
Define hypogynous, perigynous, and epigynous flowers.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Flowers are classified based on the position of the corolla, calyx, and androecium with respect to that of the ovary on the thalamus, into hypogynous, perigynous, and epigynous. The gynoecium is the female reproductive organ of a flower and is composed of one or more carpels.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A carpel is made up of three parts namely stigma, style, and ovary. Flowers are categorized into three types according to the site of calyx, corolla, and androecium to that of the ovary on the thalamus. Let's see the classification in detail:
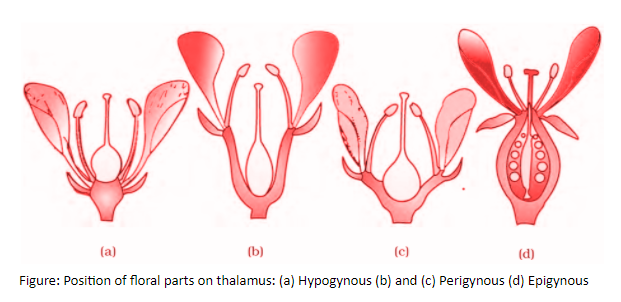
Hypogynous flowers: The flowers in which gynoecium occupies the highest position while the other parts are situated below it is called hypogynous flowers. The ovary in this variety is said to be superior, e.g., mustard, china rose, and brinjal.
Perigynous flowers: The flowers in which gynoecium is situated in the center and other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level, they are called perigynous flowers. The ovary in the perigynous type of flowers is said to be half inferior, e.g., plum rose, peach.
Epigynous flowers: In these flowers, the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it, the other parts of flower arise above the ovary. An epigynous flower's ovary is said to be inferior as in flowers of guava and cucumber, and the ray florets of sunflowers.
Note:
- A typical flower has four different types of whorls arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk or pedicel, called thalamus or receptacle.
- The calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower and the members are called sepals.
- Corolla is composed of petals.
- The androecium is composed of stamens.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A carpel is made up of three parts namely stigma, style, and ovary. Flowers are categorized into three types according to the site of calyx, corolla, and androecium to that of the ovary on the thalamus. Let's see the classification in detail:
Hypogynous flowers: The flowers in which gynoecium occupies the highest position while the other parts are situated below it is called hypogynous flowers. The ovary in this variety is said to be superior, e.g., mustard, china rose, and brinjal.
Perigynous flowers: The flowers in which gynoecium is situated in the center and other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level, they are called perigynous flowers. The ovary in the perigynous type of flowers is said to be half inferior, e.g., plum rose, peach.
Epigynous flowers: In these flowers, the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it, the other parts of flower arise above the ovary. An epigynous flower's ovary is said to be inferior as in flowers of guava and cucumber, and the ray florets of sunflowers.

Note:
- A typical flower has four different types of whorls arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk or pedicel, called thalamus or receptacle.
- The calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower and the members are called sepals.
- Corolla is composed of petals.
- The androecium is composed of stamens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




