
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable load resistor R. Draw the plots of the terminal voltage V versus i) R and ii) the current i. It is found that when R = \[4\Omega \], the current is 1A when R is increased to 9$\Omega $, the current reduces to 0.5A. Find the values of the emf E and internal resistance r.
Answer
597.3k+ views
HINT- We have to apply basic formulae to calculate emf E and internal resistance r. formulae used in this question are as follows- V = E-ir and i = $\dfrac{E}{{R + r}}$, where V is the voltage, E is the emf, R is the load resistance and r is the internal resistance. Also using the above relation we can draw our required graphs.
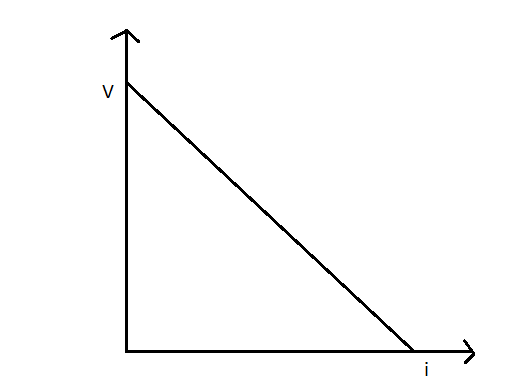
V vs i-
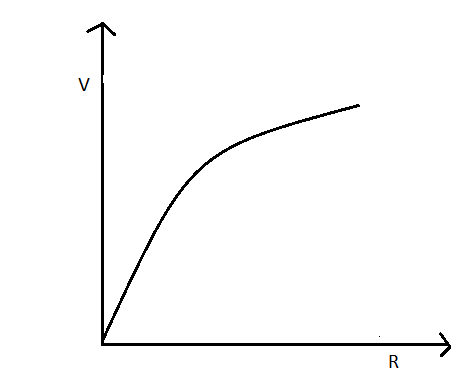
V vs R-
Now from the question, we have
Terminal voltage (V) = E – ir ………(1)
The current is given by i = $\dfrac{E}{{R + r}}$
Substituting value of i in equation (1), we get
Now, $V = E - \dfrac{{Er}}{{(R + r)}} = \dfrac{{ER}}{{R + r}} = \dfrac{E}{{(1 + \dfrac{r}{R})}}$……….(2)
According to equation (1) and (2), the graph V vs i and V vs R is shown in the following figure.
As, R=4$\Omega $ and i= 1A we have, $i = \dfrac{E}{{R + r}}$, so$1 = \dfrac{E}{{4 + r}}$ or $E = (4 + r)$…….(3)
When R=9$\Omega $ and i=0.5A we have, $i = \dfrac{E}{{9 + r}} or 2E = 9 + r$……..(4)
Equating (3) and (4), we have
2(4+r) = 9+r or r = 1$\Omega $
Thus, E = 4+r = 4+1 = 5V
Hence, we get emf E = 5V and internal resistance r = 1$\Omega $
NOTE- Basic definition of emf and internal resistance.
emf- it can be defined around a closed loop of conductor as the electromagnetic work that would be done on an electric charge if it travels once around the loop.
Internal resistance- internal resistance refers to the opposition to the flow of current offered by the cells and batteries themselves resulting in the generation of heat. Internal resistance is measured in ohms.
The emf of a cell is always greater than the potential difference across the cell.
V vs i-

V vs R-

Now from the question, we have
Terminal voltage (V) = E – ir ………(1)
The current is given by i = $\dfrac{E}{{R + r}}$
Substituting value of i in equation (1), we get
Now, $V = E - \dfrac{{Er}}{{(R + r)}} = \dfrac{{ER}}{{R + r}} = \dfrac{E}{{(1 + \dfrac{r}{R})}}$……….(2)
According to equation (1) and (2), the graph V vs i and V vs R is shown in the following figure.
As, R=4$\Omega $ and i= 1A we have, $i = \dfrac{E}{{R + r}}$, so$1 = \dfrac{E}{{4 + r}}$ or $E = (4 + r)$…….(3)
When R=9$\Omega $ and i=0.5A we have, $i = \dfrac{E}{{9 + r}} or 2E = 9 + r$……..(4)
Equating (3) and (4), we have
2(4+r) = 9+r or r = 1$\Omega $
Thus, E = 4+r = 4+1 = 5V
Hence, we get emf E = 5V and internal resistance r = 1$\Omega $
NOTE- Basic definition of emf and internal resistance.
emf- it can be defined around a closed loop of conductor as the electromagnetic work that would be done on an electric charge if it travels once around the loop.
Internal resistance- internal resistance refers to the opposition to the flow of current offered by the cells and batteries themselves resulting in the generation of heat. Internal resistance is measured in ohms.
The emf of a cell is always greater than the potential difference across the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




