
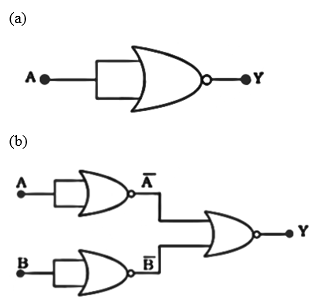
Write the truth table for the circuits given in figure. Considering of NOR gate only. Identify the logic operations (OR, AND, NOT) performed by the two circuits.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In the above solved question, we have used Boolean operations for some basic logic gates such as OR, AND, NOT gates. We drew truth tables for the combinations of basic logic gates, which represents their functions for all combinations of input signals.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Logic gates are important digital devices that are mainly based on the Boolean functions. Logic gates take one or more binary (0 or 1) input signal, and carry out logical operations on them and give one binary (0 or 1) output.
Boolean operations for several basic gates-
1. For OR gate: $Y = X + Y$
2. For AND gate: $Y = X·Y$.
3. For NOT gate: $Y=\overline{X}$
Now using the above described Boolean functions, we can make truth tables for the figures mentioned in the question.
1. Truth table for diagram (a)-
It is a NOR gate, which has both input A and output Y.
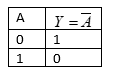
So, the operation will be $Y=\overline{A}$.
As, $Y=\overline{X+Y}=\overline{A+A}=\overline{A}$
2. Truth table for diagram (b)-
It is a three NOR gates circuit, it’s output will be $Y=\overline{\overline{A}+\overline{B}}$
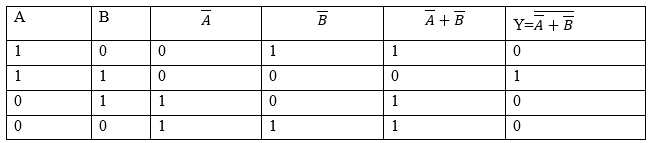
If you observe carefully, this gate essentially is an AND gate.
Note: According to their mode of operations, logic gates have a lot of applications.
Logic gates are usually found in circuits such as safety thermostat, push-button lock, automatic watering system, light activated burglar alarm system.
Logic gates can be found in IC circuits.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Logic gates are important digital devices that are mainly based on the Boolean functions. Logic gates take one or more binary (0 or 1) input signal, and carry out logical operations on them and give one binary (0 or 1) output.
Boolean operations for several basic gates-
1. For OR gate: $Y = X + Y$
2. For AND gate: $Y = X·Y$.
3. For NOT gate: $Y=\overline{X}$
Now using the above described Boolean functions, we can make truth tables for the figures mentioned in the question.
1. Truth table for diagram (a)-
It is a NOR gate, which has both input A and output Y.
So, the operation will be $Y=\overline{A}$.
As, $Y=\overline{X+Y}=\overline{A+A}=\overline{A}$

2. Truth table for diagram (b)-
It is a three NOR gates circuit, it’s output will be $Y=\overline{\overline{A}+\overline{B}}$

If you observe carefully, this gate essentially is an AND gate.
Note: According to their mode of operations, logic gates have a lot of applications.
Logic gates are usually found in circuits such as safety thermostat, push-button lock, automatic watering system, light activated burglar alarm system.
Logic gates can be found in IC circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




