
Convert Ethanol to But-1-yne.
Answer
533.6k+ views
Hint: First, convert the alcohol into a haloalkane. Now take acetylene and convert it into sodium acetylide. Now add the haloalkane and sodium acetylide which will form an alkyne containing a higher number of a carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Ethanol is a compound of alcohol groups having a $-OH$functional group. Its formula is $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH$. It is a 2 carbon compound.
But-1-yne is a compound of the alkyne group having a triple bond. Its formula is $HC\equiv C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$. It is a 4 carbon compound.
When alcohols are reacted with hydrobromic acid in the presence of little sulfuric acid it forms bromoalkane.
When acetylene or ethyne is reacted with sodamide in liquid ammonia it forms sodium acetylide. Now, this sodium acetylide can be converted into the required alkyne by adding the haloalkane of the required number of a carbon atom.
To convert ethanol to but-1-yne:
We have to convert a 2 carbon compound to a 4 carbon compound.
First, convert the ethanol to bromoethane with hydrobromic acid and a little amount of ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ Next, take acetylene and react with $NaN{{H}_{2}}$ to form sodium acetylide. Now, add the bromoethane and acetylide to form but-1-yne. This reaction is useful for making higher alkynes have triple bonds at the first carbon atom.
The reaction and mechanism are given below:
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\to HC\equiv C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$
The mechanism of the reaction is:
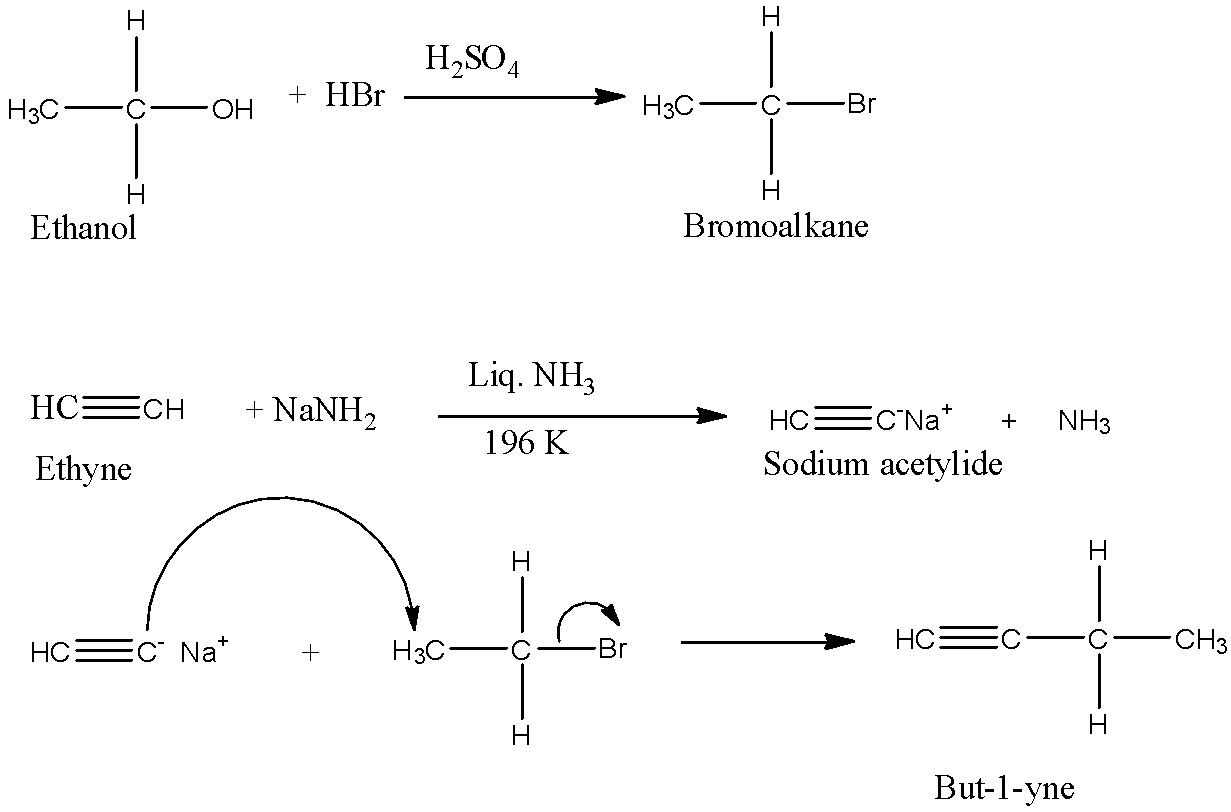
Note: When 2 moles of $NaN{{H}_{3}}$ are reacted with the ethyne or acetylene, both the hydrogen of the ethyne are replaced with the sodium atom. Now, this sodium acetylide can be used to make alkynes in which the triple bond is not at the first carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Ethanol is a compound of alcohol groups having a $-OH$functional group. Its formula is $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH$. It is a 2 carbon compound.
But-1-yne is a compound of the alkyne group having a triple bond. Its formula is $HC\equiv C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$. It is a 4 carbon compound.
When alcohols are reacted with hydrobromic acid in the presence of little sulfuric acid it forms bromoalkane.
When acetylene or ethyne is reacted with sodamide in liquid ammonia it forms sodium acetylide. Now, this sodium acetylide can be converted into the required alkyne by adding the haloalkane of the required number of a carbon atom.
To convert ethanol to but-1-yne:
We have to convert a 2 carbon compound to a 4 carbon compound.
First, convert the ethanol to bromoethane with hydrobromic acid and a little amount of ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ Next, take acetylene and react with $NaN{{H}_{2}}$ to form sodium acetylide. Now, add the bromoethane and acetylide to form but-1-yne. This reaction is useful for making higher alkynes have triple bonds at the first carbon atom.
The reaction and mechanism are given below:
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\to HC\equiv C-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$
The mechanism of the reaction is:

Note: When 2 moles of $NaN{{H}_{3}}$ are reacted with the ethyne or acetylene, both the hydrogen of the ethyne are replaced with the sodium atom. Now, this sodium acetylide can be used to make alkynes in which the triple bond is not at the first carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




