
The mirror image of the point (1,2,3) in a plane is $\left( \dfrac{-7}{3},\dfrac{-4}{3},\dfrac{-1}{3} \right)$. Which of the following points lies on the plane?
[a] (-1,-1,1)
[b] (1,1,1)
[c] (1,-1,1)
[d] (-1,-1,-1)
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that the midpoint of the line joining the object with the image lies on the plane. Hence find the coordinates of a point on the plane. Use the fact that the line joining the image with the object is normal to the plane. Hence find the normal vector of the plane. Now, use the fact that any line in the plane is perpendicular to the normal vector of the plane. Hence find which of the options lies on the plane.
Complete step by step solution:
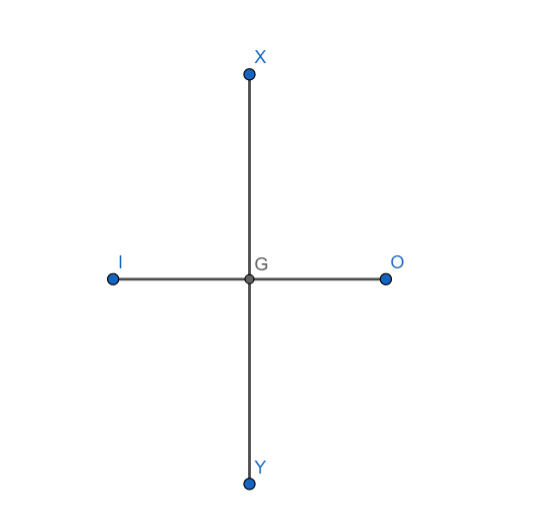
Consider a plane mirror XY. Let O be the object and let I be the image of the object O in the mirror XY. The following two properties are satisfied:
[1] IO is perpendicular to XY
[2] G is the midpoint of IO.
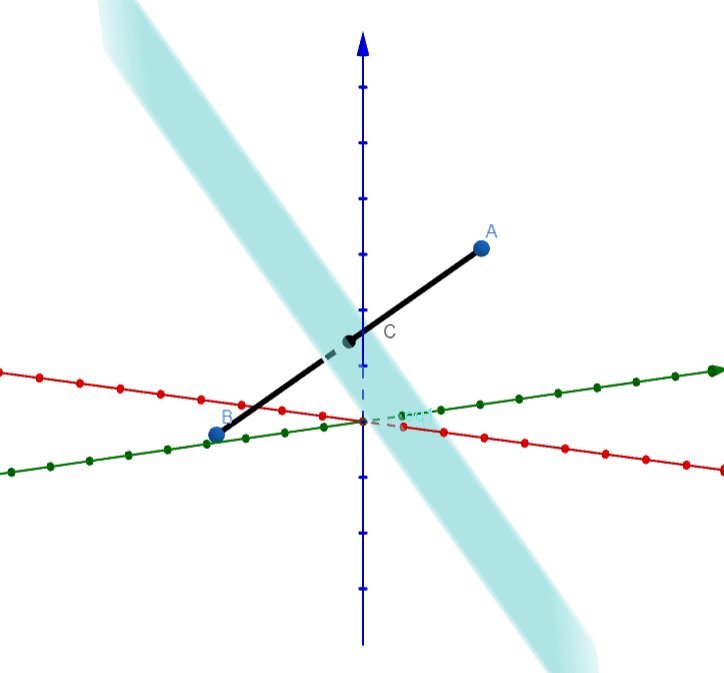
Hence, we have C is the midpoint of $A\left( 1,2,3 \right)$ and $B\left( \dfrac{-7}{3},\dfrac{-4}{3},\dfrac{-1}{3} \right)$
Hence by midpoint theorem, we have
$C\equiv \left( \dfrac{1-\dfrac{7}{3}}{2},\dfrac{2-\dfrac{4}{3}}{2},\dfrac{3-\dfrac{1}{3}}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{-2}{3},\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)$
Also, we have AB is perpendicular to the plane mirror.
Now, we have
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{AB}=Pv\left( B \right)-Pv\left( A \right)=\dfrac{-7}{3}\widehat{i}-\dfrac{4}{3}\widehat{j}-\dfrac{1}{3}\widehat{k}-\widehat{i}-2\widehat{j}-3\widehat{k} \\
& =\dfrac{-10}{3}\widehat{i}-\dfrac{10}{3}\widehat{j}-\dfrac{10}{3}\widehat{k} \\
\end{align}$
We know that if $\overrightarrow{v}$ is normal to a plane P, then $n\overrightarrow{v}$ is also normal to the plane P, where n is any scalar.
Since $\overrightarrow{AB}$ is normal to the plane mirror, we have
$\dfrac{-3}{10}\overrightarrow{AB}$ is also normal to the plane mirror
Hence, we have
$\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}$ is also normal to the plane mirror.
We know that the equation of a plane, whose normal is $\overrightarrow{n}=a\widehat{i}+b\widehat{j}+c\widehat{k}$ and passes through $A\left( {{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}},{{z}_{o}} \right)$ is given by
$a\left( x-{{x}_{0}} \right)+b\left( y-{{y}_{0}} \right)+c\left( z-{{z}_{0}} \right)=0$
Since $\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}$ is normal to the plane mirror and the plane passes through $C\left( \dfrac{-2}{3},\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)$, we have
$\begin{align}
& 1\left( x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right)+1\left( y-\dfrac{1}{3} \right)+1\left( z-\dfrac{4}{3} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x+y+z-1=0 \\
\end{align}$
which is the required equation of the plane mirror.
Now, we check option wise which of the options satisfies the equation of the mirror.
Option [a]:
We have x = -1, y = - 1 and x = 1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = -1-1+1-1 = -2.
Hence option [a] does not lie on the mirror
Option [b]:
We have x = 1, y = 1 and z =1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = 1+1+1-1 = 2
Hence option [b] does not lie on the mirror
Option [c]:
We have x = 1, y = -1 and z =1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = 1-1+1-1 = 0
Hence option [c] lies on the mirror
Option [d]:
We have x = -1, y = -1 and z =-1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = -1-1-1-1 = -4
Hence option [d] does not lies on the mirror
Hence option [c] is the only correct answer.
Note: Alternatively, we can use the vector equation of the plane to verify which of the points lie on the plane.
Let $\overrightarrow{r}$ be the position vector of any point P on the plane.
Since $\overrightarrow{CP}$is perpendicular to the normal, we have
$\overrightarrow{CP}.\left( \widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} \right)=0$
Now, we know that
\[\overrightarrow{CP}=Pv\left( P \right)-Pv\left( C \right)\]
Hence, we have
$\overrightarrow{CP}=\overrightarrow{r}-\left( \dfrac{-2}{3}\widehat{i}+\dfrac{1}{3}\widehat{j}+\dfrac{4}{3}\widehat{k} \right)$
Hence, we have
\[\left( \overrightarrow{r}-\left( \dfrac{-2}{3}\widehat{i}+\dfrac{1}{3}\widehat{j}+\dfrac{4}{3}\widehat{k} \right) \right)\cdot \left( \widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} \right)=0\], which is the required equation of the plane.
Check which of the options [a], [b], [c] and [d] satisfies the equation and hence find the answer.
Complete step by step solution:

Consider a plane mirror XY. Let O be the object and let I be the image of the object O in the mirror XY. The following two properties are satisfied:
[1] IO is perpendicular to XY
[2] G is the midpoint of IO.

Hence, we have C is the midpoint of $A\left( 1,2,3 \right)$ and $B\left( \dfrac{-7}{3},\dfrac{-4}{3},\dfrac{-1}{3} \right)$
Hence by midpoint theorem, we have
$C\equiv \left( \dfrac{1-\dfrac{7}{3}}{2},\dfrac{2-\dfrac{4}{3}}{2},\dfrac{3-\dfrac{1}{3}}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{-2}{3},\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)$
Also, we have AB is perpendicular to the plane mirror.
Now, we have
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{AB}=Pv\left( B \right)-Pv\left( A \right)=\dfrac{-7}{3}\widehat{i}-\dfrac{4}{3}\widehat{j}-\dfrac{1}{3}\widehat{k}-\widehat{i}-2\widehat{j}-3\widehat{k} \\
& =\dfrac{-10}{3}\widehat{i}-\dfrac{10}{3}\widehat{j}-\dfrac{10}{3}\widehat{k} \\
\end{align}$
We know that if $\overrightarrow{v}$ is normal to a plane P, then $n\overrightarrow{v}$ is also normal to the plane P, where n is any scalar.
Since $\overrightarrow{AB}$ is normal to the plane mirror, we have
$\dfrac{-3}{10}\overrightarrow{AB}$ is also normal to the plane mirror
Hence, we have
$\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}$ is also normal to the plane mirror.
We know that the equation of a plane, whose normal is $\overrightarrow{n}=a\widehat{i}+b\widehat{j}+c\widehat{k}$ and passes through $A\left( {{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}},{{z}_{o}} \right)$ is given by
$a\left( x-{{x}_{0}} \right)+b\left( y-{{y}_{0}} \right)+c\left( z-{{z}_{0}} \right)=0$
Since $\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}$ is normal to the plane mirror and the plane passes through $C\left( \dfrac{-2}{3},\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{4}{3} \right)$, we have
$\begin{align}
& 1\left( x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right)+1\left( y-\dfrac{1}{3} \right)+1\left( z-\dfrac{4}{3} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x+y+z-1=0 \\
\end{align}$
which is the required equation of the plane mirror.
Now, we check option wise which of the options satisfies the equation of the mirror.
Option [a]:
We have x = -1, y = - 1 and x = 1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = -1-1+1-1 = -2.
Hence option [a] does not lie on the mirror
Option [b]:
We have x = 1, y = 1 and z =1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = 1+1+1-1 = 2
Hence option [b] does not lie on the mirror
Option [c]:
We have x = 1, y = -1 and z =1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = 1-1+1-1 = 0
Hence option [c] lies on the mirror
Option [d]:
We have x = -1, y = -1 and z =-1
Hence, we have
x+y+z-1 = -1-1-1-1 = -4
Hence option [d] does not lies on the mirror
Hence option [c] is the only correct answer.
Note: Alternatively, we can use the vector equation of the plane to verify which of the points lie on the plane.
Let $\overrightarrow{r}$ be the position vector of any point P on the plane.
Since $\overrightarrow{CP}$is perpendicular to the normal, we have
$\overrightarrow{CP}.\left( \widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} \right)=0$
Now, we know that
\[\overrightarrow{CP}=Pv\left( P \right)-Pv\left( C \right)\]
Hence, we have
$\overrightarrow{CP}=\overrightarrow{r}-\left( \dfrac{-2}{3}\widehat{i}+\dfrac{1}{3}\widehat{j}+\dfrac{4}{3}\widehat{k} \right)$
Hence, we have
\[\left( \overrightarrow{r}-\left( \dfrac{-2}{3}\widehat{i}+\dfrac{1}{3}\widehat{j}+\dfrac{4}{3}\widehat{k} \right) \right)\cdot \left( \widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} \right)=0\], which is the required equation of the plane.
Check which of the options [a], [b], [c] and [d] satisfies the equation and hence find the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




