
Which of the following compounds does not react with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$?
(A)- HCHO
(B)- ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$
(C)- $C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$
(D)- $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: The chemical name of $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ is sodium bisulfite or sodium hydrogen sulphite. It is a white crystalline solid and has rotten egg-like smell. It reacts with compounds having carbonyl groups to form an addition-product.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium bisulphate (or sodium hydrogen sulphite) reacts with carbonyl compounds mostly aldehydes (RCHO) and some ketones (RCOR) where the hydrocarbon chain, i.e. R-group is a small aliphatic chain like methyl ketone. Aromatic ketones generally do not react with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ due to steric effects of large benzene ring,
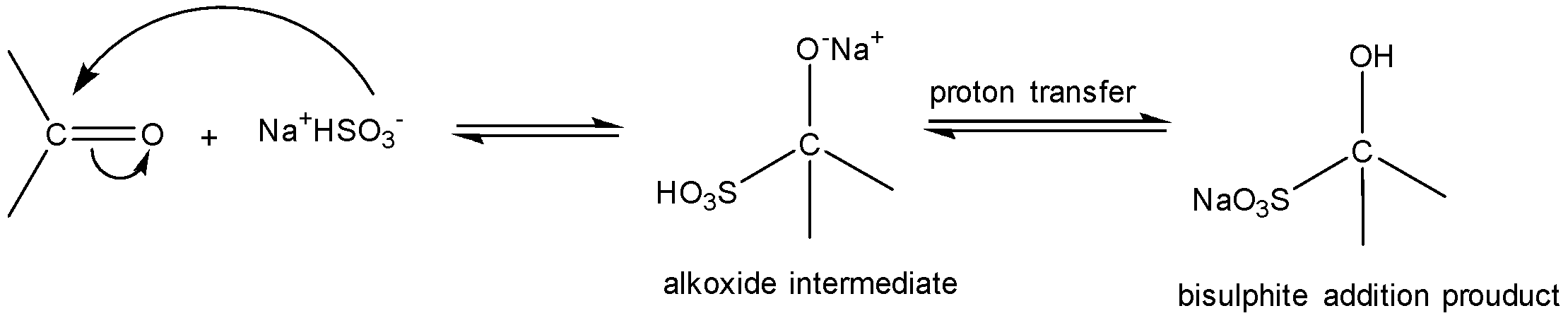
$NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ addition to aldehydes and ketones is a nucleophilic addition reaction. Nucleophile ($HSO_{3}^{-}$) attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. A tetrahedral alkoxide is formed as an intermediate. Final proton transfer occurs to give bisulfite addition compounds. If a large or bulky R-group is present adjacent to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon then the addition of $HSO_{3}^{-}$ is hindered.
HCHO (formaldehyde), $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$(acetaldehyde) are aldehydes and thus react with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ easily to addition products. However, reactivity of ketones is less than that of aldehydes. $C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ (acetone) has only methyl substituents and $HSO_{3}^{-}$ addition can occur.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ (acetophenone) has one phenyl group attached and the attack of the nucleophile is sterically favourable. Hence, ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ does give addition reaction with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The addition bisulphite product formed by nucleophilic addition of $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ to carbonyl compounds is crystalline and water soluble. It is converted back to the carbonyl compound on treatment with mineral acid or base.
Note: Note that the reaction of a carbonyl compound with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ nucleophile attack to carbonyl carbon occurs from sulphur (bisulfite ion) and not oxygen. Sulphur is less electronegative than oxygen and has lesser tendency than oxygen to hold electrons on it. Therefore, sulphur behaves as a better nucleophile than oxygen.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium bisulphate (or sodium hydrogen sulphite) reacts with carbonyl compounds mostly aldehydes (RCHO) and some ketones (RCOR) where the hydrocarbon chain, i.e. R-group is a small aliphatic chain like methyl ketone. Aromatic ketones generally do not react with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ due to steric effects of large benzene ring,
$NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ addition to aldehydes and ketones is a nucleophilic addition reaction. Nucleophile ($HSO_{3}^{-}$) attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. A tetrahedral alkoxide is formed as an intermediate. Final proton transfer occurs to give bisulfite addition compounds. If a large or bulky R-group is present adjacent to the electrophilic carbonyl carbon then the addition of $HSO_{3}^{-}$ is hindered.

HCHO (formaldehyde), $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$(acetaldehyde) are aldehydes and thus react with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ easily to addition products. However, reactivity of ketones is less than that of aldehydes. $C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ (acetone) has only methyl substituents and $HSO_{3}^{-}$ addition can occur.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ (acetophenone) has one phenyl group attached and the attack of the nucleophile is sterically favourable. Hence, ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ does give addition reaction with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The addition bisulphite product formed by nucleophilic addition of $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ to carbonyl compounds is crystalline and water soluble. It is converted back to the carbonyl compound on treatment with mineral acid or base.
Note: Note that the reaction of a carbonyl compound with $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ nucleophile attack to carbonyl carbon occurs from sulphur (bisulfite ion) and not oxygen. Sulphur is less electronegative than oxygen and has lesser tendency than oxygen to hold electrons on it. Therefore, sulphur behaves as a better nucleophile than oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




