
A Carnot engine absorbs an amount of $Q$ heat from a reservoir at an absolute temperature $T$ and rejects heat to a sink at a temperature of $\dfrac{T}{3}$ . The amount of heat rejected is
A) $\dfrac{Q}{4}$
B) $\dfrac{Q}{3}$
C) $\dfrac{Q}{2}$
D) $\dfrac{{2Q}}{3}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We should know that, a carnot engine is an thermodynamical system which takes some amount of heat from a fixed reservoir temperature and rejects the heat at sink at fixed temperature and beyween this it performs some mechanical work, using general relations of carnot engine, we will solve for rejected amunt of heat by the engine.
Complete answer:
We know that the efficiency of Carnot Heat Engine is given as: -
${\eta _{carnot}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$ … (1)
where
${T_2} = $Lower Absolute Temperature = Temperature of the Sink
and, ${T_1} = $Higher Absolute Temperature = Temperature of the Source
Also, the Efficiency of Carnot Engine in terms of work done can be given as: -
${\eta _{carnot}} = \dfrac{W}{{{Q_1}}} = \dfrac{{{Q_1} - {Q_2}}}{{{Q_1}}}$ … (2)
where
$W = $Work Done in the process
${Q_1} = $Heat taken up from the Source
${Q_2} = $Heat transferred to the Sink
The above-given problem can be illustrated by a diagram given as follows: -
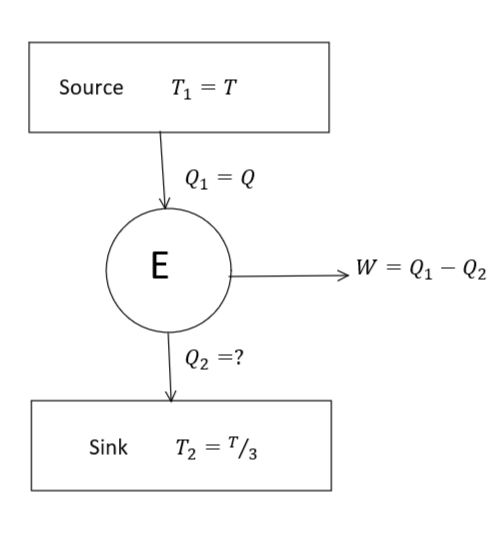
From eq. (1) and (2), we get
$\dfrac{{{Q_1} - {Q_2}}}{{{Q_1}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$
$1 - \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{{{Q_1}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$ … (3)
Substituting the given values in eq. (3), we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{Q}=\dfrac {T/3}{T}$
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = \dfrac{Q}{3}$
Thus, the amount of heat rejected is $\dfrac{Q}{3}$.
Hence, the correct option is (B) $\dfrac{Q}{3}$.
Note: Since this is a problem of multiple-choice question (numerical-based), it is essential that given conditions are analyzed carefully to give an accurate solution. While writing an answer to this kind of numerical problem, always keep in mind to use the mathematical proven relations to find the solution.
Complete answer:
We know that the efficiency of Carnot Heat Engine is given as: -
${\eta _{carnot}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$ … (1)
where
${T_2} = $Lower Absolute Temperature = Temperature of the Sink
and, ${T_1} = $Higher Absolute Temperature = Temperature of the Source
Also, the Efficiency of Carnot Engine in terms of work done can be given as: -
${\eta _{carnot}} = \dfrac{W}{{{Q_1}}} = \dfrac{{{Q_1} - {Q_2}}}{{{Q_1}}}$ … (2)
where
$W = $Work Done in the process
${Q_1} = $Heat taken up from the Source
${Q_2} = $Heat transferred to the Sink
The above-given problem can be illustrated by a diagram given as follows: -

From eq. (1) and (2), we get
$\dfrac{{{Q_1} - {Q_2}}}{{{Q_1}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$
$1 - \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{{{Q_1}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{T_2}}}{{{T_1}}}$ … (3)
Substituting the given values in eq. (3), we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{Q_2}}}{Q}=\dfrac {T/3}{T}$
$ \Rightarrow {Q_2} = \dfrac{Q}{3}$
Thus, the amount of heat rejected is $\dfrac{Q}{3}$.
Hence, the correct option is (B) $\dfrac{Q}{3}$.
Note: Since this is a problem of multiple-choice question (numerical-based), it is essential that given conditions are analyzed carefully to give an accurate solution. While writing an answer to this kind of numerical problem, always keep in mind to use the mathematical proven relations to find the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




