{\text{ Pt F}}_{\text{6}}^{\text{ - }}$
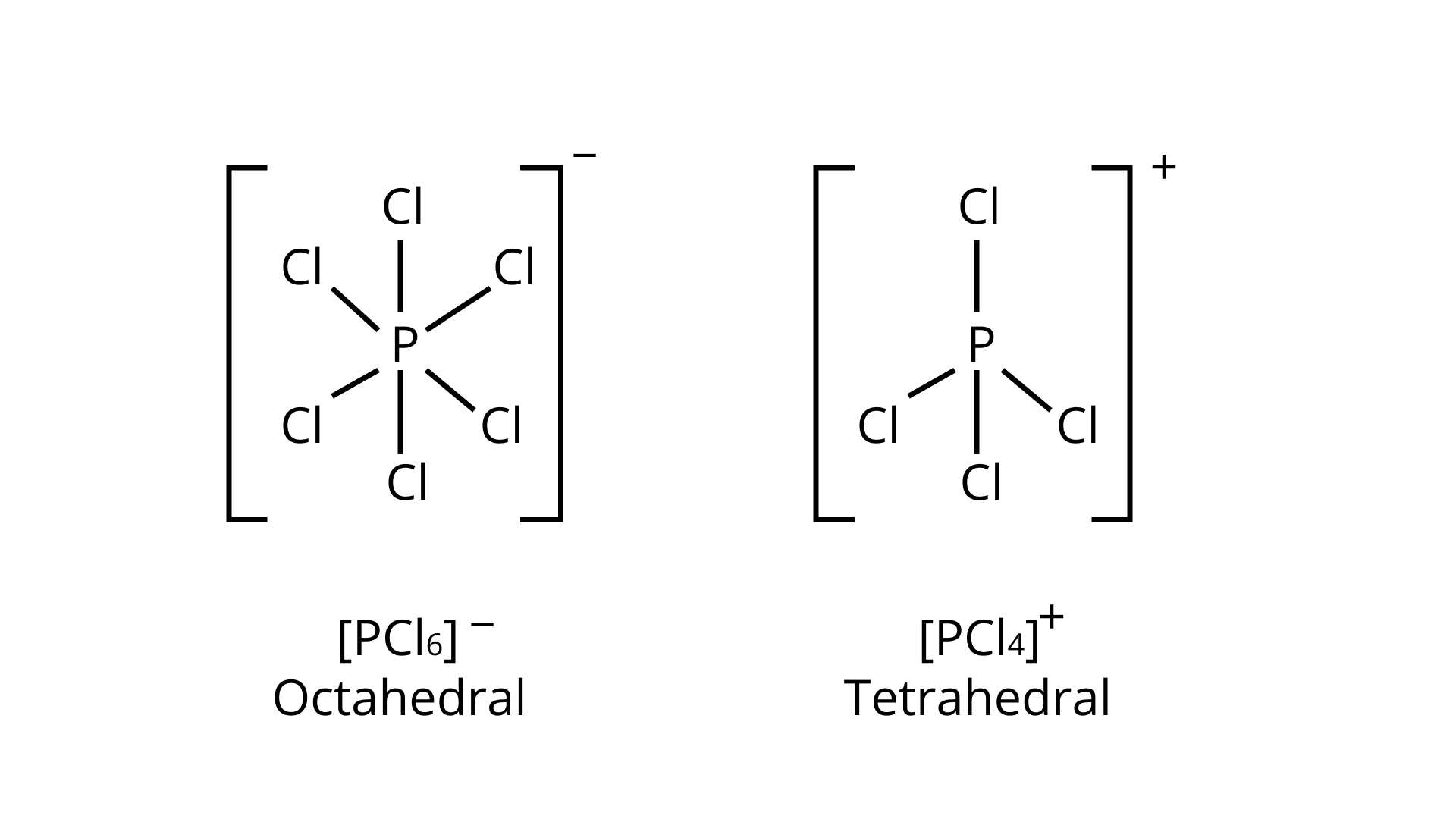
25. In solid state ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is a _________.
(i) covalent solid
(ii) octahedral structure
(iii) ionic solid with ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ }}$ octahedral and ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_4}} \right]^ - }{\text{ }}$ tetrahedra
(iv) ionic solid with ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_4}} \right]^ + }{\text{ }}$ tetrahedral and ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_6}} \right]^ - }{\text{ }}$ octahedra
Ans. Correct option is (iv)
The ionic bonding promotes the crystalline structure of ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ in the solid state by attempting to exist as oppositely charged ions like ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_4}} \right]^ + }{\text{ }}$ and ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_6}} \right]^ - }{\text{ }}$. Also, ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_4}} \right]^ + }{\text{ }}$ and ${\left[ {{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_6}} \right]^ - }{\text{ }}$ are tetrahedral and octahedral, respectively. These structures fit together well, giving the solid structure extra stability.
26. Reduction potentials of some ions are given below. Arrange them in decreasing order of oxidising power.
Ion | $\mathrm{ClO}_{4}^{-}$ | $\mathrm{lO}_{4}^{-}$ | $\mathrm{BrO}_{4}^{-}$ |
Reduction potential $E^{\ominus} / V$ | $E^{\ominus}=1.19 \mathrm{~V}$ | $E^{\ominus}=1.74 \mathrm{~V}$ | $E^{\ominus}=1.74 \mathrm{~V}$ |
(i) ${\text{ClO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > IO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > BrO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}$– $
(ii) ${\text{IO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > BrO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > ClO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ }}$
(iii) ${\text{BrO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > IO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > ClO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ }}$
(iv) ${\text{BrO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > ClO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > IO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}$
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
The ability of a substance to be decreased is known as its reduction potential. As the substance's reduction potential rises, so does its power to reduce. It signifies the chemical's oxidising power (the ability of the material to cause other substances to lose electrons, which is known as oxidising power) grows.
As a result, the oxidising power is listed in decreasing order ${\text{BrO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > IO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ > ClO}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ }}$
27. Which of the following is an isoelectronic pair?
(i) ${\text{IC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ , Cl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
(ii) ${\text{BrO}}_{\text{2}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ , Br}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$
(iii) ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ , BrF}}$
(iv) ${\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^{\text{--}}}{\text{ , }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
$BrO_{2}^{-\text{ }}(35+2\times 8+1=52)$ and $BrF_{2}^{\text{ }+\text{ }}(35+2\times 9-1=52)$
52 electrons are present in both $BrO_{2}^{-\text{ }}BrF_{2}$
II. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note : In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
28. If chlorine gas is passed through hot ${\text{NaOH}}$ solution, two changes are observed in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are ________ and _________.
(i) 0 to +5
(ii) 0 to +3
(iii) 0 to –1
(iv) 0 to +1
Ans. Correct option is (i) and (iii)
$6 \mathrm{NaOH}+3 \mathrm{Cl}_{2} \rightarrow 5 \mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{NaClO}_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$
Chlorine gas oxidation number ranges from 0 to –1 to 0 to +5.
29. Which of the following options are not in accordance with the property mentioned against them?
(i) ${{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ Oxidising power.
(ii) ${\text{MI > MBr > MCl > MF}}$ Ionic character of metal halide.
(iii) ${{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$ Bond dissociation enthalpy.
(iv) ${\text{HI < HBr < HCl < HF}}$ Hydrogen-halogen bond strength.
Ans. Correct option is (ii), (iii)
${\text{MI > MBr > MCl > MF}}$ is an iconic character of metal halide
${{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > }}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a bond dissociation enthalpy
30. Which of the following is correct for ${{\text{P}}_4}$ molecule of white phosphorus?
(i) It has 6 lone pairs of electrons.
(ii) It has six P–P single bonds.
(iii) It has three P–P single bonds.
(iv) It has four lone pairs of electrons.
Ans. Correct option is (ii) and (iv)
Tetrahedral geometry characterises the structure of a white phosphorus molecule.
Phosphorus has a valency of 5, and there are four phosphorus atoms in total. As a result, there will be a total of $4{\text{ }} \times 5 = 20$ valence electrons.
As a result, each P atom will have one lone pair of electrons, and each covalent bond (two electrons) will be established.
In a molecule of white phosphorus, there will be four lone pairs of electrons and six P-P single bonds in total.
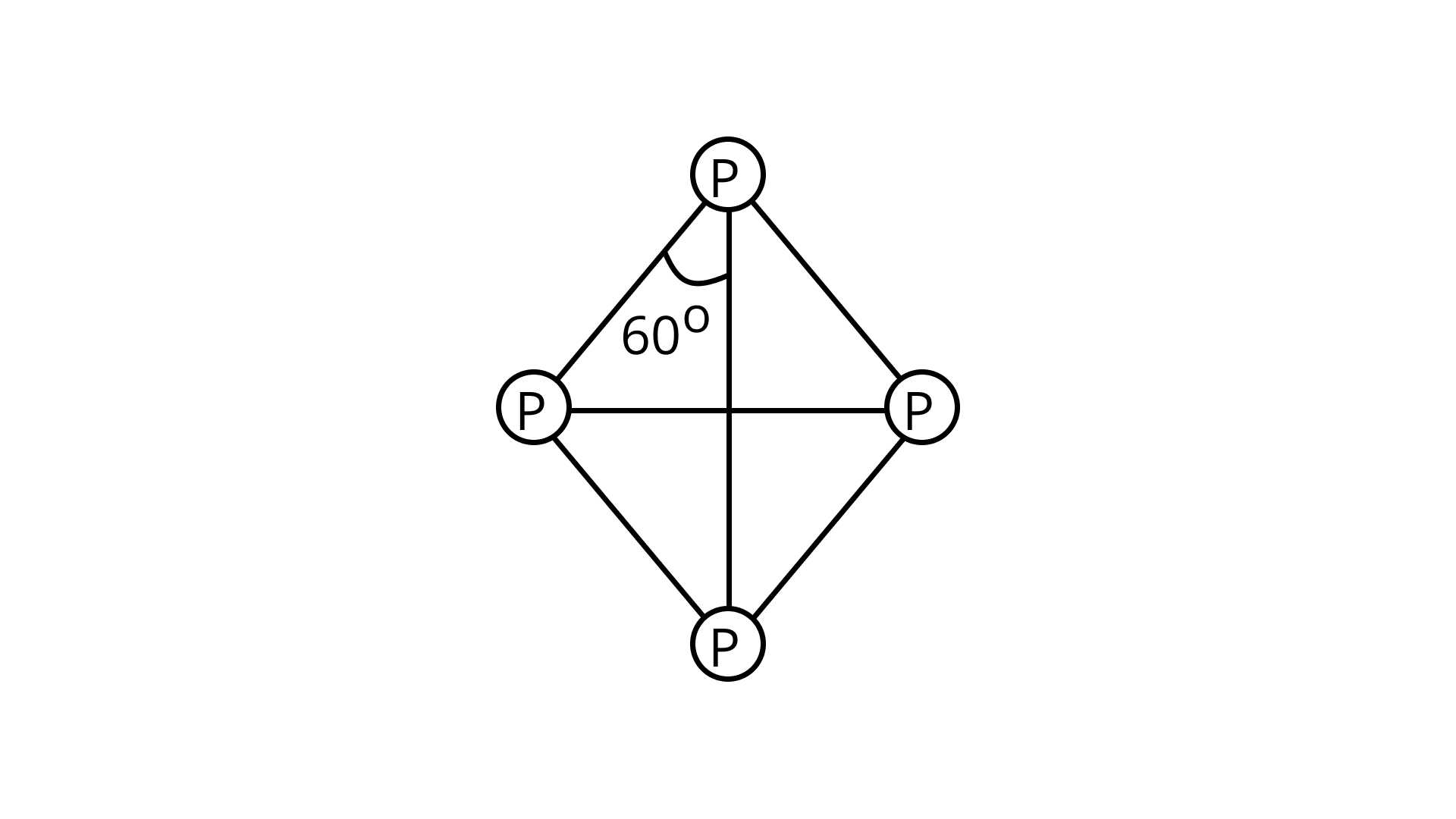
31. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Among halogens, the radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(ii) Leaving the F—F bond, all halogens have weaker X—X bonds than X—X'bonds in interhalogens.
(iii) Among interhalogen compounds maximum number of atoms are present in iodine fluoride.
(iv) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
Ans. Correct option is (i)
Due to its high electronegativity and tiny size, F is the only interhalogen with weaker X-X’ bonds and no X-X bonds.
32. Which of the following statements are correct for ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ gas?
(i) It acts as a bleaching agent in moist conditions.
(ii) It’s molecule has linear geometry.
(iii) It’s dilute solution is used as disinfectant.
(iv) It can be prepared by the reaction of dilute ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ with metal sulphide.
Ans. Correct option is (i) and (iii)
${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is employed as an antichlor, disinfectant, and preservative in the bleaching of wool and silk.
33. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) All the three N—O bond lengths in ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ are equal.
(ii) All P—Cl bond lengths in ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(iii) ${{\text{P}}_4}$ molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(iv) ${\text{PCl}}$ is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
Ans. Correct option is (iii) and (iv)
The ${{P}_{4}}$ molecule in white phosphorus has an angular strain, white phosphorus is very reactive.
${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is ionic in the solid state, with a tetrahedral cation and an octahedral anion.
34. Which of the following orders are correct as per the properties mentioned against each?
(i) ${\text{A}}{{\text{s}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < Si}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2 }}}}{\text{ < }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ Acid strength.
(ii) ${\text{As}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ Enthalpy of vapourisation.
(iii) ${\text{S < O < Cl < F}}$ More negative electron gain enthalpy.
(iv) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O > }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S > }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Se > }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Te}}$ Thermal stability.
Ans. Correct option is (i) and (iv)
(i) ${\text{A}}{{\text{s}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < Si}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2 }}}}{\text{ < }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is the order of acid
(ii) ${\text{As}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is the correct or enthalpy of vapourization
(iii) ${\text{S < O < F < Cl}}$ is the correct order of more negative gain enthalpy
(iv) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O > }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Se > }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Te}}$ is the order of thermal stability
35. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) S–S bond is present in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$.
(ii) In peroxosulphuric acid ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}$ sulphur is in +6 oxidation state.
(iii) Iron powder along with ${\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ and ${{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ is used as a catalyst in the preparation of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ by Haber’s process.
(iv) Change in enthalpy is positive for the preparation of ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ by catalytic oxidation of ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
Ans. Correct option is (i)
Oxidation state of $\mathrm{S}=+6$
(iii) Iron oxide with $\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$ is used to increase the rate of attainment of equilibrium in Haber's process.
(iv) Change in enthalpy is negative for the preparation of $\mathrm{SO}_{3}$ by catalytic oxidation of $\mathrm{SO}_{2}$.
36. In which of the following reactions conc. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is used as an oxidising reagent?
(i) ${\text{Ca}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{CaS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + 2HF}}$
(ii) ${\text{2HI + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
(iii) ${\text{Cu + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{CuS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
(iv) ${\text{NaCl + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ NaHS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + HCl}}$
Ans. Correct option is (ii) and (iii)
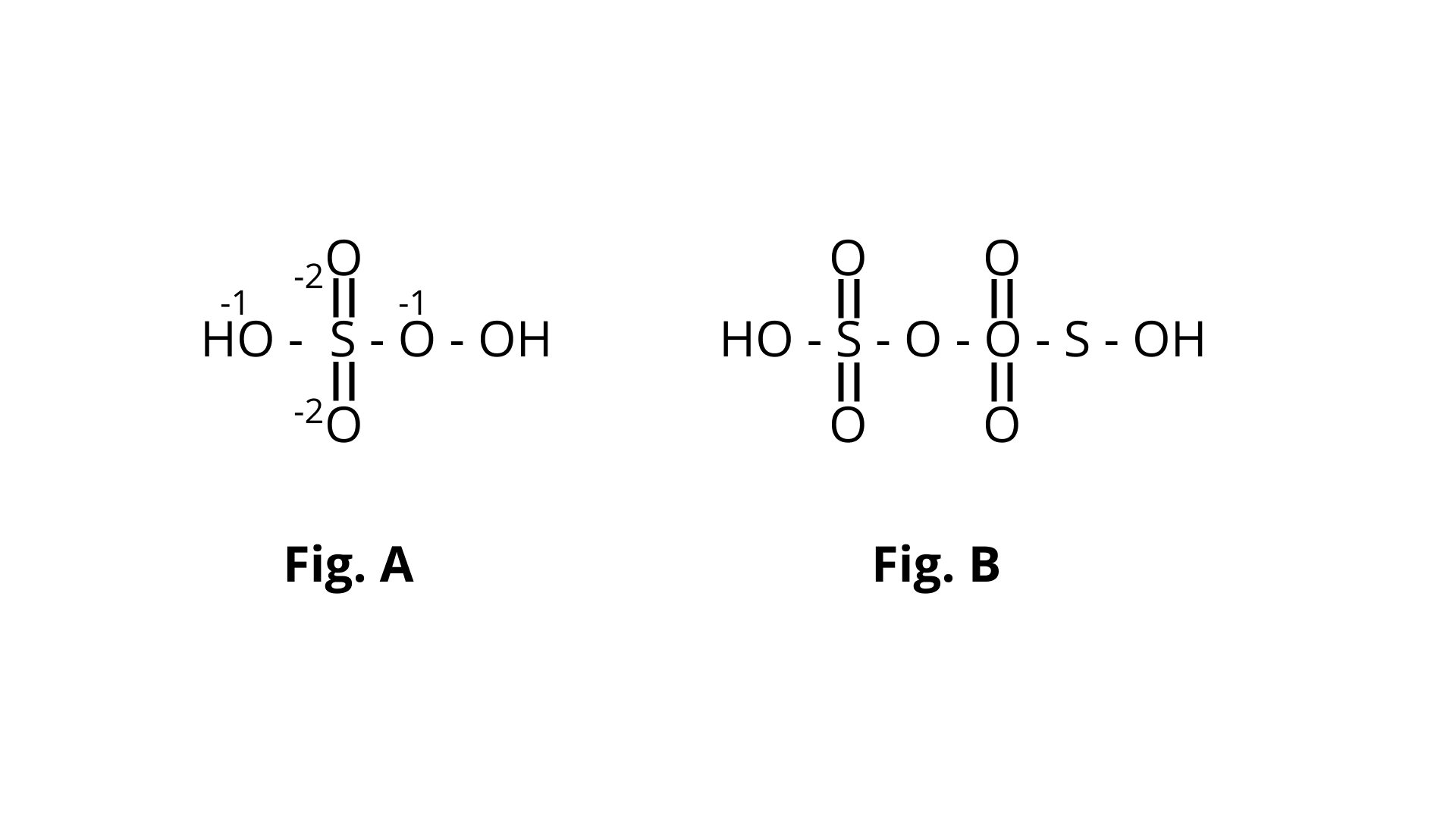
Here fig (b) contains one S-S bond.
The oxidising behaviour of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is represented by (ii) and (iii) among the aforementioned four. It oxidises ${\text{HI}}$ in reaction (ii) and then reduces to ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The oxidation state of sulphur's core atom drops from +6 to +4. It oxidises copper in (iii) and is reduced to ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
37. Which of the following statements are true?
(i) Only type of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(ii) Ionisation enthalpy of molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
(iii) Hydrolysis of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$ is a redox reaction.
(iv) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
Ans. Correct option is (i) and (ii)
(i) The modest dispersion force causes attraction in noble gases.
(ii) In nature, xenon fluorides are reactive.
III. Short Answer Type
38. In the preparation of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ by Contact Process, why is ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ not absorbed directly in water to form ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ ?
Ans. ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ generates a dense fog of sulphuric acid that does not condense quickly, it is not absorbed directly in water to form ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$.
39. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction showing catalytic oxidation of ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ by atmospheric oxygen.
Ans. ${\text{4N}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}{\text{ + 5}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{500k,9bar}}}]{{{\text{pt/Raugecatalyst}}}}{\text{4NO + 6}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
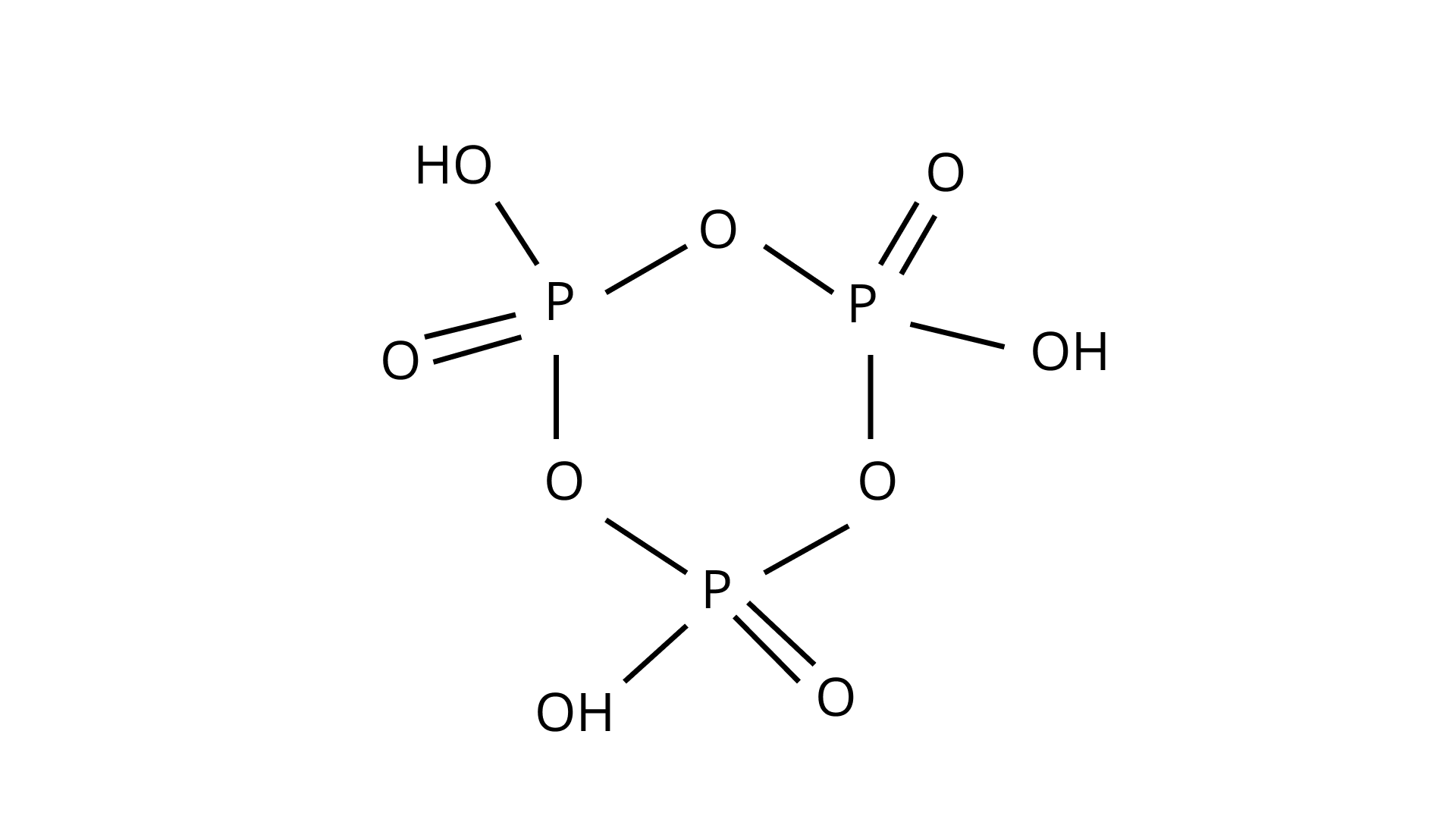
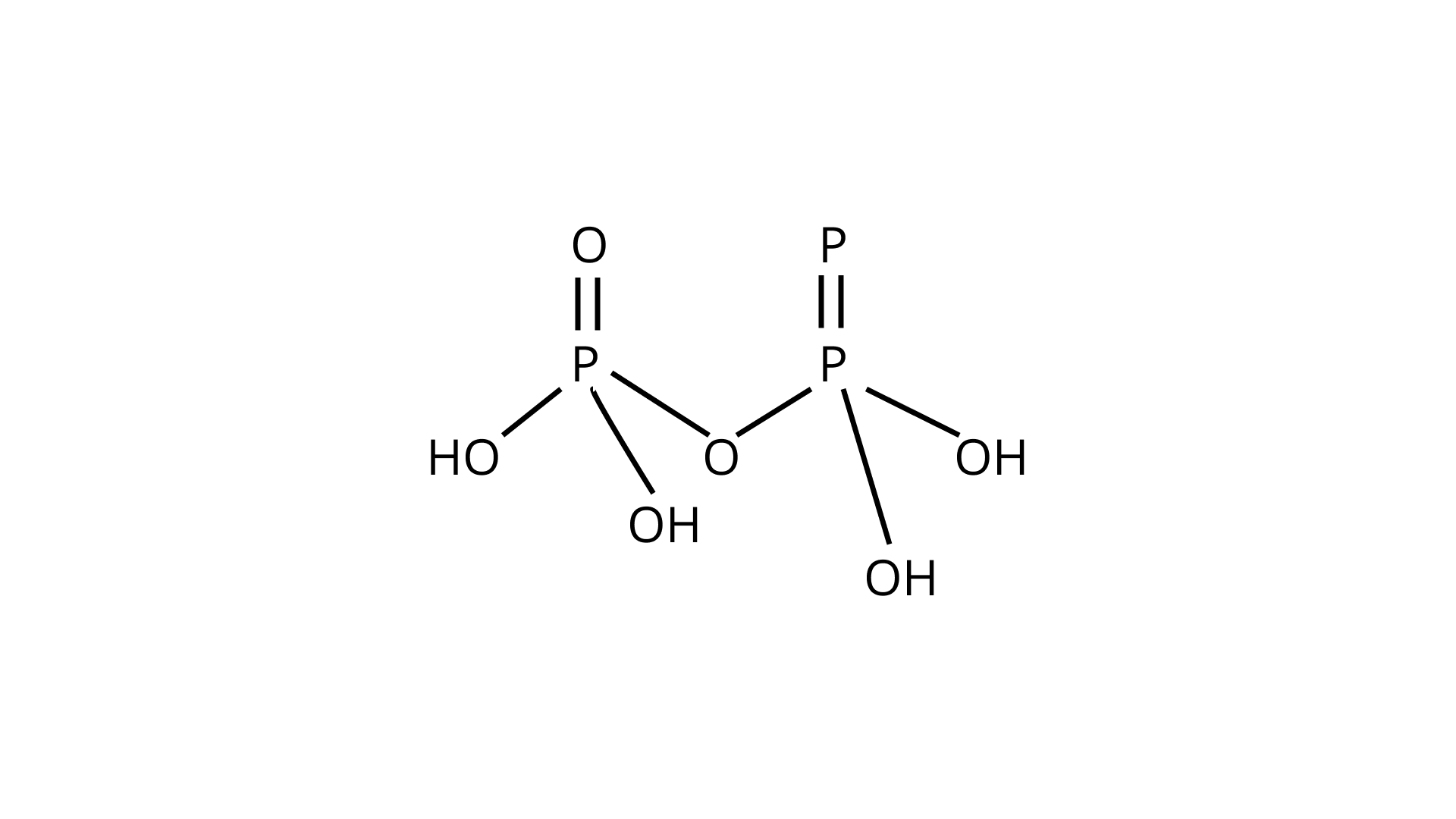
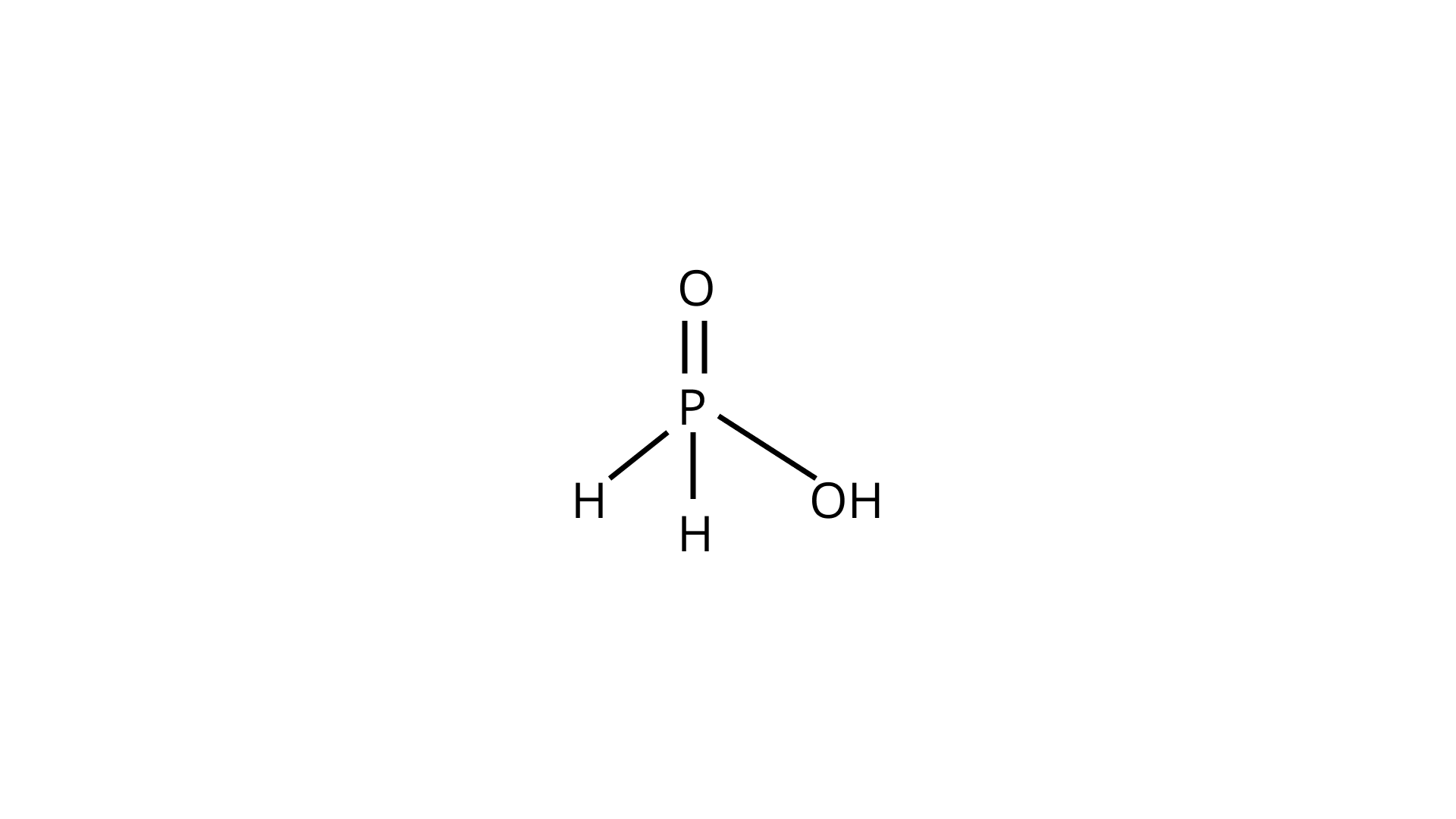
40. Write the structure of pyrophosphoric acid.
Ans.
41. ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ forms bubbles when passed slowly in water but ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ dissolves. Explain why?
Ans. ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is insoluble in water and cannot create hydrogen bonds with it, it forms bubbles, whereas ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ dissolves because it is soluble in water and can form hydrogen bonds with it.
42. In ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ , phosphorus is in ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ hybridised state but all its five bonds are not equivalent. Justify your answer with reason.
Ans. Three P—Cl bonds are arranged in one plane at a ${\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^0}$ angle. These bonds are known as equatorial bonds because they are formed between two points. The remaining two P—Cl bonds, one above the equatorial plane and the other below it, form ${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^0}$ angle with the plane. Axial bonds are the name for these types of bonds. Because axial bond pairs are subjected to greater repulsive interaction than equatorial bond pairs, axial bonds are slightly longer and hence slightly weaker than equatorial bonds, making the ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ molecule more reactive.
43. Why is nitric oxide paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtained on cooling it is diamagnetic?
Ans. ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ exists as a monomer with one unpaired electron in the gaseous state, but it dimerises to ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ in the solid state, leaving no unpaired electron, making the solid form diamagnetic.
44. Give reason to explain why ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ exists but ${\text{FC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ does not exist.
Ans. Chlorine has vacant d-orbitals, which become excited upon bonding when electrons from the 3p-orbital are promoted to the 3d-orbital, giving it a covalency of three.
Due to the lack of unoccupied d-orbitals in the second energy shell, fluorine cannot expand its octet. As a result, it can only have one covalency.
45. Out of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ and ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$, which one has higher bond angle and why?
Ans. Oxygen is more electronegative than sulphur, the bond angle of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ is greater, and the bod pair electron of an OH bond will be closer to oxygen, causing bond-pair bond-pair repulsion between bond pairs of two OH bonds.
46. ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$ is known but ${\text{SC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{6}}}$ is not. Why?
Ans. Six F atoms can be accommodated around sulphur due to fluorine's tiny size, however the chloride ion is comparably bigger, resulting in interatomic repulsion.
47. In reaction with ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ , phosphorus forms two types of halides ‘A’ and ‘B’. Halide A is yellowish-white powder but halide ‘B’ is colourless oily liquid. Identify A and B and write the formulas of their hydrolysis products.
Ans. A is ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$(yellowish white powder)
${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ + 10C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{4PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$
B is ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$(colourless oily liquid)
Hydrolysis of the following product
$\mathrm{PCl}_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{PO}_{3}+3 \mathrm{HCl}$
$\mathrm{PCl}_{5}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{PO}_{4}+5 \mathrm{HCl}$
48. In the ring test of ${\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}$ ion, ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}$ ion reduces nitrate ion to nitric oxide, which combines with ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{(aq)}}$ ion to form brown complex. Write the reactions involved in the formation of brown rings.
Ans.
$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}+3 \mathrm{Fe}^{2+}+4 \mathrm{H}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}++3 \mathrm{Fe}^{3+}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$
$\left[\mathrm{Fe}\left(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right)_{6}\right]^{2+}+\mathrm{NO} \rightarrow \underset{(\text { brown ring })}{\left[\mathrm{Fe}\left(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right)_{5}(\mathrm{NO})\right]^{2+}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}}$
49. Explain why the stability of oxoacids of chlorine increases in the order given below:
${\text{HClO < HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ < HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
Ans. Oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine, the negative charge on chlorine disperses from C ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ to ${\text{ClO}}_4^ - $ ion as the number of oxygen atoms linked to chlorine grows. As a result, ion stability will improve in the following order:
As the stability of the conjugate base rises, the acidic strength of the corresponding acid increases in the following order:
${\text{HClO < HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ < HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ < HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
50. Explain why ozone is thermodynamically less stable than oxygen
Ans. Due its disintegration into oxygen results in the release of heat $\Delta {\text{H}}$ is negative) and an increase in entropy ($\Delta {\text{S}}$ is positive), ozone is thermodynamically unstable in comparison to oxygen. These two reactions combine to produce a substantial negative Gibbs energy change (${{\Delta G}}$) for its conversion to oxygen.
51. ${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ reacts with water according to equation ${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ + 6}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \to {\text{ 4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$. Calculate the volume of ${\text{0}}{\text{.1 M NaOH}}$ solution required to neutralise the acid formed by dissolving ${\text{1}}{\text{.1 g of }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ in }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
Ans. ${{\text{P}}_{{\text{4}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ + 6}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \to {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ (i)
Next is neutralization
${\text{4 \times }}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{3}}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + 2NaOH}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{HP}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{3}}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ (ii)
On addition of 2 equations
$\mathrm{P}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}+8 \mathrm{NaOH} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{HPO}_{3}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$
$\mathrm{P}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}(\text { mol.mass })=(4 \times 31+16 \times 6)=220$
${\text{Number of moles of}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ = }}\frac{{{\text{MolarMass}}}}{{{\text{Givenmass}}}}{\text{ = }}\frac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.1}}}}{{{\text{220}}}}$
The product formed is neutralized 8 moles of ${\text{NaOH}}$
${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ = 8 }\times{ }}\frac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.1}}}}{{{\text{220}}}}{\text{ = }}\frac{{{\text{8}}{\text{.8}}}}{{{\text{220}}}}{\text{molNaOH}}$
Molarity of ${\text{NaOH}}$ in 1 litre ${\text{ = 0}}{\text{.1M}}$
$\text { Molarity }=\frac{\text { No.of Moles }}{\text { Volume in litres }}$
$\text { Volume }=\frac{\text { No.of Moles }}{\text { Molarity }}$
$=\frac{8.8}{220} \times \frac{1}{0.1}=0.4 \mathrm{~L}$
52. White phosphorus reacts with chlorine and the product hydrolyses in the presence of water. Calculate the mass of ${\text{HCl}}$ obtained by the hydrolysis of the product formed by the reaction of 62 g of white phosphorus with chlorine in the presence of water
Ans. $P_{4}+6 \mathrm{Cl}_{2} \rightarrow 4 P C l_{3} \ldots$ (i)
$\left.\mathrm{PCl}_{3}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{PO}_{3}+3 \mathrm{HCl}\right\} \times 4$
On adding eq. (i) and (ii)
$\mathrm{P}_{4}+6 \mathrm{Cl}_{2}+12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{PO}_{3}+12 \mathrm{HCl}$
$1 \mathrm{~mol}$ of white phosphorus produces $12 \mathrm{~mol}$ of $\mathrm{HCl}$
$62 \mathrm{~g}$ of white phosphorus has been taken which is equivalent to $\frac{62}{124}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~mol}$. Therefore $6 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{HCl}$ will be formed.
Mass of $6 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{HCl}=6 \times 36.5=219.0 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{HCl}$
53. Name three oxoacids of nitrogen. Write the disproportionation reaction of that oxoacid of nitrogen in which nitrogen is in +3 oxidation state.
Ans. Three oxoacids are
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, Nitrous acid}}$
$\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{, Nitric acid}}$
$\left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ hyponitrous acid,}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
${\text{3HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{disproportionation}}}}{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + 2NO}}$
54. Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with ${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{10}}}}$. Write the reaction involved. Also write the resonating structures of the oxide of nitrogen formed.
Ans. On interaction with ${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{10}}}}$ forms an oxide of nitrogen, ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{}}$,nd metaphosphoric acid, 3, nitric acid is formed. ${\text{HP}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
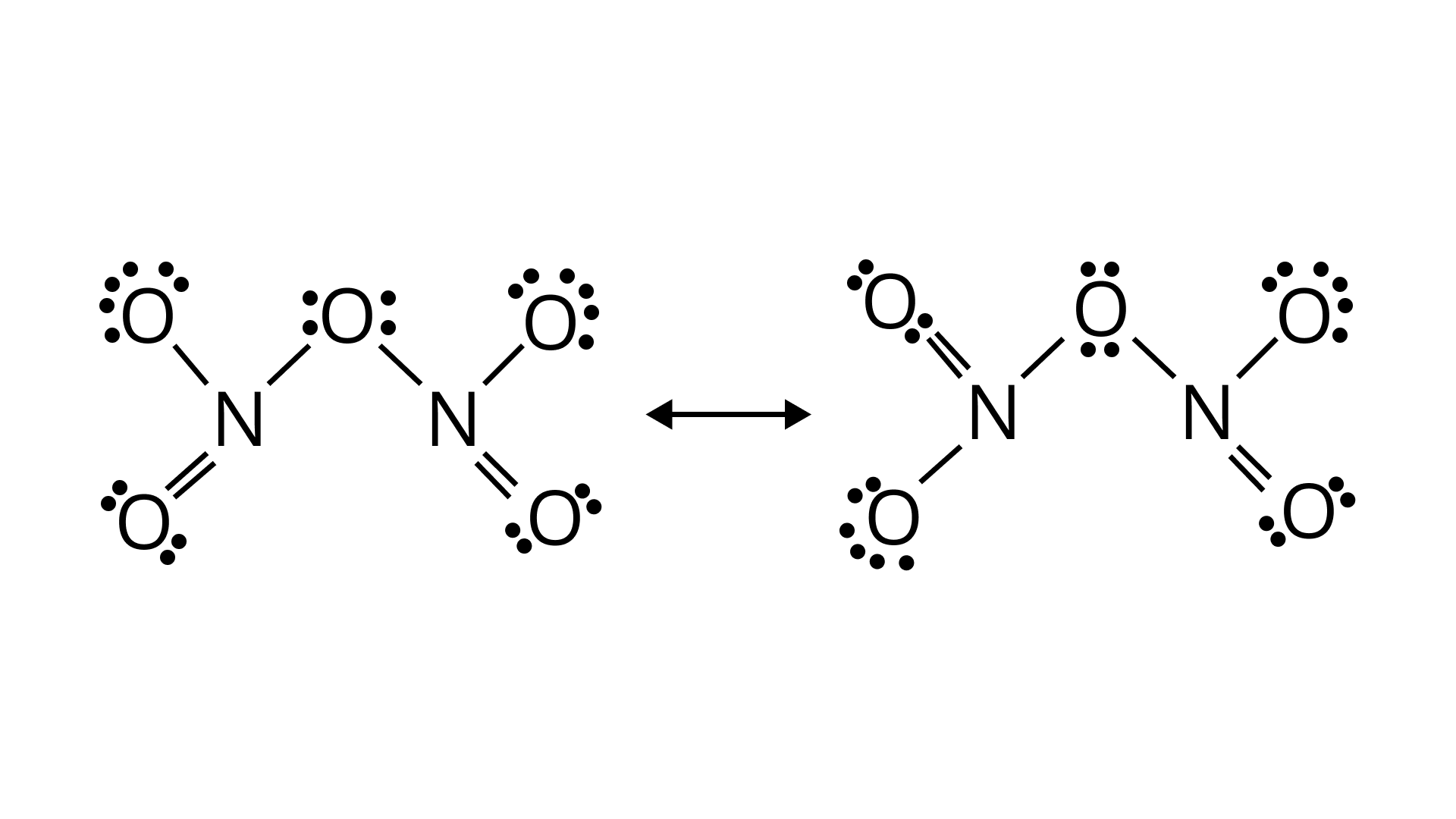
${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{10}}}} \to {\text{4HP}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}$
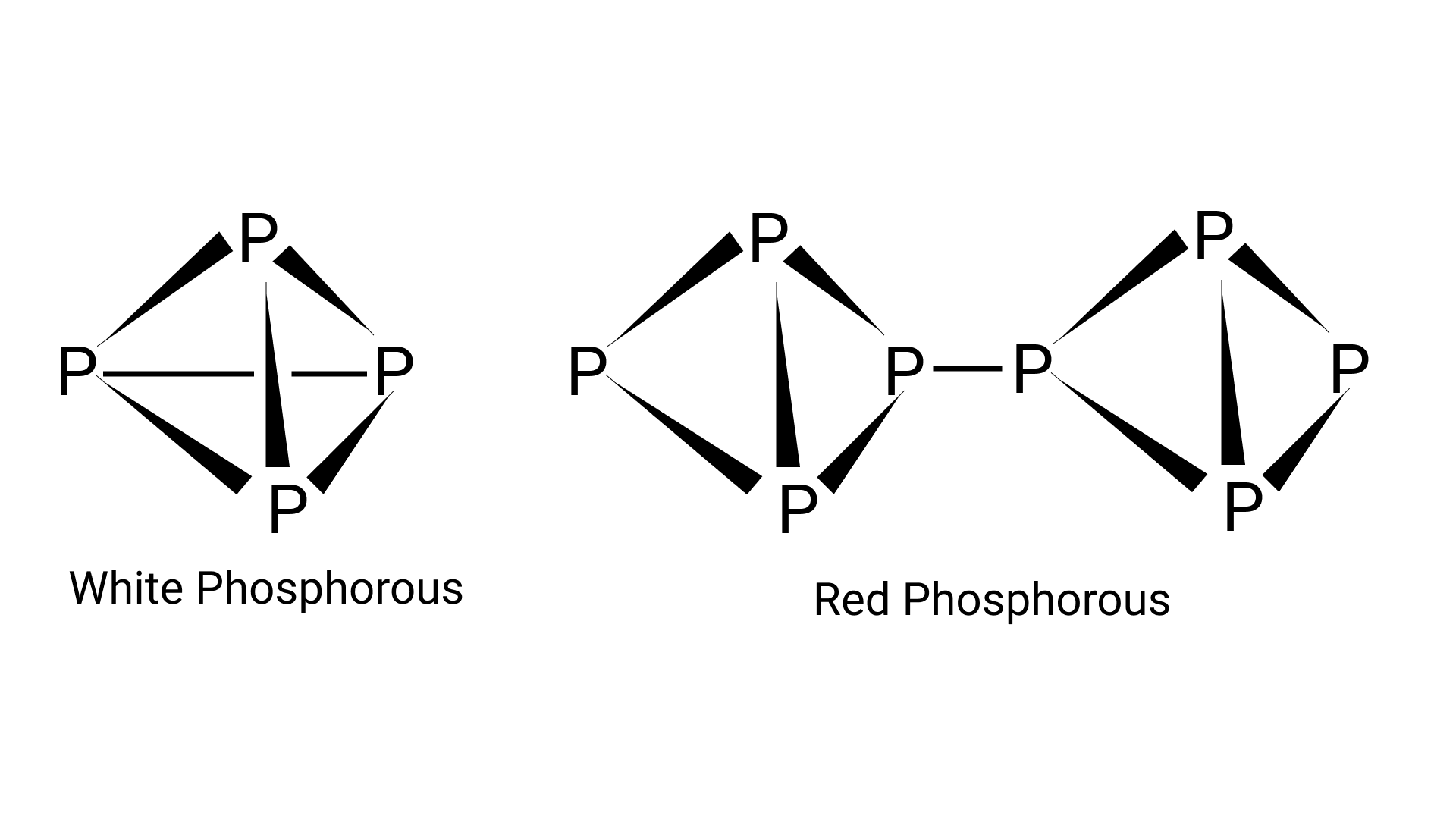
55. Phosphorus has three allotropic forms — (i) white phosphorus (ii) red phosphorus and (iii) black phosphorus. Write the difference between white and red phosphorus since their structure and reactivity.
Ans. The crystal structure of red phosphorus features a sophisticated network of bonding, whereas white phosphorus is made up of ${{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecules. To avoid natural combustion, white phosphorus must be stored in water, but red phosphorus is stable in air.
56. Give an example to show the effect of concentration of nitric acid on the formation of oxidation products.
Ans. When nitric acid is mixed with copper metal, it produces distinct oxidation products.
${\text{3Cu + 8HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(dil}}{\text{.)}} \to {\text{3Cu(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2NO + 4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
${\text{Cu + 4HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(Conc)}} \to {\text{3Cu(N}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{3}}}}{{\text{)}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{ + 2N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{O}}$
57. ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver salt is obtained, which dissolves on adding excess aqueous ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ solution. Write the reactions involved to explain what happens.
Ans.
${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ + 2Ag}} \to {\text{2AgCl + PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$
${\text{AgCl + 2N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{[Ag(N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{] + Cl - }}$
58. Phosphorus forms several oxoacids. Out of these oxoacids phosphinic acid has strong reducing properties. Write its structure and write a reaction showing its reducing behaviour
Ans. The following reaction with silver nitrate demonstrates phosphinic acid reducing behaviour:
${\text{4AgN}}{{\text{o}}_{{\text{3}}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{O + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{4Ag + 4HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
IV. Matching Type
Note : Match the items of Column I and Column II in the following questions.
59. Match the compounds given in Column I with the hybridisation and shape given in Column II and mark the correct option
Column I | Column II |
(A) ${\text{Xe }}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$ | (1) ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{3}}}$ – distorted octahedral |
(B) ${\text{Xe }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ | (2) ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^2}$ - square planar |
(C) ${\text{Xe O}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ | (3) ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ - pyramidal |
(D) ${\text{Xe }}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ | (4) ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^2}$ - $square pyramidal |
Code :
(i) A (1) | B (3) | C (4) | D (2) |
(ii) A (1) | B (2) | C (4) | D (3) |
(iii) A (4) | B (3) | C (1) | D (2) |
(iv) A (4) | B (1) | C (2) | D (3) |
Ans. Correct option is (i)
In $\mathrm{XeF}_{6}$, the central Xe atom undergoes sp $^{3} \mathrm{~d}^{3}$ hybridisation and the molecular geometry is distorted octahedral with 1 lone pair and 6 bond pairs of electrons.
In $\mathrm{XeO}_{3}$, the central Xe atom undergoes $\mathrm{sp}^{3}$ hybridisation and the molecular geometry is pyramidal with 1 lone pair and 3 bonding domains of electrons.
In $\mathrm{XeOF}_{4}$, the central $\mathrm{Xe}$ atom undergoes $\mathrm{sp}^{3} \mathrm{~d}^{2}$ hybridization and the molecular geometry is square pyramidal with 1 lone pair and 5 bond pairs of electrons.
In $\mathrm{XeF}_{4}$, the central $\mathrm{Xe}$ atom undergoes $\mathrm{sp}^{3} \mathrm{~d}^{2}$ hybridization and the molecular geometry is square planar with 2 lone pairs and 4 bond pairs of electrons.
60. Match the formulas of oxides given in Column I with the type of oxide given in Column II and mark the correct option.
Column I | Column II |
(A) ${\text{P}}{{\text{b}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ | (1) Neutral oxide |
(B) ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ | (2) Acidic oxide |
(C) ${\text{M}}{{\text{n}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$ | (3) Basic oxide |
(D) ${\text{B}}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ | (4) Mixed oxide |
Code :
(i) A (1) | B (2) | C (3)0 | D (4) |
(ii) A (4) | B (1) | C (2) | D (3) |
(iii) A (3) | B (2) | C (4) | D (1) |
(iv) A (4) | B (3) | C (1) | D (2) |
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
A. $\mathrm{Pb}_{3} \mathrm{O}_{4}$ is a mixed ore
B. $\mathrm{N}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ is a neutral oxide
C. $\mathrm{Mn}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}$ is acidic oxide
D. $\mathrm{Bi}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$ is basic oxide
61. Match the items of Columns I and II and mark the correct option.
Column I | Column II |
(A) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ | (1) Highest electron gain enthalpy |
(B) ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ | (2) Chalcogen |
(C) ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}$ | (3) Tear gas |
(D) Sulphur | (4) Storage batteries |
Code:
(i) A (4) | B (3) | C (1) | D (2) |
(ii) A (3) | B (4) | C (1) | D (2) |
(iii) A (4) | B (1) | C (2) | D (3) |
(iv) A (2) | B (1) | C (3) | D (4) |
(i) A (4) | B (3) | C (1) | D (2) |
(ii) A (3) | B (4) | C (1) | D (2) |
(iii) A (4) | B (1) | C (2) | D (3) |
(iv) A (2) | B (1) | C (3) | D (4) |
Ans. Correct option is (i)
${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_3}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ stands for chloropicrin, which is known as tear gas. ${\text{Cl}}$ is the element of highest electron gain enthalpy. Sulphur is the element belonging to 16th group, also known as chalcogens.
62. Match the species given in Column I with the shape given in Column II and mark the correct option.
Column I | Column II |
(A) ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ | (1) Tetrahedral |
(B) ${\text{Br}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}$ | (2) Pyramidal |
(C) ${\text{BrO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }}{\text{ }}$ | (3) Seesaw shaped |
(D) ${\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{ + }}$ | (4) Bent T-shaped |
Code:
(i) A (3) | B (2) | C (1) | D (4) |
(ii) A (3) | B (4) | C (2) | D (1) |
(iii) A (1) | B (2) | C (3) | D (4) |
(iv) A (1) | B (4) | C (3) | D (2) |
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
63. Match the items of Columns I and II and mark the correct option.
Column I | Column II |
(A) Its partial hydrolysis does not change oxidation state of central atom | (1) ${\text{He}}$ |
(B) It is used in modern diving apparatus | (2) ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$ |
(C) It is used to provide inert atmosphere for filling electrical bulbs | (3) ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ |
(D) Its central atom is in ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridisation | (4) ${\text{Ar}}$ |
Code:
(i) A (1) | B (4) | C (2) | D (3) |
(ii) A (1) | B (2) | C (3) | D (4) |
(iii) A (2) | B (1) | C (4) | D (3) |
(iv) A (1) | B (3) | C (2) | D (4) |
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
V. Assertion and Reason Type
Note : In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(i) Both assertion and reason are correct statements, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both assertion and reason are correct statements, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(iii) Assertion is correct, but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(v) Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
64. Assertion : ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ is less reactive than ${{\text{P}}_4}$.$
Reason : Nitrogen has more electron gain enthalpy than phosphorus.
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
Nitrogen gas has a complete octet structure for both atoms and is unreactive due to the presence of a strong triple bond. On the other hand, phosphor has bonds with unstable angles strains compared to nitrogen, therefore it burns quickly, thus readily reacts. Nitrogen has a lower electron gain enthalpy than phosphorus.
65. Assertion : ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ makes iron passive.
Reason : ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
Ans. Correct option is (iii)
${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ forms an oxide layer on the surface of iron. This is also known as corrosion or rusting.
66. Assertion : ${\text{HI}}$ cannot be prepared by the reaction of ${\text{KI}}$ with concentrated ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
Reason : ${\text{HI}}$ has lowest H–X bond strength among halogen acids
Ans. Correct option is (ii)
Because ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is a stronger oxidising agent and ${\text{HI}}$ is a stronger reducing agent, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ oxidizes and is reduced to ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
67. Assertion : Both rhombic and monoclinic sulphur exist as ${{\text{S}}_8}$ but oxygen exists as ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ .
Reason : Oxygen forms pπ – pπ multiple bonds due to small size and small bond length but ${\text{p\pi - p\pi }}$ bonding is not possible in sulphur.
Ans. Correct option is (i)
The rhombic and the monoclinic forms of sulphur exist as ${{\text{S}}_8}$ . Oxygen forms a ${\text{p\pi - p\pi }}$ multiple bond due to its small size and short bond length, but ${\text{p\pi - p\pi }}$ bonding is not possible because of sulphur's larger atomic size.
68. Assertion : ${\text{NaCl}}$ reacts with concentrated ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ to give colourless fumes with pungent smell. But on adding ${\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ the fumes become greenish yellow.
Reason : ${\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ oxidises ${\text{HCl}}$ to chlorine gas which is greenish yellow.
Ans. Correct option is (i)
When ${\text{NaCl}}$ reacts with concentrated ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, it produces colourless fumes with a pungent smell, but when ${\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is added, the fumes turn greenish yellow. ${\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ oxidizes ${\text{HCl}}$ to chlorine gas, which then turns greenish yellow.
69. Assertion : ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$ cannot be hydrolysed but ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ can be.
Reason : Six F atoms in ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$ prevent the attack of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ on sulphur atom of ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$
Ans. Correct option is (i)
Here, the ${\text{S}}$ atom is surrounded by 6 F atoms, so it's complected for ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ to attack ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}$, but in case of ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$, it's surrounded by 4F atoms, so it's to attack ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
VI. Long Answer Type
70. An amorphous solid “A” burns in air to form a gas “B” which turns lime water milky. The gas is also produced as a by-product during roasting of sulphide ore. This gas decolourises acidified aqueous ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution and reduces ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{3 + }}}}{\text{ to F}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}$. Identify the solid “A” and the gas “B” and write the reactions involved.
Ans. Gas 'B' is produced as a by-product during the roasting of sulphide, so gas 'B' must be ${\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
${\text{42ZnS + 3}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2}}}} \to {\text{2ZnO + 2S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(B)}}$
Since gas 'B' is formed when amorphous solid 'A' burns in air, amorphous solid 'A' must be sulphur, ${{\text{S}}_8}$.
${{\text{S}}_{{\text{8}}}}{\text{(A) + 8O}} \to {\text{8}}{{\text{S}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{(B)}}$
71. On heating lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas “A”. The gas “A” on cooling changes to colourless solid “B”. Solid “B” on heating with ${\text{NO}}$ changes to a blue solid ‘C’. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ and write reactions involved and draw the structures of ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Ans. Here, ‘A’ is ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}$(Nitrogen dioxide)
‘B’ is ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_4}$(dinitrogen tetraoxide)
‘C’ is ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}$(dinitrogen trioxide)
A brown gas is produced when lead nitrate(II) is heated
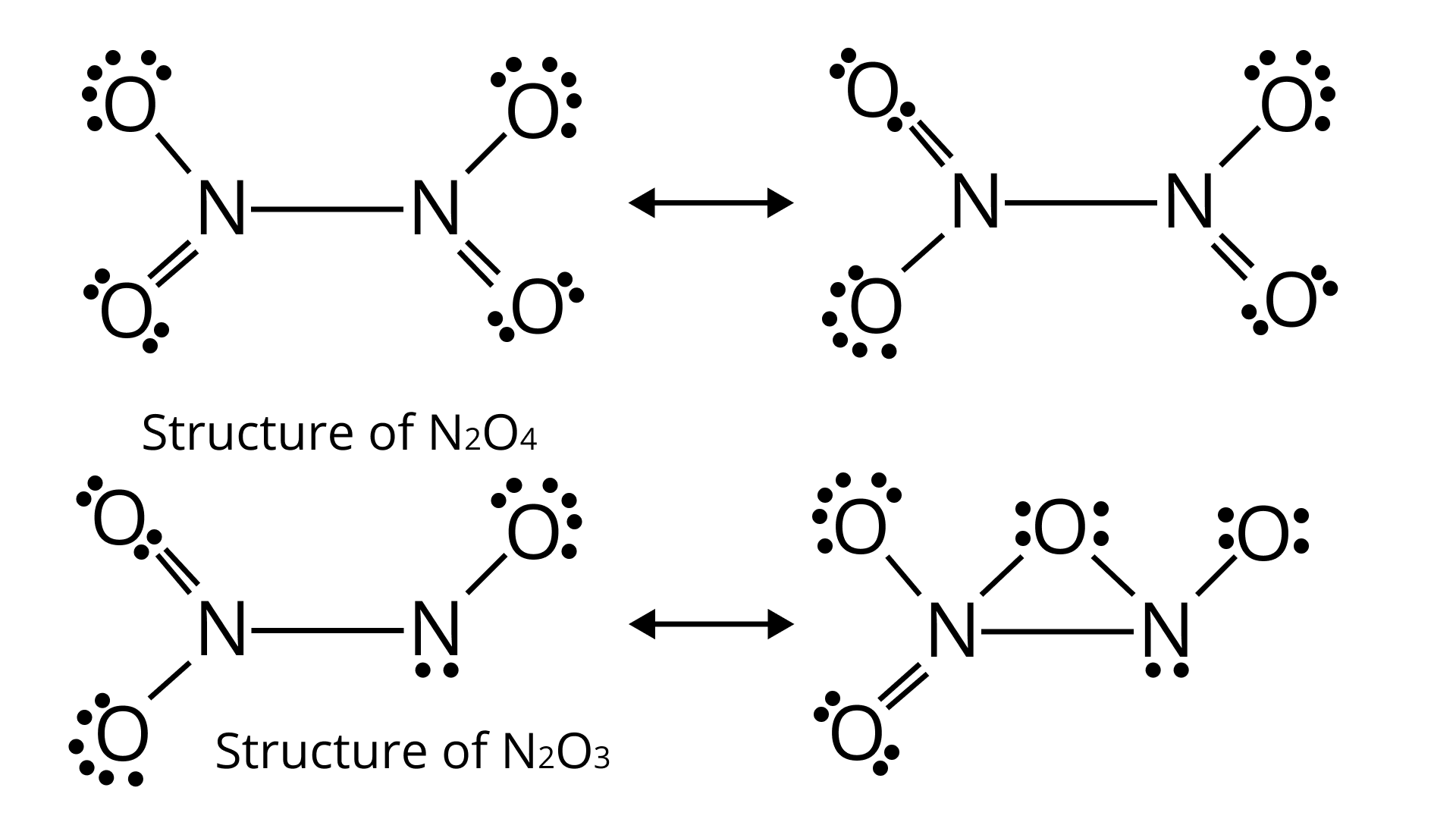
${\text{2Pb}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Heat}}}}{\text{2PbO + 4N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
${\text{2N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Cooling}}}}{\text{}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
${\text{2NO + }}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Heat}}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$
72. On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is a constituent of air. This gas when treated with 3 mol of hydrogen (${{\text{H}}_2}$) in the presence of a catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature. Gas C on further oxidation in moist condition gives a compound (D) which is a part of acid rain. Identify compounds (A) to (D) also give necessary equations of all the steps involved.
Ans.
${\text{A = N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
${\text{B = }}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$
${\text{C = N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
${\text{D = HN}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{3}}}}$
$\left( {\text{i}} \right){\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} \to {{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right){\text{}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 3}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{2N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
$\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right){\text{4N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + 5}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{4NO + 6}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
${\text{4NO + }}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{4N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
${\text{3N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{O}} \to {\text{2HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + NO}}$
NCERT Exemplar is a great addition to a student’s preparation. Many times, questions appear directly from the textbook not only in school-level Exams but also in competitive Exams. This pattern has occurred several times over and over again and has led to students putting a lot of faith in the NCERT Exemplar. By using the solutions from Vedantu that cover all the important solutions to every single question from the Chapter The p-Block Elements, students can study the Chapter in a more effective way.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter-7 (Book Solutions)
1. Do the p-Block Elements have a high weightage in the Class 12 CBSE Examinations?
The p-Block Element is the Chapter that carries the most marks in the Class 12 CBSE board Examinations. Fortunately, it is not a very difficult topic to study and understand. By reading through the basic theory and understanding everything that the Chapter wants to convey, students can score full marks in The p-Block Elements in their Class 12 Board Examinations. It is recommended to not skip this Chapter at any cost as it has a very high weightage.
2. Should I use the NCERT Exemplar solutions (Class 12) for Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements if I’m preparing for JEE?
JEE Mains and Advance test their students on the basis of their subject understanding and clarity of concepts. The Exam has some really complicated questions from several Chapters but a huge chunk of the questions are considered to be easy. The NCERT Exemplar is a great tool as many times, questions appear directly from the book in the Exams, even in JEE. So yes, by using this free solution PDF, you can get good marks in JEE.
3. How do I use the free solution PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Chapter 7 The p-Block Element?
After downloading the free Solution PDF from Vedantu, students are expected to use it as a way to revise the main content of the Chapter. These solutions can be referred to at any moment before the Exam and be used as an extra asset in the overall preparation. Use these solutions to check the answers that you write in your mock tests so that you can change your original answer to an answer that can guarantee you better marks on the test.
4. I have doubts about some basics from the Chapter The p-Block Elements. How do I clear them first?
Doubts make us better learners. Every doubt is important and must be solved immediately. Vedantu offers easy doubt clearing sessions that allow students to continue their preparation without overthinking on previous doubts. In order to fill the gaps in the basic concepts of the Chapter The p-Block Element for students of Class 12, watch this video from Vedantu to go through the entire core ideas from the Chapter The p-Block Elements. All the basic concepts of the Chapter are explained properly and easily in the video.
5. Am I supposed to pay an amount to download the Class 12 NCERT Exemplar solution PDF for Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements?
Absolutely not. The Class 12 NCERT Exemplar Book solution PDF is a completely free resource that can be downloaded at any time by students of Class 12 to use in their Exam preparation. You will not have to pay anything to download this resource from Vedantu. It is completely free and has been made with a lot of care and accuracy to give you the best solutions on the web! Thus, students can download the Class 12 NCERT Exemplar solution PDF for Chapter 7 to score high marks in the Exam.







































