
Polymer which has amide linkage is:
A.nylon-6,6
B.terylene
C.teflon
D.Bakelite
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: We must know that the materials made of long, repeating chains of molecules with chemical linkages are called polymers. Amide linkages are referred to as linkages between carbonyl groups and nitrogen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Amide is an organic functional group that is characterized by a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom. \[ - CO = NH2 - \] is a peptide bond which is a chemical bond formed between the carboxyl group of one molecule that reacts with the amine group of the other molecule.
Below given is an example of amide linkage.
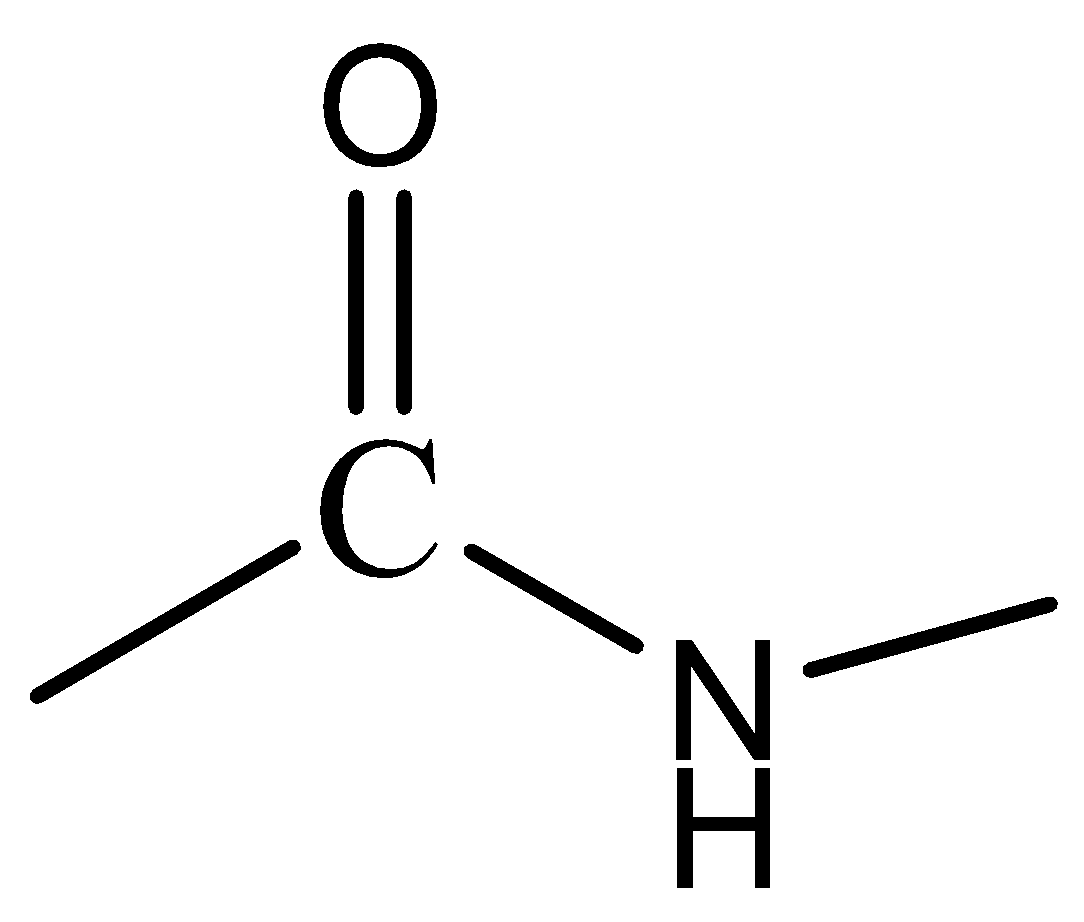
The polyamides are the polymers with repeating units that are linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides are present both naturally and artificially. Silk and wool are few examples of naturally occurring polyamides. Artificially synthesized polyamides such as nylons, aramids, and sodium poly aspartate are synthesized by step growth polymerization method.
Here, from the given options Nylon-6,6 is a polymer having amide linkages.
So, nylons are also called as polyamides due to their characteristic amide groups in the backbone chain.
Amide groups in nylon molecules are very polar, and form hydrogen bonding with each other. Due to hydrogen bonding , the nylon backbone becomes regular and symmetrical, and the structure makes the nylons crystalline.
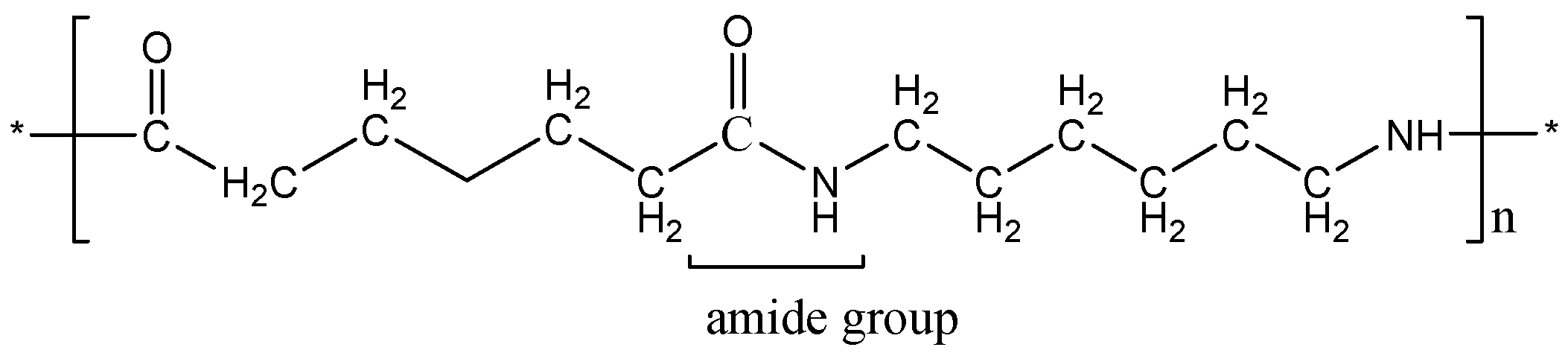
The above mentioned diagram shows the amide linkage present in Nylon-6,6 molecules. Nylon 6, 6 is a polymer formed by polymerization of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid and is a polyamide.
Note:
We must know that the polymer bakelite is formed by polymerization of phenol and formaldehyde with ether linkage. Terylene is a polymer that is formed by polymerization of ethyl alcohol and terephthalic acid with polyester bond in between. The polymerization of tetra fluro-ethylene monomers forms Teflon polymer.
Complete step by step answer:
Amide is an organic functional group that is characterized by a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom. \[ - CO = NH2 - \] is a peptide bond which is a chemical bond formed between the carboxyl group of one molecule that reacts with the amine group of the other molecule.
Below given is an example of amide linkage.

The polyamides are the polymers with repeating units that are linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides are present both naturally and artificially. Silk and wool are few examples of naturally occurring polyamides. Artificially synthesized polyamides such as nylons, aramids, and sodium poly aspartate are synthesized by step growth polymerization method.
Here, from the given options Nylon-6,6 is a polymer having amide linkages.
So, nylons are also called as polyamides due to their characteristic amide groups in the backbone chain.
Amide groups in nylon molecules are very polar, and form hydrogen bonding with each other. Due to hydrogen bonding , the nylon backbone becomes regular and symmetrical, and the structure makes the nylons crystalline.

The above mentioned diagram shows the amide linkage present in Nylon-6,6 molecules. Nylon 6, 6 is a polymer formed by polymerization of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid and is a polyamide.
Note:
We must know that the polymer bakelite is formed by polymerization of phenol and formaldehyde with ether linkage. Terylene is a polymer that is formed by polymerization of ethyl alcohol and terephthalic acid with polyester bond in between. The polymerization of tetra fluro-ethylene monomers forms Teflon polymer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




