
A 100 turns coil shown in figure carries a current of 2 amp in a magnetic field 0.2 Wb/m2. The torque acting on the coil is
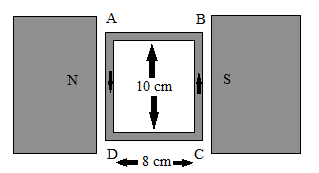
A. 0.32 Nm tending to rate the side AD out of the page
B. 0.32 Nm tending to rate the side AD into the page
C. 0.0032 Nm tending to rate the side AD out of the page
D. 0.0032 Nm tending to rate the side AD into the page
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, we are going to use the mentioned concept. The magnetic moment in a loop can be defined as the product of the current flowing and the area of the rectangular loop. Coil carrying current, number of turns is given and current is given, measure the magnetic moment. The magnetic moment is a vector quantity.
Formula Used:
$\tau = NIAB$
Complete answer:
We have been provided in the question that,
A 100 turns coil shown in figure carries a current of 2 amp in a magnetic field 0.2 Wb/m2.
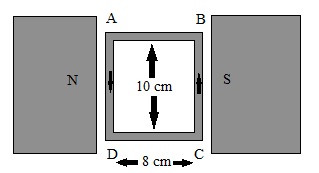
Magnetic moment determined mathematically,
$\mu = IA$
Here, A is the rectangular loop's area, and I is the current flowing through the loop.
As a result, the cross product of the magnetic moment and the magnetic field determines the torque applied to a current-carrying coil when it is put in a magnetic field.
$\tau = \mu \times B$
Magnitude of the torque is given by
$\tau = NIAB$
Where N is the number of turns, I is the current, A is the area of the loop, B is the uniform magnetic field.
Substituting the value, we get
$\tau = 100 \times 0.2 \times 2 \times (0.08 \times 0.1)$
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.32Nm$
Direction can be found using Fleming’s left-hand rule, according to this, the thumb gives the direction of the conductor's motion, the index finger gives the direction of the magnetic field, and the direction of the induced current is indicated by the middle finger. Fleming's left-hand rule, which states that if we stretch the thumb, forefinger, or the index finger and the middle finger so that they are mutually perpendicular to each other.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: The force that can cause something to revolve around an axis is measured in torque. Torque accelerates an object in an angular direction, much like force does in linear kinematics. A vector quantity that can be static or dynamic is torque.
Formula Used:
$\tau = NIAB$
Complete answer:
We have been provided in the question that,
A 100 turns coil shown in figure carries a current of 2 amp in a magnetic field 0.2 Wb/m2.

Magnetic moment determined mathematically,
$\mu = IA$
Here, A is the rectangular loop's area, and I is the current flowing through the loop.
As a result, the cross product of the magnetic moment and the magnetic field determines the torque applied to a current-carrying coil when it is put in a magnetic field.
$\tau = \mu \times B$
Magnitude of the torque is given by
$\tau = NIAB$
Where N is the number of turns, I is the current, A is the area of the loop, B is the uniform magnetic field.
Substituting the value, we get
$\tau = 100 \times 0.2 \times 2 \times (0.08 \times 0.1)$
$ \Rightarrow \tau = 0.32Nm$
Direction can be found using Fleming’s left-hand rule, according to this, the thumb gives the direction of the conductor's motion, the index finger gives the direction of the magnetic field, and the direction of the induced current is indicated by the middle finger. Fleming's left-hand rule, which states that if we stretch the thumb, forefinger, or the index finger and the middle finger so that they are mutually perpendicular to each other.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: The force that can cause something to revolve around an axis is measured in torque. Torque accelerates an object in an angular direction, much like force does in linear kinematics. A vector quantity that can be static or dynamic is torque.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




