
A point object is placed at a point Q in a glass slab as shown in the figure. The distance of the object as measured by an observer at P will be (μ = 1.5).
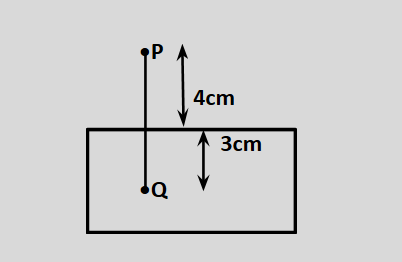
A. \[7{\text{ }}cm\]
B. \[6{\text{ }}cm\]
C. \[5{\text{ }}cm\]
D. \[7.5{\text{ }}cm\]

Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: To calculate the distance measured by the object measured by an observer from point P we will use the formula: \[{\text{refractive index(}}\mu {\text{) = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Real depth}}\left( H \right)}}{{{\text{Apparent depth}}\left( h \right)}}\]. Where Real depth is the distance object from the surface of a material medium while apparent depth is the distance of image formed due to refraction from the surface of the material medium.
Complete step by step answer:
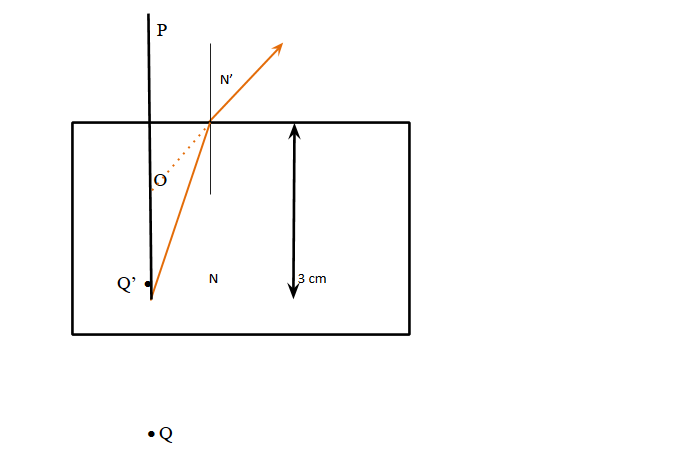
To find the required distance of the point P we have to draw a schematic diagram
which shows the image of point P formed by the refraction of light phenomenon.
The image of object Q is formed at Q’ by the phenomenon of refraction. So, from the diagram we can have the real depth is OQ and apparent depth is OQ’.
Now for calculating the apparent depth we use the formula :
\[{\text{refractive index(}}\mu {\text{) = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Real depth}}\left( H \right)}}{{{\text{Apparent depth}}\left( h \right)}}\]
We have given that:-
Real depth (OQ) = 3 cm and refractive index(μ) = 1.5
Now substituting the given value in the above expression. we get:
\[
{\text{1}}{\text{.5 = }}\dfrac{{3{\text{ cm}}}}{{{\text{Apparent depth}}\left( {{\text{OQ'}}} \right)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Apparent depth}}\left( {{\text{OQ'}}} \right){\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{3 cm}}}}{{{\text{1}}{\text{.5}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Apparent depth}}\left( {{\text{OQ'}}} \right){\text{ = 2 cm}} \\
\]
The image of point Q is formed at Q’. So, the observer at point P will see the apparent image at Q’.
Therefore, the required distance from point P is PQ’= PO + OQ’.
Hence, Option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: The formula used for solving this question came from one of the great applications of Snell’s law of refraction for the case of water and air media systems. It is one of the special cases of refraction when an object is placed in a material medium and the observer sees its image from the air medium. So for solving every system of a pair of media the same formula will not be valid. To tackle such kinds of conceptual questions one should have to derive the various formula for refraction phenomenon and also care about the condition for deriving them like:- the angle of incidence and the refraction is very small such that:- \[\tan \theta \approx \theta ,\sin \theta \approx \theta {\text{ and cos}}\theta \approx {\text{1 for very small }}\theta .\]

Complete step by step answer:
To find the required distance of the point P we have to draw a schematic diagram
which shows the image of point P formed by the refraction of light phenomenon.
The image of object Q is formed at Q’ by the phenomenon of refraction. So, from the diagram we can have the real depth is OQ and apparent depth is OQ’.
Now for calculating the apparent depth we use the formula :
\[{\text{refractive index(}}\mu {\text{) = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Real depth}}\left( H \right)}}{{{\text{Apparent depth}}\left( h \right)}}\]
We have given that:-
Real depth (OQ) = 3 cm and refractive index(μ) = 1.5
Now substituting the given value in the above expression. we get:
\[
{\text{1}}{\text{.5 = }}\dfrac{{3{\text{ cm}}}}{{{\text{Apparent depth}}\left( {{\text{OQ'}}} \right)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Apparent depth}}\left( {{\text{OQ'}}} \right){\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{3 cm}}}}{{{\text{1}}{\text{.5}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Apparent depth}}\left( {{\text{OQ'}}} \right){\text{ = 2 cm}} \\
\]
The image of point Q is formed at Q’. So, the observer at point P will see the apparent image at Q’.
Therefore, the required distance from point P is PQ’= PO + OQ’.
Hence, Option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: The formula used for solving this question came from one of the great applications of Snell’s law of refraction for the case of water and air media systems. It is one of the special cases of refraction when an object is placed in a material medium and the observer sees its image from the air medium. So for solving every system of a pair of media the same formula will not be valid. To tackle such kinds of conceptual questions one should have to derive the various formula for refraction phenomenon and also care about the condition for deriving them like:- the angle of incidence and the refraction is very small such that:- \[\tan \theta \approx \theta ,\sin \theta \approx \theta {\text{ and cos}}\theta \approx {\text{1 for very small }}\theta .\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




