
Vibrating tuning fork of frequency $n$ is placed near the open end of a long cylindrical tube. The tube has a side opening and is fitted with a movable reflecting piston. As the piston is moved through $8.75cm$, the intensity of sound changes from a maximum to minimum. If the speed of sound is $350m/s$ . Then $n$ is
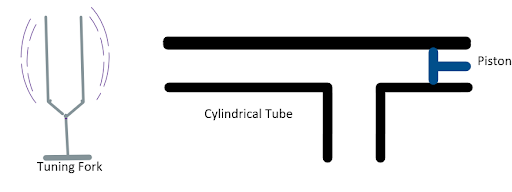
A. $500\,Hz$
B. $1000\,Hz$
C. $2000\,Hz$
D. $4000\,Hz$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: This problem is based on sound waves where we have to find $n$ i.e., frequency. We know that to find the frequency we must have the value of wavelength. As the intensity changes from maximum to minimum, the path difference will be $2l$. Use mathematical relation $f = \dfrac{v}{\lambda }$ to find the frequency of a sound wave.
Formula used:
$\text{Path Difference} = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda }}{2} - \dfrac{{(n)\lambda }}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Path Difference}= \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Here, $\lambda$ is the wavelength of sound.
$f(\text{frequency}) = \dfrac{{v(\text{velocity})}}{{\lambda (\text{wavelength})}}$
Complete step by step solution:
As the piston is moved through $l = 8.75\,cm$ (given), therefore path difference must be$2l = 2 \times 8.75 = 17.5\,cm$ … (1)
Also, the intensity changes from maximum to minimum (given)
$\text{Path Difference} = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda }}{2} - \dfrac{{(n)\lambda }}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Path Difference}= \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
i.e., From equation (1), we get
$\dfrac{\lambda }{2} = 17.5cm$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 35cm = 0.35m$
We know that,
$f(\text{frequency}) = \dfrac{{v(\text{velocity})}}{{\lambda (\text{wavelength})}}$
In this case,
$ \Rightarrow n = \dfrac{v}{\lambda } = \dfrac{{350}}{{0.35}}$
$ \therefore n = 1000\,Hz$
Thus, the frequency of a sound wave produced by a tuning fork due to a change in intensity of sound from a maximum to minimum is $1000\,Hz$.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: Since this is a numerical problem on sound waves hence, it is essential that phase difference must be calculated first as it will help us in finding the wavelength then the given parameters must be used very carefully to give an accurate solution. While writing an answer, always remember to put the units after results.
Formula used:
$\text{Path Difference} = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda }}{2} - \dfrac{{(n)\lambda }}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Path Difference}= \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Here, $\lambda$ is the wavelength of sound.
$f(\text{frequency}) = \dfrac{{v(\text{velocity})}}{{\lambda (\text{wavelength})}}$
Complete step by step solution:
As the piston is moved through $l = 8.75\,cm$ (given), therefore path difference must be$2l = 2 \times 8.75 = 17.5\,cm$ … (1)
Also, the intensity changes from maximum to minimum (given)
$\text{Path Difference} = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda }}{2} - \dfrac{{(n)\lambda }}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Path Difference}= \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
i.e., From equation (1), we get
$\dfrac{\lambda }{2} = 17.5cm$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 35cm = 0.35m$
We know that,
$f(\text{frequency}) = \dfrac{{v(\text{velocity})}}{{\lambda (\text{wavelength})}}$
In this case,
$ \Rightarrow n = \dfrac{v}{\lambda } = \dfrac{{350}}{{0.35}}$
$ \therefore n = 1000\,Hz$
Thus, the frequency of a sound wave produced by a tuning fork due to a change in intensity of sound from a maximum to minimum is $1000\,Hz$.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: Since this is a numerical problem on sound waves hence, it is essential that phase difference must be calculated first as it will help us in finding the wavelength then the given parameters must be used very carefully to give an accurate solution. While writing an answer, always remember to put the units after results.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)




