
What is a position vector?
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: One end of the position vector is always fixed and the other end of the position vector kept on moving either on clockwise or in anti-clockwise so use this concept to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step solution -
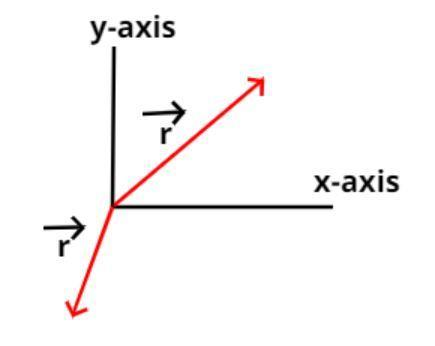
Position vector, straight line having one end fixed to a body and the other end attached to a moving point and used to describe the position of the point relative to the body. As the point moves, the position vector will change in length or in direction or in both length and direction, as shown in the figure.
Here we show the position vector (r) in two dimensional space (i.e. in x and y-axis).
The coordinates of r is
$\left( {r\cos \theta ,r\sin \theta } \right)$ general polar coordinates of position vector (r) where $\theta $ is taken from the positive direction of the x-axis moving anti-clockwise.
So the position vector r is written as,
$ \Rightarrow \vec r = r\cos \theta \hat i + r\sin \theta \hat j$, where $\hat i,\hat j$ are the direction of x and y axis respectively.
So as we see that the position vector has magnitude as well as direction so position vector is a vector quantity not a scalar quantity as in scalar quantity there is only magnitude.
For different points the position vector is different so as the magnitude as well as the direction as shown in the figure.
In three dimensional the position vector $\left( {\vec r} \right)$ is given as
$ \Rightarrow \vec r = x\hat i + y\hat j + z\hat k$
Where, $\hat i$ = unit vector along x direction, $\hat j$ = unit vector along y direction and $\hat k$ = unit vector along z direction.
So, this is the required answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept is position vector is nothing but a moving point w.r.t. the fixed point or the body either in clockwise or in anti-clockwise position vector can be 2-D or 3-D.
Complete step-by-step solution -

Position vector, straight line having one end fixed to a body and the other end attached to a moving point and used to describe the position of the point relative to the body. As the point moves, the position vector will change in length or in direction or in both length and direction, as shown in the figure.
Here we show the position vector (r) in two dimensional space (i.e. in x and y-axis).
The coordinates of r is
$\left( {r\cos \theta ,r\sin \theta } \right)$ general polar coordinates of position vector (r) where $\theta $ is taken from the positive direction of the x-axis moving anti-clockwise.
So the position vector r is written as,
$ \Rightarrow \vec r = r\cos \theta \hat i + r\sin \theta \hat j$, where $\hat i,\hat j$ are the direction of x and y axis respectively.
So as we see that the position vector has magnitude as well as direction so position vector is a vector quantity not a scalar quantity as in scalar quantity there is only magnitude.
For different points the position vector is different so as the magnitude as well as the direction as shown in the figure.
In three dimensional the position vector $\left( {\vec r} \right)$ is given as
$ \Rightarrow \vec r = x\hat i + y\hat j + z\hat k$
Where, $\hat i$ = unit vector along x direction, $\hat j$ = unit vector along y direction and $\hat k$ = unit vector along z direction.
So, this is the required answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept is position vector is nothing but a moving point w.r.t. the fixed point or the body either in clockwise or in anti-clockwise position vector can be 2-D or 3-D.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




