
An object of 5 cm height is placed at 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10cm. Find the image distance, height, magnification of the image and characteristics of the image?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Draw an X-Y plane and position a concave lens with an optical centre at the origin such that the curved side is facing the negative Y-axis. The lens should have a focal length of 10 cm. Now, on the primary axis, we position a 5 cm tall item 20 cm away from the optical centre. The focus and the object are located at (-10, 0) and (-20, 0), respectively.
Complete answer:
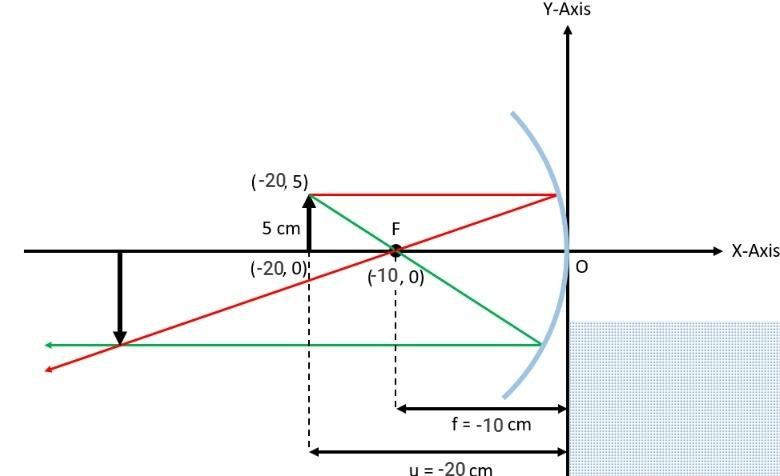
Now, in order to build the ray diagram, we first choose a ray that is parallel to the major axis (red line) and another ray that traverses the focus (green line). After being reflected by the mirror, these two rays come together at a point to produce the picture of the item.Since the object is located between the focus and centre of curvature of the concave mirror, the image will be formed away from the curvature ($v > 20$) and the image will be real, inverted, and for magnification we will check it.
To calculate the image distance, we will use the mirror’s formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Since both the focus and the object are on the negative side of the Y-axis, therefore
$f = - 10cm $
$u = - 20cm $
So,
$\dfrac{1}{{ - 10}} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{ - 20}}$
$v = - 20cm$
Therefore, the image is formed on the negative side of the Y-axis and at a distance of 20 cm from the optical centre of the mirror.
For the height of image, we use the formula of Magnification (m) which is calculated using the formula
$m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u}$
Image height is calculated by this formula. We know the object height, u and v therefore, the image height is given by
$\dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}} = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u} = \dfrac{{20}}{{ - 20}}$
Putting ${h_o} = 5cm$we get
${h_i} = - 5cm$
The image formed is inverted with a height same as object i.e., 5cm. Property of image: Real, inverted, same size as object
Note: In the ray diagram-based questions, students get confused with the sign convention and can commit silly mistakes. The ideal way to resolve these problems is to draw the ray diagram on an X-Y plane, as was done in this question, to eliminate any confusion. Also don’t forget to use sign convection in the magnification formula.
Complete answer:

Now, in order to build the ray diagram, we first choose a ray that is parallel to the major axis (red line) and another ray that traverses the focus (green line). After being reflected by the mirror, these two rays come together at a point to produce the picture of the item.Since the object is located between the focus and centre of curvature of the concave mirror, the image will be formed away from the curvature ($v > 20$) and the image will be real, inverted, and for magnification we will check it.
To calculate the image distance, we will use the mirror’s formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Since both the focus and the object are on the negative side of the Y-axis, therefore
$f = - 10cm $
$u = - 20cm $
So,
$\dfrac{1}{{ - 10}} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{ - 20}}$
$v = - 20cm$
Therefore, the image is formed on the negative side of the Y-axis and at a distance of 20 cm from the optical centre of the mirror.
For the height of image, we use the formula of Magnification (m) which is calculated using the formula
$m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u}$
Image height is calculated by this formula. We know the object height, u and v therefore, the image height is given by
$\dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}} = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u} = \dfrac{{20}}{{ - 20}}$
Putting ${h_o} = 5cm$we get
${h_i} = - 5cm$
The image formed is inverted with a height same as object i.e., 5cm. Property of image: Real, inverted, same size as object
Note: In the ray diagram-based questions, students get confused with the sign convention and can commit silly mistakes. The ideal way to resolve these problems is to draw the ray diagram on an X-Y plane, as was done in this question, to eliminate any confusion. Also don’t forget to use sign convection in the magnification formula.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




