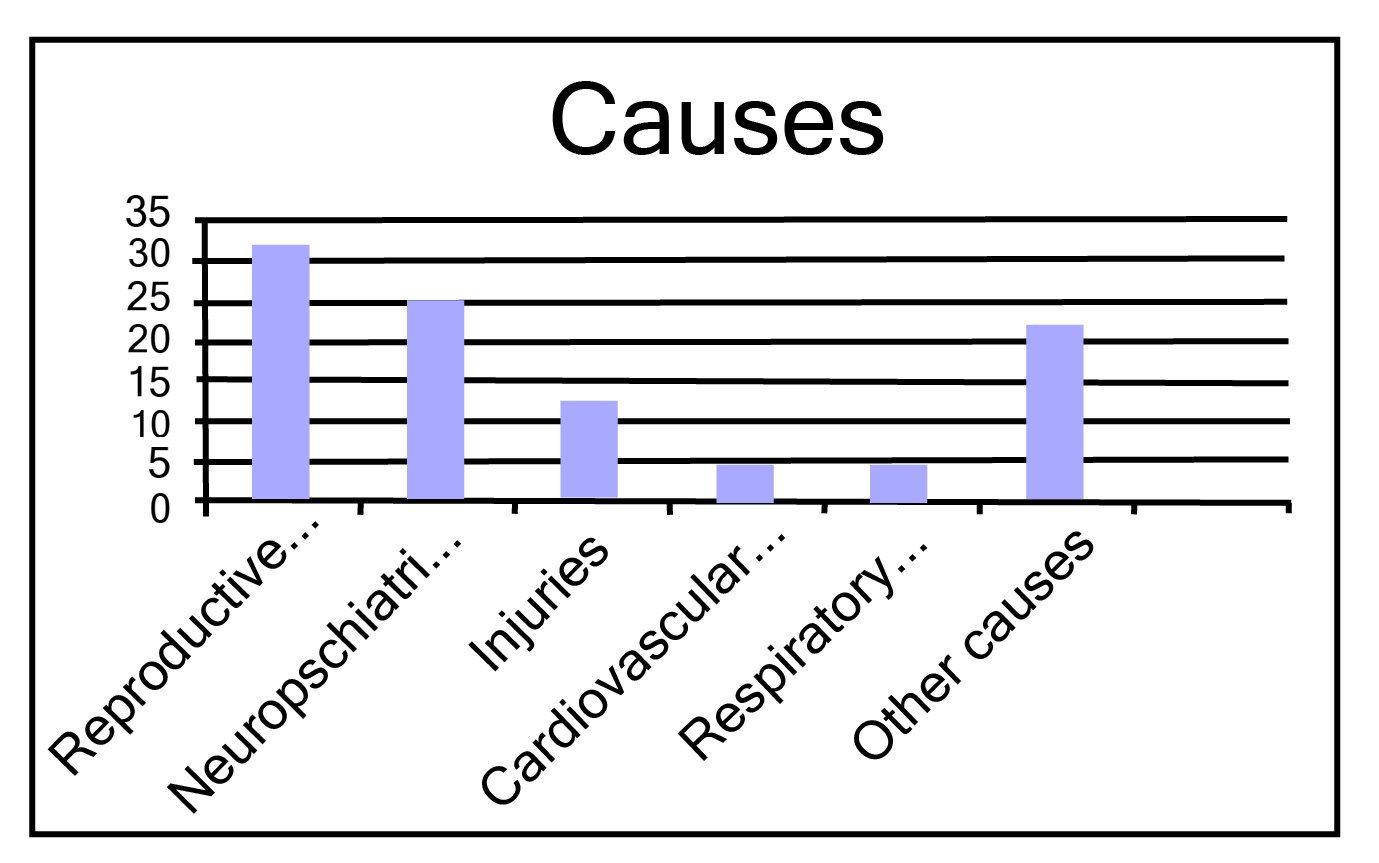
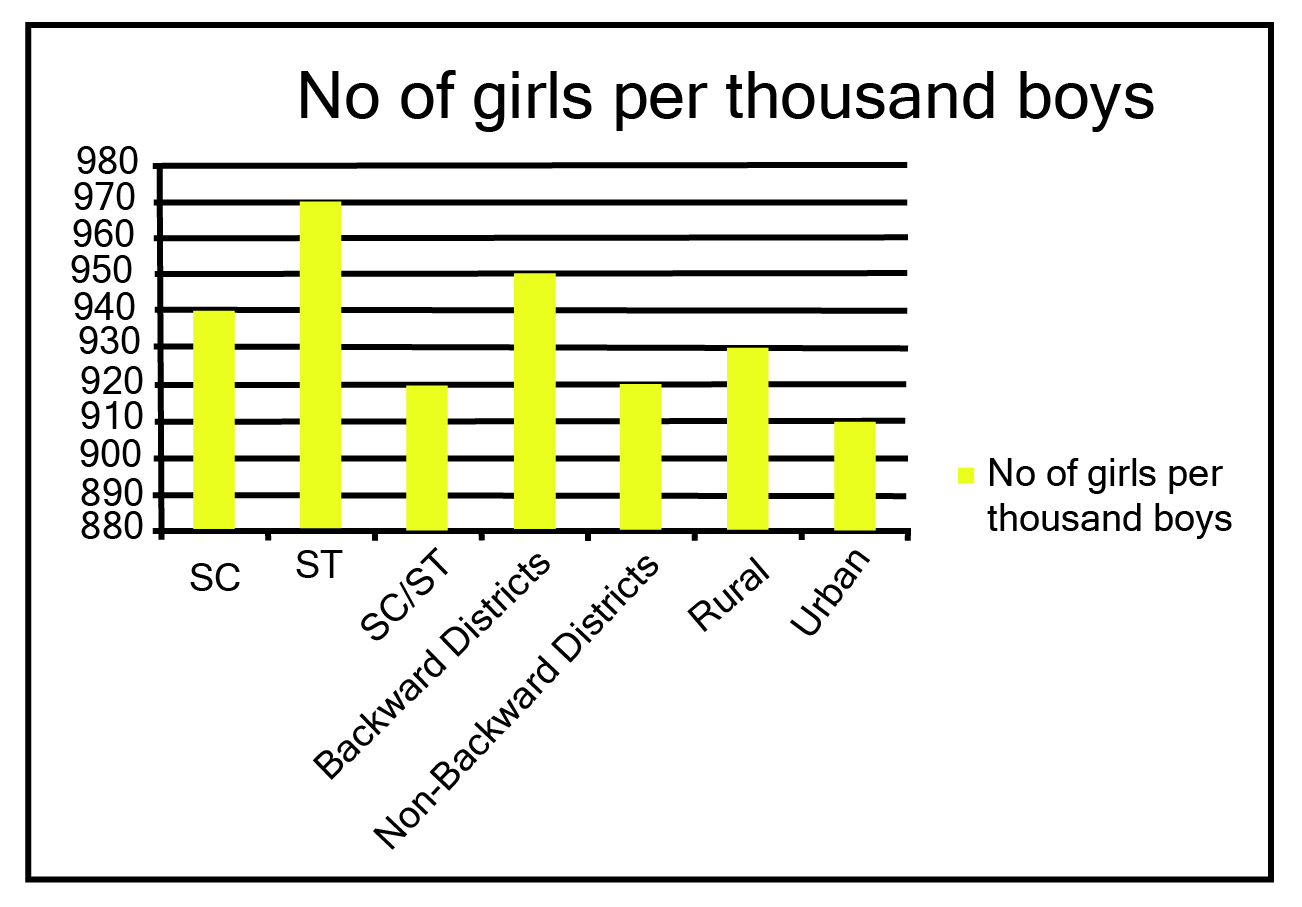
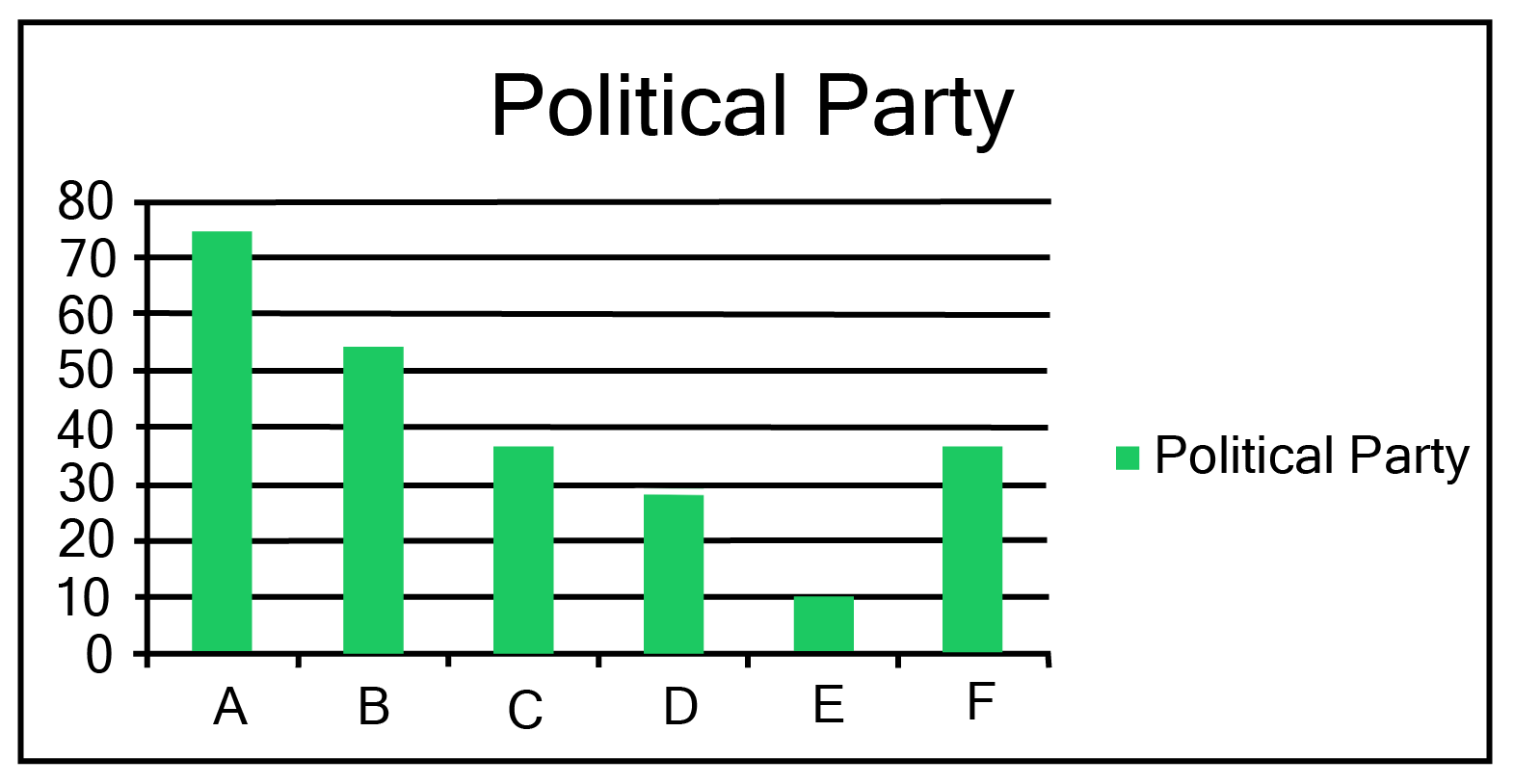
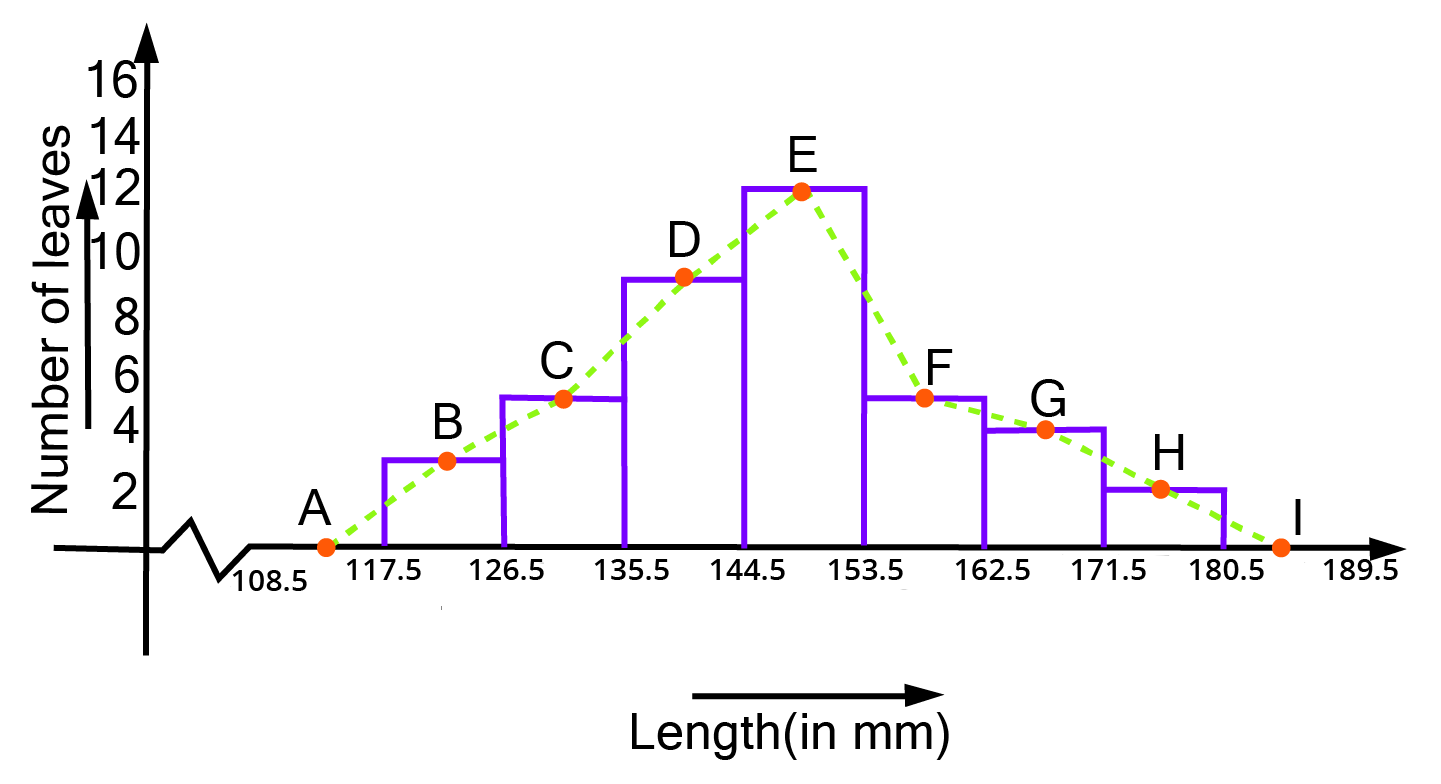
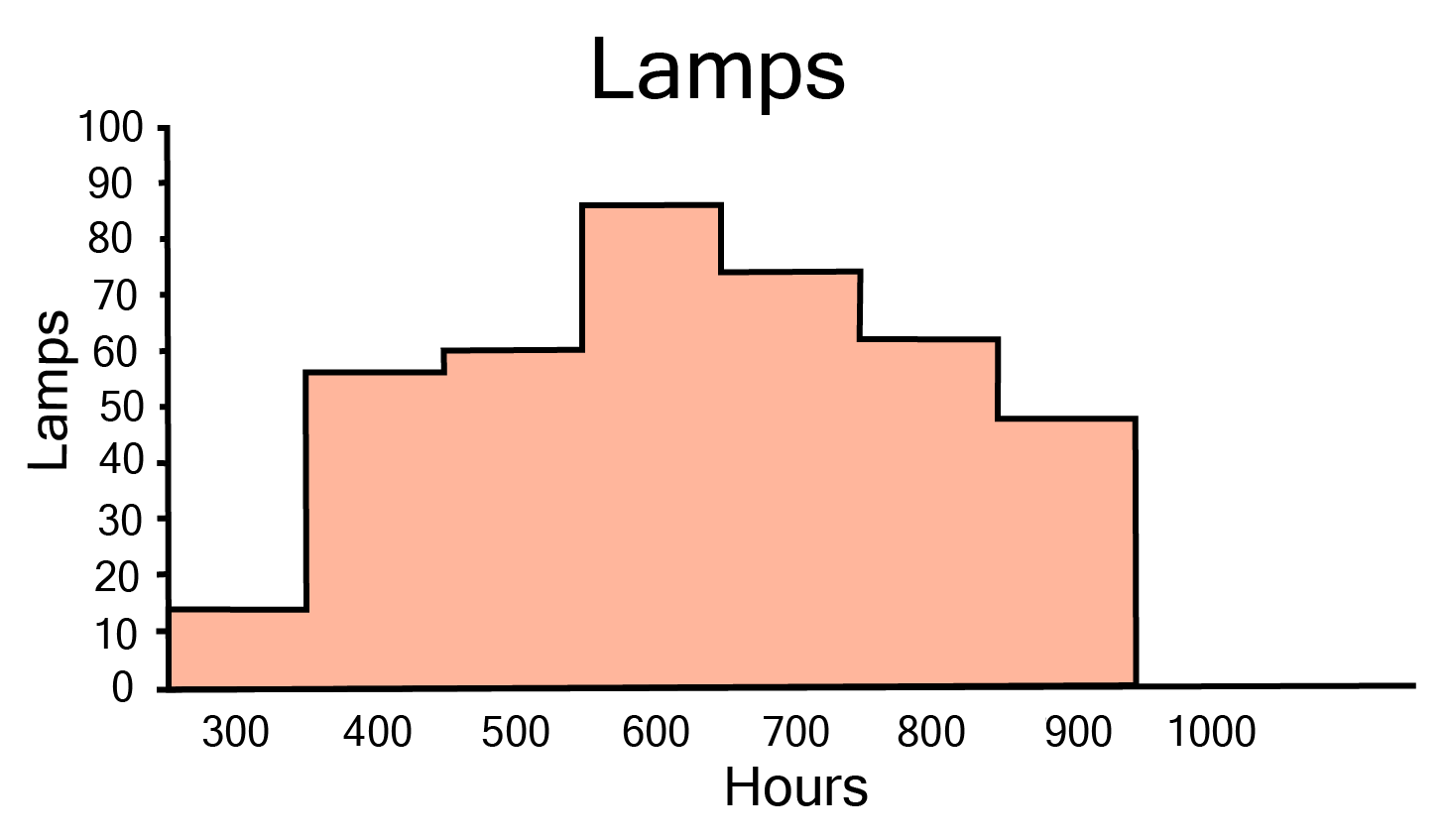
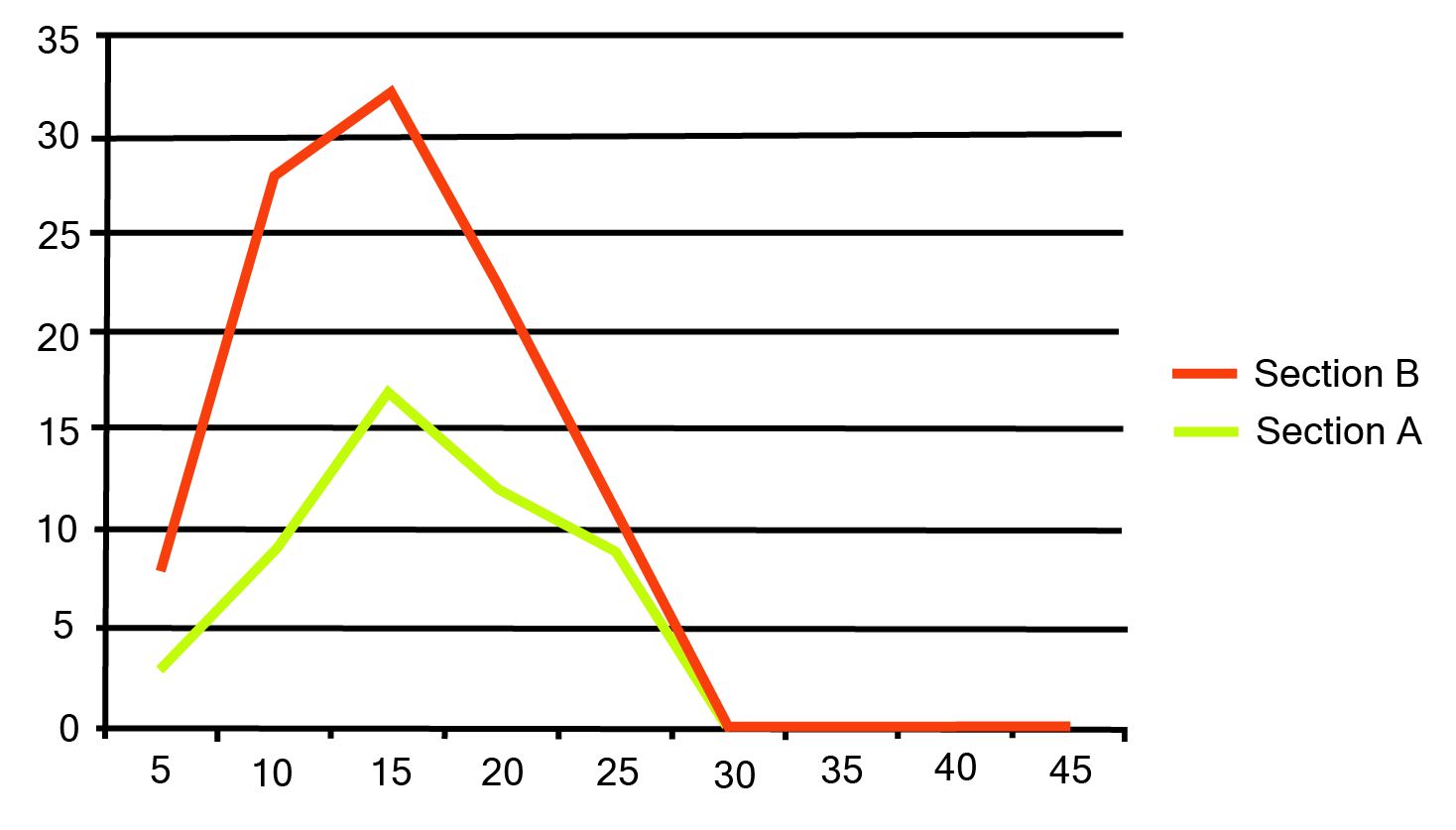
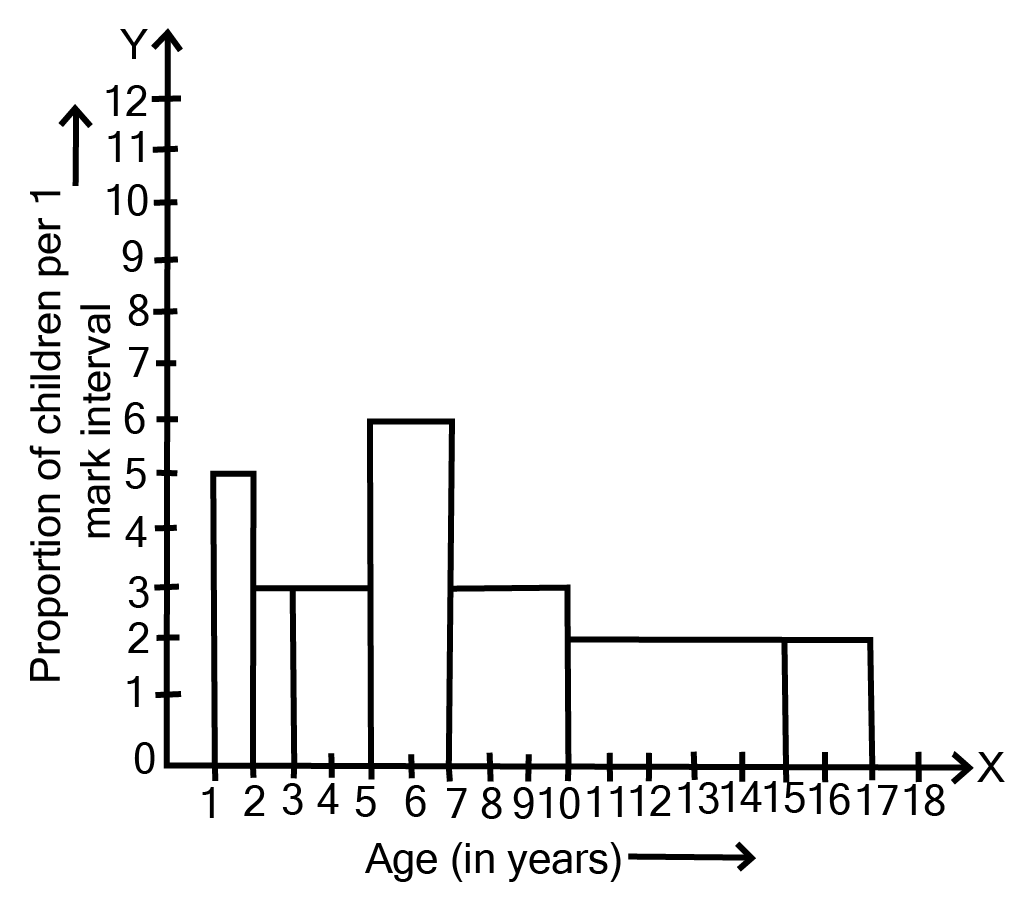
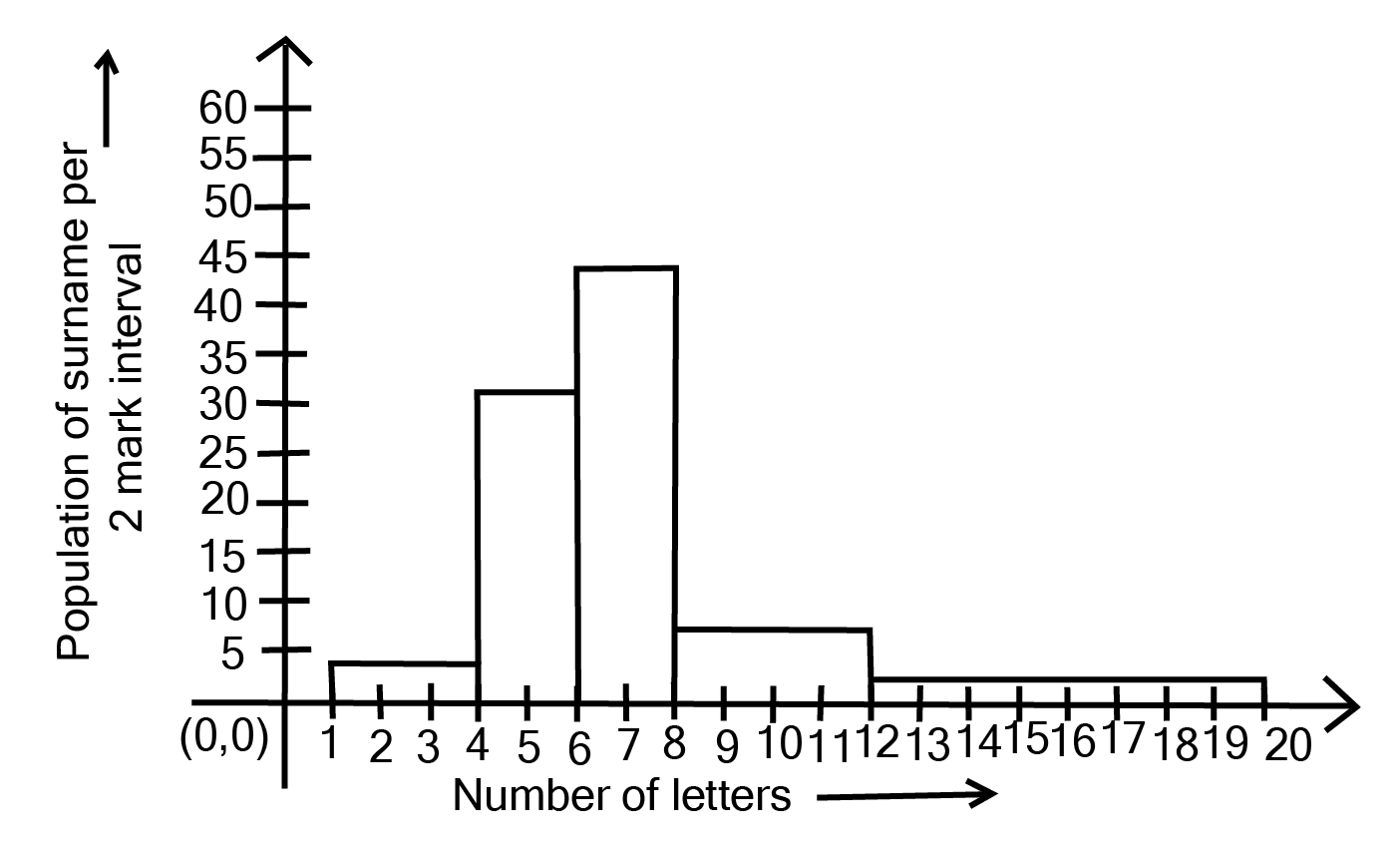
Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 NCERT Solutions 2025-26: FREE PDF Download
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 - 2025-26
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 - 2025-26
1. Where can I find Exercise 12.1 Class 9 Maths Statistics solutions?
Exercise 12.1 Class 9 Maths Statistics solutions are available on Vedantu, where all NCERT questions are solved in a clear and structured format.
2. Are the Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions based on NCERT?
Yes, the Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions on Vedantu are prepared strictly according to the NCERT textbook.
3. Can I download Exercise 12.1 Class 9 Statistics PDF?
Yes, Exercise 12.1 Class 9 Statistics PDF can be accessed through the NCERT Solutions page on Vedantu for easy reference.
4. Do the Class 9 Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions include all textbook questions?
Yes, the Class 9 Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions on Vedantu include answers to all questions given in the NCERT exercise.
5. Are Ex 12.1 Class 9 Maths Statistics solutions useful for homework?
Yes, Ex 12.1 Class 9 Maths Statistics solutions on Vedantu are suitable for homework as they follow NCERT answer format.
6. Do the Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 answers show steps clearly?
Yes, the Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 answers on Vedantu show step-by-step working as expected in school exams.
7. Are the 12.1 Class 9 Statistics solutions aligned with the latest syllabus?
Yes, the 12.1 Class 9 Statistics solutions on Vedantu are aligned with the latest NCERT and CBSE syllabus.
8. Can private candidates use Class 9 Maths Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions?
Yes, private candidates following the NCERT curriculum can use Class 9 Maths Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions available on Vedantu.
9. Are Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions suitable for school tests?
Yes, the Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1 solutions on Vedantu are written in an exam-appropriate format suitable for school tests.
10. Which website provides clear NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Statistics Exercise 12.1?
Vedantu provides clear and well-structured NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics Exercise 12.1.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video