
Metal M of radius 50nm is crystallized fcc type and made of cubic crystal such that the face of unit cells is aligned with the face of cubic crystal. If the total number of metal atoms of M at all faces of cubic crystal is $6X{{10}^{30}}$ , then the area of one face of cubic crystal is $AX{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}}.$find the value of A.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: A face centered cubic (FCC) unit cell contains atoms at all the corners and at the centre of all the faces of the cube. Each atom in a face -centered cubic located at the face-centre is shared between two adjacent unit cells and only \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] of each atom belongs to a unit cell.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider one face of unit cell,
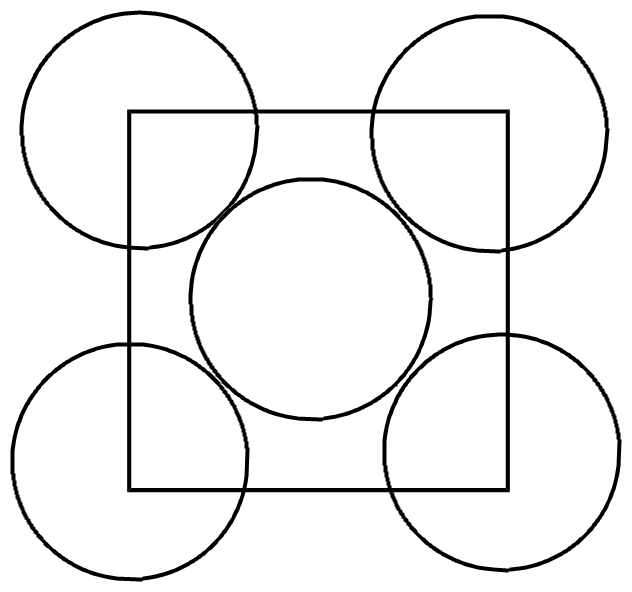
No of atoms on one face= $4(corners)X\dfrac{1}{8}+1(facecentre)X\dfrac{1}{2}(facecentreshare)=\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}=1$ per face
No of metal atoms of M at all metal faces of cubic crystal = $6X{{10}^{30}}$
Therefore, number of atoms on once face =$6X{{10}^{30}}X\dfrac{1}{6}={{10}^{30}} atoms$
Hence number of unit cells at one face of crystal = ${{10}^{30}}$ atoms
So the number of unit cells at the edge of the crystal = $\sqrt{{{10}^{30}}}={{10}^{15}}$
Metal M radius (r) = 50nm
Now, edge length of the unit cell = \[\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}Xr=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}X50nm\]
Edge length of cubic crystal = \[\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}X50X{{10}^{15}}nm\]
So, area of face crystal = $\begin{align}
& ={{(edge\text{ }length\text{ }of\text{ }cubic\text{ }crystal)}^{2}}={{(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}X50X{{10}^{15}})}^{2}}n{{m}^{2}}=\dfrac{16}{2}X50X50X{{10}^{30}}X{{10}^{-18}}{{m}^{2}} \\
& =2X{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, $AX{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}}=2X{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}}$
Hence , the value of A = 2.
Note: We know that any crystal lattice is made up of very large unit cells and every lattice point as occupied by one constituent particle (atom, molecule or ion). We must consider three types of cubic unit cells and for simplicity assume that the constituent particle is an atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider one face of unit cell,

No of atoms on one face= $4(corners)X\dfrac{1}{8}+1(facecentre)X\dfrac{1}{2}(facecentreshare)=\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}=1$ per face
No of metal atoms of M at all metal faces of cubic crystal = $6X{{10}^{30}}$
Therefore, number of atoms on once face =$6X{{10}^{30}}X\dfrac{1}{6}={{10}^{30}} atoms$
Hence number of unit cells at one face of crystal = ${{10}^{30}}$ atoms
So the number of unit cells at the edge of the crystal = $\sqrt{{{10}^{30}}}={{10}^{15}}$
Metal M radius (r) = 50nm
Now, edge length of the unit cell = \[\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}Xr=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}X50nm\]
Edge length of cubic crystal = \[\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}X50X{{10}^{15}}nm\]
So, area of face crystal = $\begin{align}
& ={{(edge\text{ }length\text{ }of\text{ }cubic\text{ }crystal)}^{2}}={{(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}X50X{{10}^{15}})}^{2}}n{{m}^{2}}=\dfrac{16}{2}X50X50X{{10}^{30}}X{{10}^{-18}}{{m}^{2}} \\
& =2X{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, $AX{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}}=2X{{10}^{16}}{{m}^{2}}$
Hence , the value of A = 2.
Note: We know that any crystal lattice is made up of very large unit cells and every lattice point as occupied by one constituent particle (atom, molecule or ion). We must consider three types of cubic unit cells and for simplicity assume that the constituent particle is an atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




