
Which of the following does not react with $NaHS{O_3}$ (sodium bisulphite)?
A.
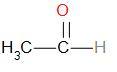
B.
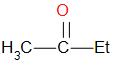
C.
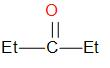
D.
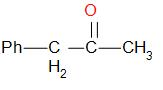




Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint:$NaHS{O_3}$ is known as sodium bisulfite or sodium hydrogen sulphite. It is a crystalline solid which is white in colour and it smells like rotten eggs. $NaHS{O_3}$ reacts with organic compounds containing carbonyl groups giving Addition products.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium Bisulphite reacts with carbonyl compounds majorly with aldehydes and ketones having a small aliphatic chain. It generally does not react with aromatic ketones due to steric hindrance posed by the large sized benzene ring.
The addition of sodium bisulphite is a nucleophilic addition. It breaks into its constituent ions, that are, sodium cation and hydrogen sulphite anion. The anion acts as the nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon which is electrophilic in nature. An alkoxide intermediate is formed having a tetrahedral shape. Finally, intermolecular proton transfer takes place in the compound from the bisulphite group to the oxygen atom giving the final addition product.
Bisulphite ion is large in size and thus faces high steric hindrance if larger substituent groups are present on the carbonyl carbon. Thus, the reaction preferably takes place in case of aldehydes and methyl ketones.
In option A, we have an aldehyde.
In option B and D, we have methyl ketones.
While in option C, The given ketone has two Ethyl groups attached to it. The incoming nucleophile faces higher steric hindrance and reaction does not take place.
Thus, the correct answer is C.
Note:
The reaction of sodium bisulfite with carbonyl compounds occurs from the Sulphur atom and not the oxygen. Sulphur is less electronegative than oxygen and thus has a higher tendency to donate electrons. As a result, it is a better nucleophile as compared to oxygen.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium Bisulphite reacts with carbonyl compounds majorly with aldehydes and ketones having a small aliphatic chain. It generally does not react with aromatic ketones due to steric hindrance posed by the large sized benzene ring.
The addition of sodium bisulphite is a nucleophilic addition. It breaks into its constituent ions, that are, sodium cation and hydrogen sulphite anion. The anion acts as the nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon which is electrophilic in nature. An alkoxide intermediate is formed having a tetrahedral shape. Finally, intermolecular proton transfer takes place in the compound from the bisulphite group to the oxygen atom giving the final addition product.
Bisulphite ion is large in size and thus faces high steric hindrance if larger substituent groups are present on the carbonyl carbon. Thus, the reaction preferably takes place in case of aldehydes and methyl ketones.
In option A, we have an aldehyde.
In option B and D, we have methyl ketones.
While in option C, The given ketone has two Ethyl groups attached to it. The incoming nucleophile faces higher steric hindrance and reaction does not take place.
Thus, the correct answer is C.
Note:
The reaction of sodium bisulfite with carbonyl compounds occurs from the Sulphur atom and not the oxygen. Sulphur is less electronegative than oxygen and thus has a higher tendency to donate electrons. As a result, it is a better nucleophile as compared to oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




