
A light ray travels from optically denser medium to optically rarer medium, if the angle of incidence and refraction at point of incidence are $\angle i$ and $\angle r$ respectively, then find the angle of deviation in terms of $\angle i$ and $\angle r$.
$\begin{align}
& A)\angle i+\angle r \\
& B)\dfrac{\angle i}{\angle r} \\
& C)\angle i-\angle r \\
& D)\angle r-\angle i \\
\end{align}$
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Alternate angles in geometry are always equal. Students need to consider the angle of incidence in this particular question for the case of alternate angles.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve the above question, it is much necessary to know some of the properties of light when it propagates across two media. Before that, let us learn about the different angles associated with a refracting surface.
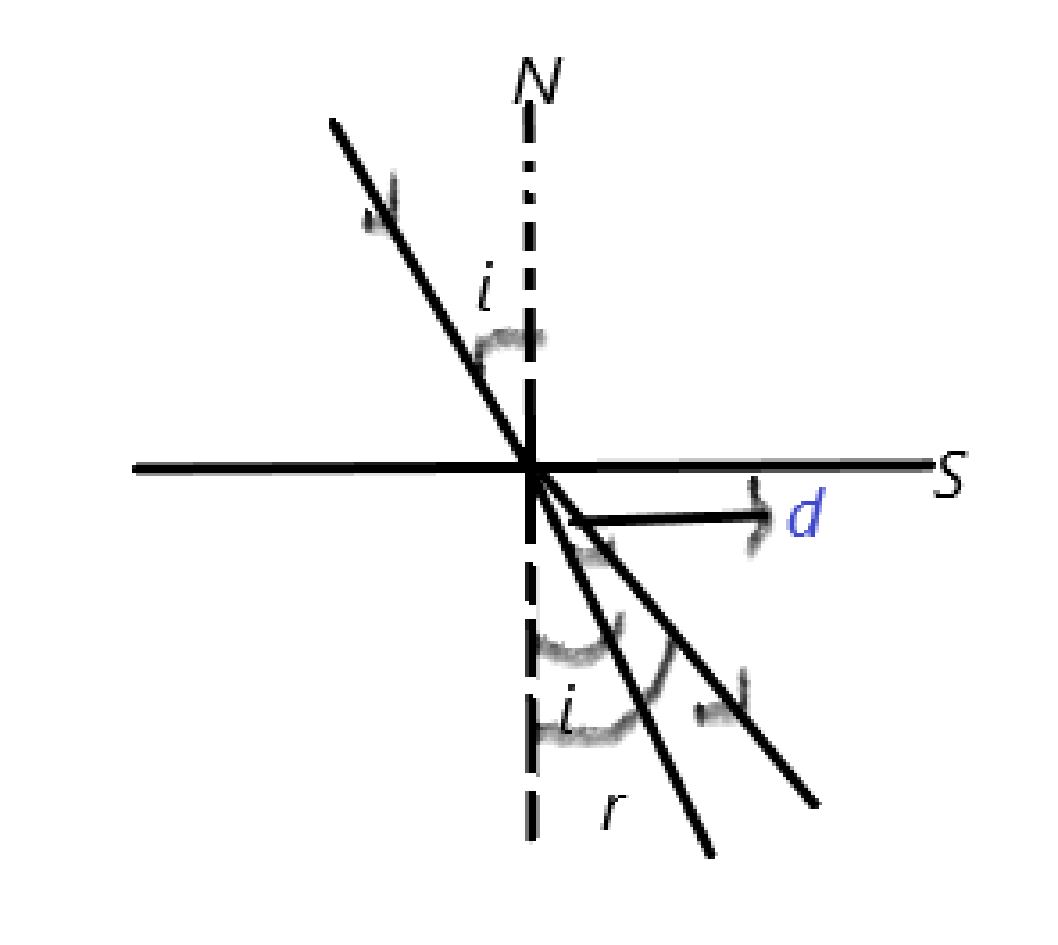
In the above picture, S represents the refracting surface, N is the normal drawn to the surface, i is the angle of incidence, r is the angle of refraction and d is the angle of deviation.
The angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the surface, the angle of refraction is the angle made by the refracted beam with the normal to the surface and the angle of deviation measures the extent to which the refracted beam moves towards or away from the normal to the surface.
Important - When light moves from denser medium to lighter medium, the refracted ray moves away from the normal, and when light moves from rarer to denser medium, the refracted ray moves towards the normal.
In the question we are given that light ray is moving from optically denser to rarer medium, so the refracted ray will move away from the normal to the surface.
From the above figure, we can come to the mathematical calculations as,
$\begin{align}
& r=d+i \\
& d=r-i \\
& \\
\end{align}$………(1)
Here we have used the idea that the alternate angles in a geometrical system are always equal.
From equation (1), we can conclude that if $\angle d$ is the angle of deviation, then it can be calculated as,
$\angle d=\angle r-\angle i$
Therefore from the above calculations, we can see that the answer is option- D $\angle r-\angle i$
Additional Information:
If we consider the case of a prism, the calculation of the angle of deviation will require a quantity known as the angle of the prism, denoted by A.
Note: The cases for reflection and refraction are different. In reflection, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, but in case of refractions, the angles are not equal and are related by the angle of deviation.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve the above question, it is much necessary to know some of the properties of light when it propagates across two media. Before that, let us learn about the different angles associated with a refracting surface.

In the above picture, S represents the refracting surface, N is the normal drawn to the surface, i is the angle of incidence, r is the angle of refraction and d is the angle of deviation.
The angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the surface, the angle of refraction is the angle made by the refracted beam with the normal to the surface and the angle of deviation measures the extent to which the refracted beam moves towards or away from the normal to the surface.
Important - When light moves from denser medium to lighter medium, the refracted ray moves away from the normal, and when light moves from rarer to denser medium, the refracted ray moves towards the normal.
In the question we are given that light ray is moving from optically denser to rarer medium, so the refracted ray will move away from the normal to the surface.
From the above figure, we can come to the mathematical calculations as,
$\begin{align}
& r=d+i \\
& d=r-i \\
& \\
\end{align}$………(1)
Here we have used the idea that the alternate angles in a geometrical system are always equal.
From equation (1), we can conclude that if $\angle d$ is the angle of deviation, then it can be calculated as,
$\angle d=\angle r-\angle i$
Therefore from the above calculations, we can see that the answer is option- D $\angle r-\angle i$
Additional Information:
If we consider the case of a prism, the calculation of the angle of deviation will require a quantity known as the angle of the prism, denoted by A.
Note: The cases for reflection and refraction are different. In reflection, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, but in case of refractions, the angles are not equal and are related by the angle of deviation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




