
Three charges $1\mu C$, $1\mu C$ and $2\mu C$ are kept at the vertices A, B and C respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC of \[10cm\] side. The resultant force on the charge at the vertex C is:
A) $0.9 N$
B) $1.8 N$
C) $2.72 N$
D) $3.12 N$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The given charges are kept at the vertices A, B and c respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC of \[10cm\]. Also we have to find the resultant force on the charge at the vertex C.
Consider a closed ABC triangle, and C will take a force on the charge. The diagram shown below.
Complete step by step answer:
The diagram will be like this,
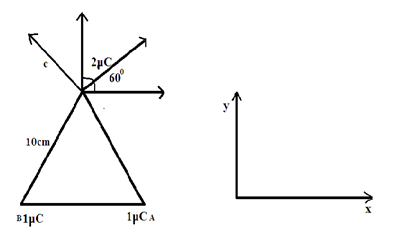
An equiangular triangle has three equal sides and angles. It will always have an angle of ${60^ \circ }$ in each corner.
Component of force due to B and A in x direction acting on C cancel out each other
\[\therefore {F_x} = 0\]
In $y$ direction forces add up
We get ${F_x} = \dfrac{{k(1\mu C)(2\mu C)}}{{{{(10 \times {{10}^{ - 2}})}^2}}} \times \sin 60 \times 2$
Substitute the values, and $\sin 60 = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times 1 \times {{10}^{ - 6}} \times 2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{100 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \times 2$
Cancelling the same term and multiply to the remaining terms, we get
So we get,
$ \Rightarrow 3.1176N$
So, The correct answer is option (D).
Additional information:
In geometry, a triangle may be a closed, two-dimensional shape with three straight sides. A triangle is also a polygon. A triangle with all sides equilateral, a triangle with two sides equal is called isosceles, and a triangle with all sides a different length is called scalene.
Note: Triangles are often broadly classified into two types, which are:
Triangle based on the lengths of their sides
A) According to the lengths of their sides, triangles can be classified into three types with are:
i) Scalene
ii) Isosceles
iii) Equilateral
Triangles based on the their interior angles
B) According to the their interior angles, triangles can be classified into three types with are:
i) Acute-angled
ii) Obtuse-angled
iii) Right-angled
Consider a closed ABC triangle, and C will take a force on the charge. The diagram shown below.
Complete step by step answer:
The diagram will be like this,

An equiangular triangle has three equal sides and angles. It will always have an angle of ${60^ \circ }$ in each corner.
Component of force due to B and A in x direction acting on C cancel out each other
\[\therefore {F_x} = 0\]
In $y$ direction forces add up
We get ${F_x} = \dfrac{{k(1\mu C)(2\mu C)}}{{{{(10 \times {{10}^{ - 2}})}^2}}} \times \sin 60 \times 2$
Substitute the values, and $\sin 60 = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{9 \times {{10}^9} \times 1 \times {{10}^{ - 6}} \times 2 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{100 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \times 2$
Cancelling the same term and multiply to the remaining terms, we get
So we get,
$ \Rightarrow 3.1176N$
So, The correct answer is option (D).
Additional information:
In geometry, a triangle may be a closed, two-dimensional shape with three straight sides. A triangle is also a polygon. A triangle with all sides equilateral, a triangle with two sides equal is called isosceles, and a triangle with all sides a different length is called scalene.
Note: Triangles are often broadly classified into two types, which are:
Triangle based on the lengths of their sides
A) According to the lengths of their sides, triangles can be classified into three types with are:
i) Scalene
ii) Isosceles
iii) Equilateral
Triangles based on the their interior angles
B) According to the their interior angles, triangles can be classified into three types with are:
i) Acute-angled
ii) Obtuse-angled
iii) Right-angled
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




