
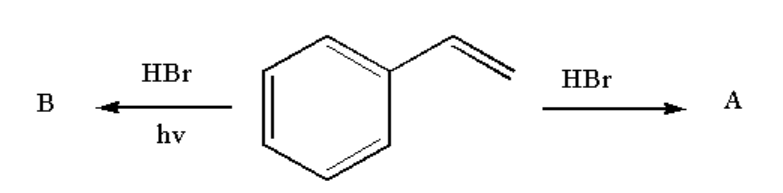
Analyse the following reaction and identify the nature of A and B.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The chemical name of HBr is hydrogen bromide. In the given reaction it should be noted that one reaction is taking place in presence of light and other in the absence of light. The reaction taking place in the presence of light forms free radicals.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction of a given compound with hydrogen bromide is an electrophilic addition reaction.
In an electrophilic addition reaction, the substrate is first attacked by an electrophile which results in the addition of an atom or molecule across multiple bonds.
In the first step, hydrogen bromide breaks to form hydrogen ion and bromide ion.
The reaction is shown below.
\[HBr \to {H^ + } + B{r^ - }\]
Image: Step 1: Formation of electrophile
In the second step, the hydrogen ion attack the double bond and a carbocation complex is formed.
The reaction is shown below.
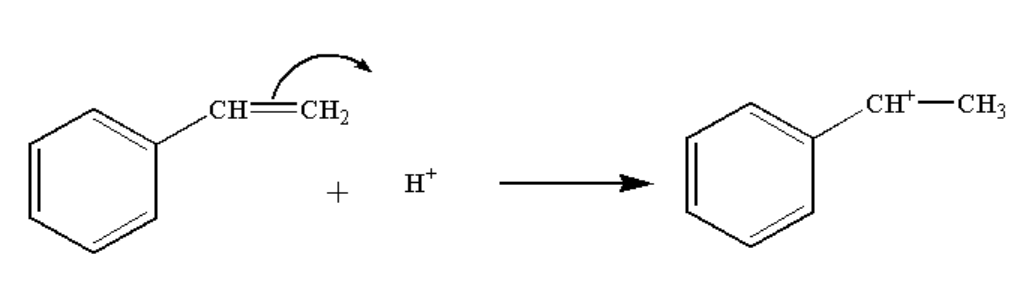
Image: Step 2: Formation of carbocation
In the third step, the bromide ion attacks the carbocation to form the compound A.
The reaction is shown below.
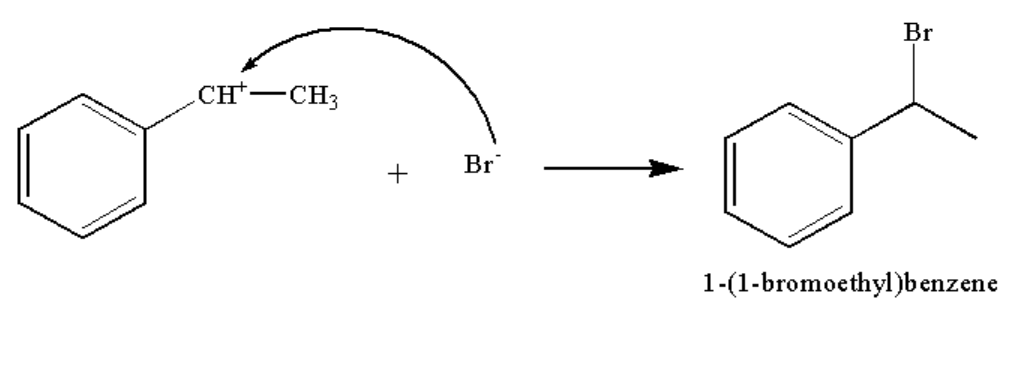
Image: Step 3: Formation of compound A
The reaction of a given compound with hydrogen bromide in presence of light is a free radical addition reaction.
Free radical addition reaction involves the addition of free radicals. Free radicals are formed by homolytic cleavage.
The hydrogen bromide undergoes homolysis to form a free radical of hydrogen and bromine.
The reaction is shown below.
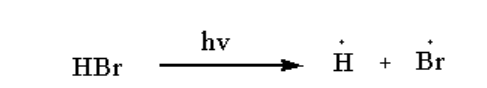
Image: Step 1: Free radical formation
Next, bromine radical is added to the compound
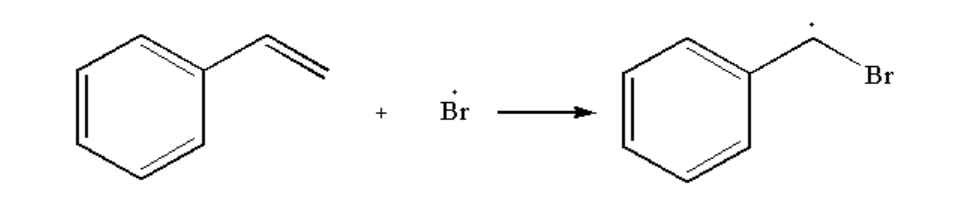
Image: Step 2
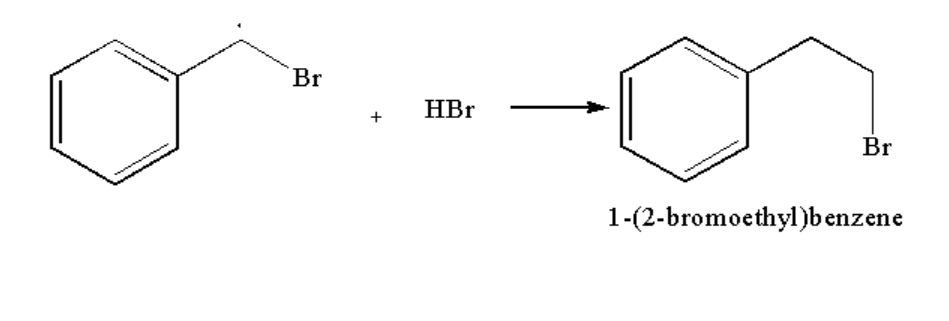
Image: Step 3: Formation of compound B
Therefore compound A is 1-(1-bromoethylbenzene) and compound B is 1-(2-bromoethyl)benzene.
Note: The anti-Markovnikov free radical addition of haloalkane only takes place in HBr in presence of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide starts the chain reaction in the initiation step..
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction of a given compound with hydrogen bromide is an electrophilic addition reaction.
In an electrophilic addition reaction, the substrate is first attacked by an electrophile which results in the addition of an atom or molecule across multiple bonds.
In the first step, hydrogen bromide breaks to form hydrogen ion and bromide ion.
The reaction is shown below.
\[HBr \to {H^ + } + B{r^ - }\]
Image: Step 1: Formation of electrophile
In the second step, the hydrogen ion attack the double bond and a carbocation complex is formed.
The reaction is shown below.

Image: Step 2: Formation of carbocation
In the third step, the bromide ion attacks the carbocation to form the compound A.
The reaction is shown below.

Image: Step 3: Formation of compound A
The reaction of a given compound with hydrogen bromide in presence of light is a free radical addition reaction.
Free radical addition reaction involves the addition of free radicals. Free radicals are formed by homolytic cleavage.
The hydrogen bromide undergoes homolysis to form a free radical of hydrogen and bromine.
The reaction is shown below.

Image: Step 1: Free radical formation
Next, bromine radical is added to the compound

Image: Step 2

Image: Step 3: Formation of compound B
Therefore compound A is 1-(1-bromoethylbenzene) and compound B is 1-(2-bromoethyl)benzene.
Note: The anti-Markovnikov free radical addition of haloalkane only takes place in HBr in presence of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide starts the chain reaction in the initiation step..
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




