
Draw a well labelled diagram of a dry cell and explain its construction.
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Electric cells are used to power devices such as clocks, calculators, and phones. It is a minor source of power. It's also known as a dry cell or a pencil cell. Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy by this device. A dry cell is a non-rechargeable main cell that cannot be used again. These cells are used in a variety of household items such as radios, transistors, tape recorders, calculators, and so on.
Complete answer:
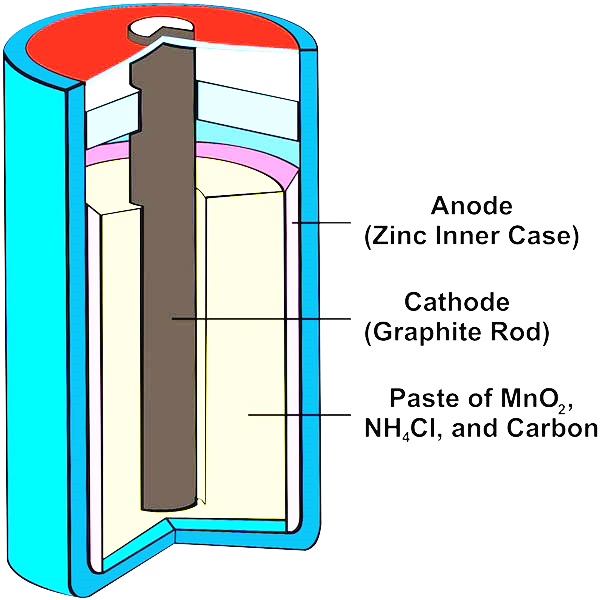
The dry cell is one of many electrochemical cell types. The electrolyte is immobilised as a paste in a dry cell, with just enough moisture to allow current to flow. Since it has no free liquid, unlike a wet cell, a dry cell can run in any direction without spilling.
It consists of a zinc jar on one side of the cell with a narrow brass cap labelled positive (+) and a metal base on the other side of the cell labelled negative (-).
A carbon rod is inserted in the cell's middle, surrounded by a muslin bag containing a mixture of manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]) and charcoal (C).
The electrolyte is a moist paste of ammonium chloride (\[N{H_4}Cl\]), plaster of Paris, starch, and other materials, and the zinc container's outer body (except the base) is insulated with thick cardboard or plastic.
Working:
As a cell is attached to a light bulb, the chemical reaction within the cell speeds up, and current begins to circulate through the bulb. As a result, the lamp illuminates.
These dry cells have a limited amount of power.
Note:
A typical dry cell has a zinc anode, which is typically in the shape of a cylindrical tub, and a carbon cathode, which is usually in the shape of a central rod. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride, which is applied to the zinc anode as a paste. A second paste made of ammonium chloride and manganese dioxide fills the vacuum between the electrolyte and the carbon cathode, with the latter serving as a depolariser. Ammonium chloride is substituted with zinc chloride in some projects, which are mostly sold as "heavy duty."
Complete answer:

The dry cell is one of many electrochemical cell types. The electrolyte is immobilised as a paste in a dry cell, with just enough moisture to allow current to flow. Since it has no free liquid, unlike a wet cell, a dry cell can run in any direction without spilling.
It consists of a zinc jar on one side of the cell with a narrow brass cap labelled positive (+) and a metal base on the other side of the cell labelled negative (-).
A carbon rod is inserted in the cell's middle, surrounded by a muslin bag containing a mixture of manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]) and charcoal (C).
The electrolyte is a moist paste of ammonium chloride (\[N{H_4}Cl\]), plaster of Paris, starch, and other materials, and the zinc container's outer body (except the base) is insulated with thick cardboard or plastic.
Working:
As a cell is attached to a light bulb, the chemical reaction within the cell speeds up, and current begins to circulate through the bulb. As a result, the lamp illuminates.
These dry cells have a limited amount of power.
Note:
A typical dry cell has a zinc anode, which is typically in the shape of a cylindrical tub, and a carbon cathode, which is usually in the shape of a central rod. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride, which is applied to the zinc anode as a paste. A second paste made of ammonium chloride and manganese dioxide fills the vacuum between the electrolyte and the carbon cathode, with the latter serving as a depolariser. Ammonium chloride is substituted with zinc chloride in some projects, which are mostly sold as "heavy duty."
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




