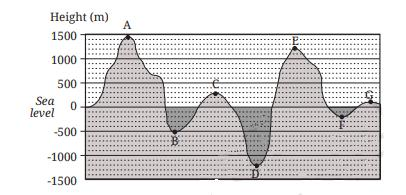
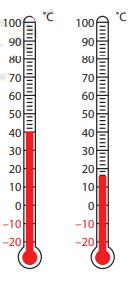
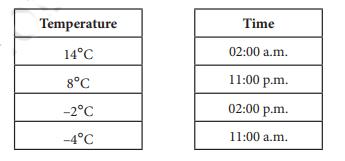
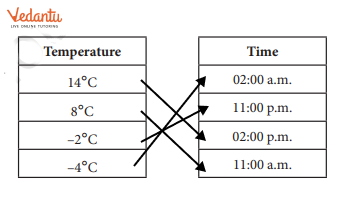
Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 The Other Side Of Zero Exercise 10.3 - 2025-26
1. What does NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 cover?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 explains how integers are used in real-life situations like temperatures, bank balances, and elevations with clear step-by-step solutions.
2. How can Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 help with exams?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 provides detailed explanations of integer concepts, helping students practise and prepare effectively for their Maths exams.
3. Are Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 aligned with the CBSE syllabus?
Yes, Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 are fully aligned with the CBSE syllabus, ensuring students cover all key topics in their curriculum.
4. What type of problems are solved in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 Solve problems related to the practical use of integers, such as understanding negative and positive numbers in real-life contexts like temperatures and heights.
5. How can NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 improve understanding of integers?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 provide clear, detailed steps that help students understand the rules of working with integers in various situations, improving their overall Maths skills.
6. What are integers in Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3?
In NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3, integers refer to whole numbers, both positive and negative, which are used in various real-world contexts like temperatures and elevations.
7. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 explain negative integers?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 explain negative integers with real-life examples such as temperatures below zero and depths below sea level, helping students understand their practical usage.
8. Can NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 help in real-life situations?
Yes, the solutions help students apply integer concepts to real-life situations like financial balances and changes in altitude, improving their problem-solving skills beyond the classroom.
9. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 help in understanding positive and negative numbers?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 clearly differentiate between positive and negative numbers, helping students easily identify and work with them in real-world contexts.
10. Are step-by-step solutions provided in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3?
Yes, NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 provide detailed, step-by-step solutions for each problem, allowing students to follow the methods and understand the logic behind each answer.
11. How does Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 help with practice?
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 offer practice problems that reinforce students’ understanding of integers, enabling them to apply these concepts effectively in exams.
12. Why are integers important in NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3?
Integers are essential in NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3 as they form the basis of many real-world scenarios, such as calculating losses, gains, and understanding heights and depths. The solutions make these concepts clear and understandable.