
A bar with a crack at its center buckles as a result of temperature rise of \[32{\text{ }}^\circ {\text{C}}\]. If the fixed distance \[{L_0}\] is \[3.77{\text{ m}}\] and the coefficient of linear expansion of the bar is \[25 \times {10^{ - 6}}^\circ {{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}\], then the rise \[x\] of the center is-
A) \[5.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{m}}\]
B) \[6.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{m}}\]
C) \[7.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{m}}\]
D) \[8.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{m}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of the linear expansion will be used. The ratio of increment of length to the original length with the rise of \[1\] degree in temperature is called coefficient of linear expansion.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that the linear expansion is that phenomenon in which the object expands due to certain reasons only in one direction. The ratio of increment of length to the original length with the rise of \[1\] degree in temperature is called coefficient of linear expansion. According to the question the diagram should look like this-
Here after the buckling phenomenon occurs the condition looks like the following,
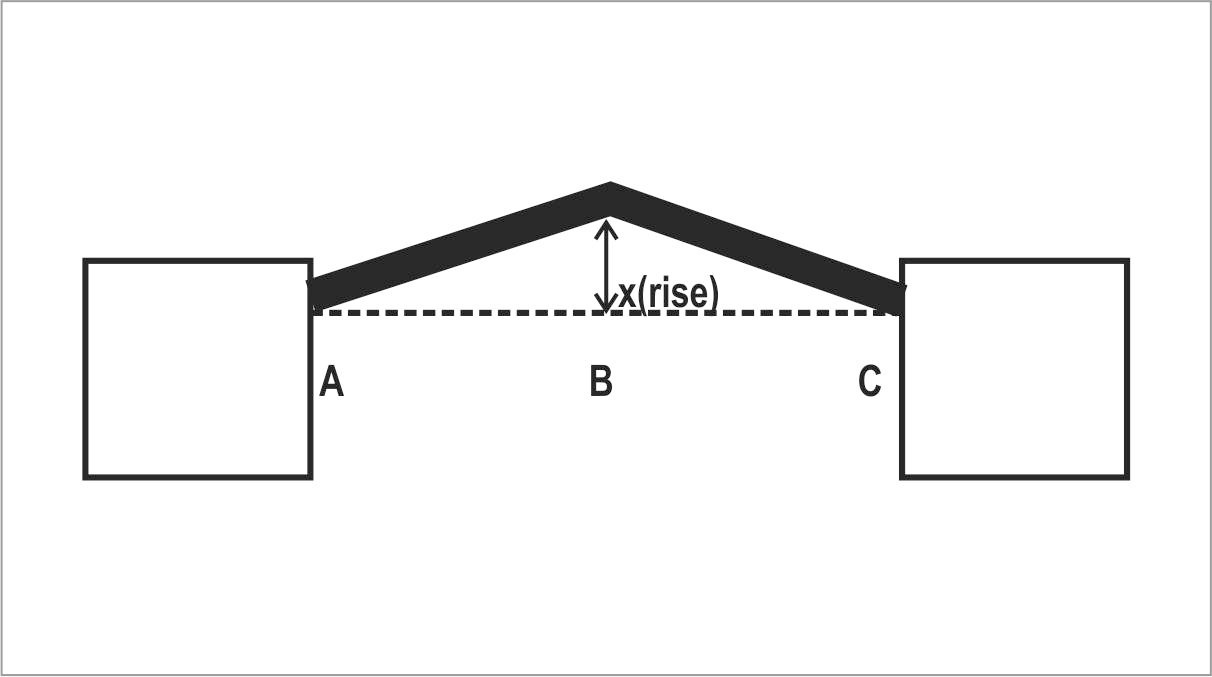
From the above diagram it is clear that as buckling was even as the end supports were considered fixed in nature hence,
\[BC = \dfrac{{{L_0}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow BC = \dfrac{{3.77}}{2} = 1.885{\text{m}}\]
Now, using formula \[\Delta I = \dfrac{{{L_0}}}{2}\alpha \Delta T\] we get
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta I = 1.885 \times 25 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 32\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta I = 1.508 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{m}}\]
Now, as we know that \[AB = \dfrac{{{L_0}}}{2} + \Delta I\]
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 1.885 + 1.508 \times {10^{ - 3}}\]
After simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 1.886508{\text{m}}\]
By using, Pythagoras’ theorem we get
\[{\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2} = B{C^2} + {x^2}\]
Now, we substitute the values in the above expression as,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {1.886508} \right)^2} = {\left( {1.885} \right)^2} + {x^2}\]
Simplifying the above expression and obtain,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} = {\left( {1.886508} \right)^2} - {\left( {1.885} \right)^2} = 0.00568743406\]
After simplification we get,
\[\therefore x = 0.07541 \approx 7.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}\;{\text{m}}\]
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: Buckling is a phenomenon which occurs when there is a sudden change in the shape, or we can say there is deformation of a body under load. Buckling can occur in elongated bodies such as columns as well as on 2D structures such as on plates. These linear expansions are not really visible to the naked eye during the process. Hence these standard mathematical formulae can be applied. Here we have also considered that the side walls are static, and no expansion has taken place through them. We should also remember that there is a difference between bending and buckling.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that the linear expansion is that phenomenon in which the object expands due to certain reasons only in one direction. The ratio of increment of length to the original length with the rise of \[1\] degree in temperature is called coefficient of linear expansion. According to the question the diagram should look like this-

Here after the buckling phenomenon occurs the condition looks like the following,

From the above diagram it is clear that as buckling was even as the end supports were considered fixed in nature hence,
\[BC = \dfrac{{{L_0}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow BC = \dfrac{{3.77}}{2} = 1.885{\text{m}}\]
Now, using formula \[\Delta I = \dfrac{{{L_0}}}{2}\alpha \Delta T\] we get
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta I = 1.885 \times 25 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 32\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta I = 1.508 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{m}}\]
Now, as we know that \[AB = \dfrac{{{L_0}}}{2} + \Delta I\]
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 1.885 + 1.508 \times {10^{ - 3}}\]
After simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 1.886508{\text{m}}\]
By using, Pythagoras’ theorem we get
\[{\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2} = B{C^2} + {x^2}\]
Now, we substitute the values in the above expression as,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {1.886508} \right)^2} = {\left( {1.885} \right)^2} + {x^2}\]
Simplifying the above expression and obtain,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} = {\left( {1.886508} \right)^2} - {\left( {1.885} \right)^2} = 0.00568743406\]
After simplification we get,
\[\therefore x = 0.07541 \approx 7.5 \times {10^{ - 2}}\;{\text{m}}\]
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: Buckling is a phenomenon which occurs when there is a sudden change in the shape, or we can say there is deformation of a body under load. Buckling can occur in elongated bodies such as columns as well as on 2D structures such as on plates. These linear expansions are not really visible to the naked eye during the process. Hence these standard mathematical formulae can be applied. Here we have also considered that the side walls are static, and no expansion has taken place through them. We should also remember that there is a difference between bending and buckling.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




