
What is the IUPAC name of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{CHO}}$.

Answer
609k+ views
Hint- Here, we will proceed by stating what IUPAC stands for. Then, we will discuss the general rules for IUPAC naming of a chemical compound having aldehyde. Here, we will also be making the structure of the given compound.
Complete answer:
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
Since, the given chemical compound contains CHO group which means it is an aldehyde.
Aldehydes are named by replacing the suffix -ane in alkanes with -anal. If there is more than one -CHO group, the suffix is expanded to include a prefix that indicates the number of -CHO groups present (-anedial - there should not be more than 2 of these groups on the parent chain as they must occur at the ends). It is not necessary to indicate the position of the -CHO group because this group will be at the end of the parent chain and its carbon is automatically assigned as C-1.
Following rules are followed for IUPAC naming of aldehydes:
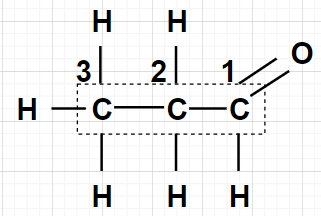
$1.$ The carbonyl group (CHO) takes precedence over alkyl groups and halogen substituents, as well as double bonds, in the numbering of the parent chain. So, the carbon of CHO group will be number as 1 as shown in the figure.
$2.$ When both double bonds (between two carbons in the parent chain) and carbonyl groups are present, the -en suffix follows the parent chain directly and the -al suffix follows the -en suffix (notice that the e is left off, -en instead of -ene). The location of the double bond(s) is(are) indicated before the parent name as before, and the -al suffix follows the -en suffix directly. Here, there is no double bond present so this step is skipped.
$3.$ If there is a choice in numbering not previously covered, the parent chain is numbered to give the substituents the lowest number at the first point of difference. Here, no substituent is present on the parent chain so this step is also skipped.
Here, there are three carbons so we will use propan and since, carbon number 1 is a carbon of the aldehyde so al will be used.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{CHO}}$ is propanal.
Note- In summary, the name of the compound is written out with the substituents in alphabetical order followed by the base name (derived from the number of carbons in the parent chain) followed by the main group attached (alcohol, aldehyde, etc). Commas are used between numbers and dashes are used between letters and numbers. There are no spaces in the name.
Complete answer:
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
Since, the given chemical compound contains CHO group which means it is an aldehyde.
Aldehydes are named by replacing the suffix -ane in alkanes with -anal. If there is more than one -CHO group, the suffix is expanded to include a prefix that indicates the number of -CHO groups present (-anedial - there should not be more than 2 of these groups on the parent chain as they must occur at the ends). It is not necessary to indicate the position of the -CHO group because this group will be at the end of the parent chain and its carbon is automatically assigned as C-1.
Following rules are followed for IUPAC naming of aldehydes:
$1.$ The carbonyl group (CHO) takes precedence over alkyl groups and halogen substituents, as well as double bonds, in the numbering of the parent chain. So, the carbon of CHO group will be number as 1 as shown in the figure.
$2.$ When both double bonds (between two carbons in the parent chain) and carbonyl groups are present, the -en suffix follows the parent chain directly and the -al suffix follows the -en suffix (notice that the e is left off, -en instead of -ene). The location of the double bond(s) is(are) indicated before the parent name as before, and the -al suffix follows the -en suffix directly. Here, there is no double bond present so this step is skipped.
$3.$ If there is a choice in numbering not previously covered, the parent chain is numbered to give the substituents the lowest number at the first point of difference. Here, no substituent is present on the parent chain so this step is also skipped.
Here, there are three carbons so we will use propan and since, carbon number 1 is a carbon of the aldehyde so al will be used.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{CHO}}$ is propanal.
Note- In summary, the name of the compound is written out with the substituents in alphabetical order followed by the base name (derived from the number of carbons in the parent chain) followed by the main group attached (alcohol, aldehyde, etc). Commas are used between numbers and dashes are used between letters and numbers. There are no spaces in the name.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




