
Why is alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogen of carbonyl compounds acidic in nature?
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: The alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogen is the hydrogen atom attached to the carbon atom adjacent to the carbon atom of the carbonyl compound. $\text{R}-\overset{*}{{\text{C}}}\,{{\text{H}}_{2}}-\text{CHO}$ , the carbon atom having $*$ has the hydrogen atoms are the alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogens of this compound. Acidity means the ability to lose $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ ions. If the compound after losing $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ ions is stable, then, it is acidic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss the acidity of alpha-hydrogens in carbonyl compounds. There are two reasons for it.
Reason (1)- In a carbonyl group $\left( \text{C=O} \right)$, the oxygen attached is extremely electronegative. As it attracts the electrons toward itself. This develops a partial positive charge on the $\alpha -$carbon and to reduce this positive charge, $\alpha -$carbon readily loses its hydrogen atom which makes it acidic in nature.
Reason (2)- After the removal of acidic hydrogen, the compound undergoes keto-enol tautomerism (a type of resonance only). This makes the compound stable due to the presence of negative charge on the electronegative oxygen atom. Like
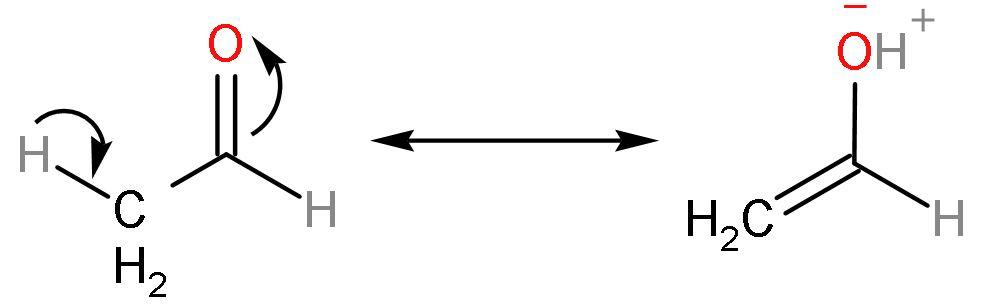
Due to this stability of keto-enol, the carbonyl compounds seem to lose their alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogen which is then acidic in nature.
Note: The alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogens of aldehydes are more acidic in nature than that of ketones because the electron donating groups like methyl of ketones decreases the polarity of the $\left( \text{C}-\text{H} \right)$ bond. Moreover, after the removal of $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ ions, the electron donating groups increases the negative charge on the negatively charged carbon atom. This makes the compound unstable and less prone to removal of alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogens. This positive inductive effect is not seen in aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss the acidity of alpha-hydrogens in carbonyl compounds. There are two reasons for it.
Reason (1)- In a carbonyl group $\left( \text{C=O} \right)$, the oxygen attached is extremely electronegative. As it attracts the electrons toward itself. This develops a partial positive charge on the $\alpha -$carbon and to reduce this positive charge, $\alpha -$carbon readily loses its hydrogen atom which makes it acidic in nature.
Reason (2)- After the removal of acidic hydrogen, the compound undergoes keto-enol tautomerism (a type of resonance only). This makes the compound stable due to the presence of negative charge on the electronegative oxygen atom. Like

Due to this stability of keto-enol, the carbonyl compounds seem to lose their alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogen which is then acidic in nature.
Note: The alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogens of aldehydes are more acidic in nature than that of ketones because the electron donating groups like methyl of ketones decreases the polarity of the $\left( \text{C}-\text{H} \right)$ bond. Moreover, after the removal of $\left[ {{\text{H}}^{+}} \right]$ ions, the electron donating groups increases the negative charge on the negatively charged carbon atom. This makes the compound unstable and less prone to removal of alpha $\left( \alpha \right)$ hydrogens. This positive inductive effect is not seen in aldehydes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




