
A ray of light suffers minimum deviation, while passing through a prism of refractive index $1.5$ and refracting angle ${{60}^{0}}$. Calculate the angle of deviation and angle of incidence.
Answer
591.6k+ views
- Hint: This problem can be solved by using the direct formula for the angle of minimum deviation in terms of the angle of refraction and the refractive index of the material of the prism. The angle of incidence can then be found out using the direct formula in terms of the angle of deviation and the refracting angle.
Formula used:
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$
$i=\dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us use the direct formula for the angle of minimum deviation while refraction through a prism in terms of the refracting angle and the refractive index of the material of the prism.
The angle of minimum deviation ${{\delta }_{m}}$, the refracting angle $A$ of the prism and the refractive index $n$ of the material of the prism, when a light ray suffers minimum deviation when passing through the prism is given by
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$ --(1)
When a light ray passes through a prism, the angle of incidence $i$, the angle of deviation $\delta $ and the refracting angle $A$ are related as
$i=\dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{{}}}}{2}$ --(2)
Now, let us analyze the question.
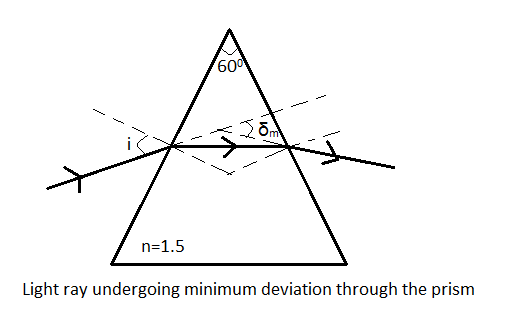
The refractive index of the material of the prism is $n=1.5$.
The refracting angle of the prism is $A={{60}^{0}}$.
Since, the ray suffers minimum deviation, let the angle of deviation be ${{\delta }_{m}}$.
Let the angle of incidence be $i$.
Using (1), we get
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$ --(3)
Putting the values of the variables in the above equation, we get
$1.5=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}}{2} \right)}=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( {{30}^{0}} \right)}=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\dfrac{1}{2}}$ $\left( \because \sin {{30}^{0}}=\dfrac{1}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 1.5\times \dfrac{1}{2}=0.75=\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.75 \right)=\dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{48.6}^{0}}=\dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$ $\left( \because {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.75 \right)\approx {{48.6}^{0}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{48.6}^{0}}\times 2={{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}$
$\Rightarrow {{97.2}^{0}}={{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\delta }_{m}}={{97.2}^{0}}-{{60}^{0}}={{37.2}^{0}}$ --(3)
Therefore, we have got the required angle of deviation.
Now, we will try to find the angle of incidence.
Using (2), we get
$i=\dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$ --(4)
Using (3) and putting the values of the variables in the above equation, we get
$i=\dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{37.2}^{0}}}{2}=\dfrac{{{97.2}^{0}}}{2}={{48.6}^{0}}$
Therefore, we have got the required angle of incidence.
Note: Students must note that in use of formula (1), the refractive index of the medium should be replaced by the relative refractive index of the material of the prism to the refractive index of the medium if the prism is kept in some other medium with a refractive index different to that of air (which has a refractive index of 1). Here we assume that the prism has been kept in air and so we can directly use the refractive index of the material of the prism, that is, glass.
Formula used:
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$
$i=\dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us use the direct formula for the angle of minimum deviation while refraction through a prism in terms of the refracting angle and the refractive index of the material of the prism.
The angle of minimum deviation ${{\delta }_{m}}$, the refracting angle $A$ of the prism and the refractive index $n$ of the material of the prism, when a light ray suffers minimum deviation when passing through the prism is given by
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$ --(1)
When a light ray passes through a prism, the angle of incidence $i$, the angle of deviation $\delta $ and the refracting angle $A$ are related as
$i=\dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{{}}}}{2}$ --(2)
Now, let us analyze the question.

The refractive index of the material of the prism is $n=1.5$.
The refracting angle of the prism is $A={{60}^{0}}$.
Since, the ray suffers minimum deviation, let the angle of deviation be ${{\delta }_{m}}$.
Let the angle of incidence be $i$.
Using (1), we get
$n=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)}$ --(3)
Putting the values of the variables in the above equation, we get
$1.5=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}}{2} \right)}=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\sin \left( {{30}^{0}} \right)}=\dfrac{\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)}{\dfrac{1}{2}}$ $\left( \because \sin {{30}^{0}}=\dfrac{1}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 1.5\times \dfrac{1}{2}=0.75=\sin \left( \dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.75 \right)=\dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{48.6}^{0}}=\dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$ $\left( \because {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.75 \right)\approx {{48.6}^{0}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{48.6}^{0}}\times 2={{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}$
$\Rightarrow {{97.2}^{0}}={{60}^{0}}+{{\delta }_{m}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\delta }_{m}}={{97.2}^{0}}-{{60}^{0}}={{37.2}^{0}}$ --(3)
Therefore, we have got the required angle of deviation.
Now, we will try to find the angle of incidence.
Using (2), we get
$i=\dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2}$ --(4)
Using (3) and putting the values of the variables in the above equation, we get
$i=\dfrac{{{60}^{0}}+{{37.2}^{0}}}{2}=\dfrac{{{97.2}^{0}}}{2}={{48.6}^{0}}$
Therefore, we have got the required angle of incidence.
Note: Students must note that in use of formula (1), the refractive index of the medium should be replaced by the relative refractive index of the material of the prism to the refractive index of the medium if the prism is kept in some other medium with a refractive index different to that of air (which has a refractive index of 1). Here we assume that the prism has been kept in air and so we can directly use the refractive index of the material of the prism, that is, glass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




