
Explain the structures of $Xe{F_2}$ and $Xe{F_6}$.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint:Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or theory of VSEPR is a concept used in chemistry to determine the structure of each molecule in which the electron pairs that surround their central atoms. This is also known by its two key proponents, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm as the Gillespie-Nyholm principle. The VSEPR principle is that pairs of valence electrons across an atom appear to repel each other, so it will follow a mechanism which reduces repulsion to a low minimum.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> The sum of the amount of bond pair and number of lone pairs produced by their non-bonding electrons of valence are regarded as the steric number of the central atom. It is presumed that the electron pairs reside on the surface of a sphere present on the central atom and appear to hold positions that reduce reciprocal repulsions by the maximization of their width. Therefore, the total geometry they are going to adopt is determined by the number of electron pairs. (or groups).
> Xenon difluoride, with a chemical composition of $Xe{F_2}$, is a strong fluorinating agent and one of the most stable compounds of xenon. This is humidity-sensitive, as other covalent inorganic fluorides. This decomposes with light or water vapor but is retained in storage otherwise intact. Xenon difluoride is a crystalline structure thick, pure. The odour is nauseating and the pressure of the steam is weak.
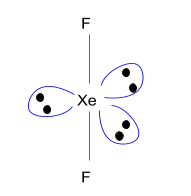
> As $Xe{F_2}$ has $s{p^3}d\left( {\dfrac{S}{8} = \dfrac{{8 + 7 \times 2}}{8} = \dfrac{{22}}{8}} \right)$ hybridisation, which means that it has 2 bond pair and 3 lone pair, the structure of $Xe{F_2}$ is linear.
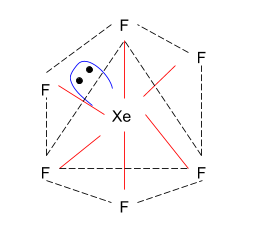
> The noble gas component in composition $Xe{F_6}$ is xenon hexafluoride. This is one of the three discrete xenon fluorides, the two $Xe{F_2}$ and $Xe{F_4}$ being the two others. Everything established at regular temperatures is exergonic and stable. $Xe{F_6}$ is the most efficient fluorinating agent of the series. This is a colourless material that can quickly be intensified by strong yellow vapours.
> As $Xe{F_6}$ has $s{p^3}{d^3}\left( {\dfrac{S}{8} = \dfrac{{8 + 7 \times 6}}{8} = \dfrac{{50}}{8}} \right)$ hybridisation, which means that it has 6 bond pair and 1 lone pair, the structure of $Xe{F_6}$ is a distorted octahedron.
Note: The sum of the amount and number of lone couples produced by their non-bonding electrons of valence are regarded as the steric number of the central atom. It is presumed that the electron pairs reside on the surface of a sphere present on the central atom and appear to hold positions that reduce minimum repulsions by the maximum distance. Therefore, the total geometry they are going to adopt is determined by the number of electron peers (or groups).
Complete step-by-step answer:
> The sum of the amount of bond pair and number of lone pairs produced by their non-bonding electrons of valence are regarded as the steric number of the central atom. It is presumed that the electron pairs reside on the surface of a sphere present on the central atom and appear to hold positions that reduce reciprocal repulsions by the maximization of their width. Therefore, the total geometry they are going to adopt is determined by the number of electron pairs. (or groups).
> Xenon difluoride, with a chemical composition of $Xe{F_2}$, is a strong fluorinating agent and one of the most stable compounds of xenon. This is humidity-sensitive, as other covalent inorganic fluorides. This decomposes with light or water vapor but is retained in storage otherwise intact. Xenon difluoride is a crystalline structure thick, pure. The odour is nauseating and the pressure of the steam is weak.
> As $Xe{F_2}$ has $s{p^3}d\left( {\dfrac{S}{8} = \dfrac{{8 + 7 \times 2}}{8} = \dfrac{{22}}{8}} \right)$ hybridisation, which means that it has 2 bond pair and 3 lone pair, the structure of $Xe{F_2}$ is linear.

> The noble gas component in composition $Xe{F_6}$ is xenon hexafluoride. This is one of the three discrete xenon fluorides, the two $Xe{F_2}$ and $Xe{F_4}$ being the two others. Everything established at regular temperatures is exergonic and stable. $Xe{F_6}$ is the most efficient fluorinating agent of the series. This is a colourless material that can quickly be intensified by strong yellow vapours.
> As $Xe{F_6}$ has $s{p^3}{d^3}\left( {\dfrac{S}{8} = \dfrac{{8 + 7 \times 6}}{8} = \dfrac{{50}}{8}} \right)$ hybridisation, which means that it has 6 bond pair and 1 lone pair, the structure of $Xe{F_6}$ is a distorted octahedron.

Note: The sum of the amount and number of lone couples produced by their non-bonding electrons of valence are regarded as the steric number of the central atom. It is presumed that the electron pairs reside on the surface of a sphere present on the central atom and appear to hold positions that reduce minimum repulsions by the maximum distance. Therefore, the total geometry they are going to adopt is determined by the number of electron peers (or groups).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




