
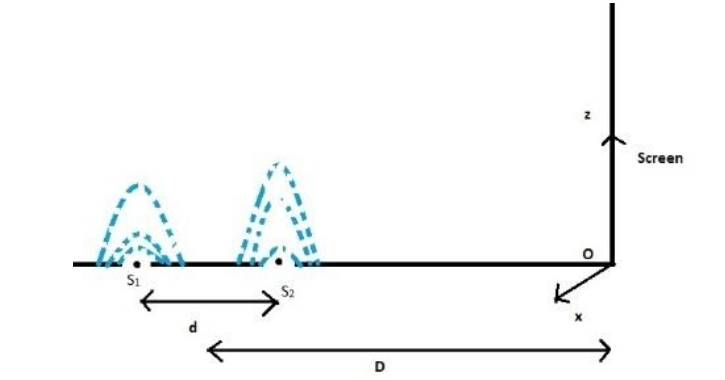
While conducting the Young's double slit experiment, a student replaced the two slits with a large opaque plate in the $x - y$ plane containing two small holes that act as two coherent point sources (${S_1},{S_2}$) emitting light of wavelength $600nm$. The student mistakenly placed the screen parallel to the $x - z$ plane (for $z > 0$) at a distance $D = 3m$, from the mid-point of ${S_1},{S_2}$, as shown schematically in the figure. The distance between the sources $d = 0.6003mm$. The origin O is at the intersection of the screen and the line joining ${S_1},{S_2}$. Which of the following is (are) true of the intensity pattern on the screen?
(A) Semi-circular bright and dark bands centred at point O
(B) The region very close to the point O will be dark
(C) Straight bright and dark bands parallel to the x-axis
(D) Hyperbolic bright and dark bands with foci symmetrically placed about O in the x-direction
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The angle at which the waves travel is small, thus path difference is equal to the distance between the two slits. The screen is perpendicular to the plane containing the slits as shown in the figure.
Formula Used: The formulae used in the solution are given here.
The path difference between two waves travelling at an angle $\theta $ is given by $\Delta x = d\cos \theta $ where $d$ is the distance between two slits.
For a small value of $\theta $, $\cos \theta = 1$, thus, $\Delta x = d$.
Complete Step by Step Solution: Young’s double-slit experiment uses two coherent sources of light placed at a small distance apart, usually, only a few orders of magnitude greater than the wavelength of light is used. Young’s double-slit experiment helped in understanding the wave theory of light. When light passes through narrow slits, it is diffracted into semi-circular waves.
As the screen is perpendicular to the plane containing the slits, therefore fringes obtained will be semi-circular.
The path difference between two waves travelling at an angle $\theta $ is given by $\Delta x = d\cos \theta $ where $d$ is the distance between two slits.
For a small value of $\theta $, $\cos \theta = 1$, thus, $\Delta x = d$.
When the two waves are in phase, i.e. the path difference is equal to an integral number of wavelengths, the summed amplitude, and therefore the summed intensity is maximum.
Given that, two coherent point sources (${S_1},{S_2}$) emitting light of wavelength $600nm$ are placed perpendicular to the screen in the $x - z$ plane. The screen is parallel to the $x - z$ plane (for $z > 0$) at a distance $D = 3m$, from the mid-point of ${S_1},{S_2}$. The distance between the sources $d = 0.6003mm$. The origin O is at the intersection of the screen and the line joining ${S_1},{S_2}$.
$\dfrac{d}{\lambda } = \dfrac{{0.6003 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{600 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}} = \dfrac{{0.6003 \times {{10}^4}}}{6} = \dfrac{{6003}}{6} = 1000.5$
At O,
$\therefore $ Path difference $d = \left( {1000 + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\lambda $.
When they are in anti-phase, i.e. the path difference is equal to half a wavelength, one and a half wavelengths, etc., then the two waves cancel and the summed intensity is zero.
Hence, it is darker at O.
Hence, options A and B are the correct answers.
Note: The observation of interference effects definitively indicates the presence of overlapping waves. Thomas Young postulated that light is a wave and is subject to the superposition principle; his great experimental achievement was to demonstrate the constructive and destructive interference of light. In a modern version of Young’s experiment, differing in its essentials only in the source of light, a laser equally illuminates two parallel slits in an otherwise opaque surface. The light passing through the two slits is observed on a distant screen. When the widths of the slits are significantly greater than the wavelength of the light, the rules of geometrical optics hold—the light casts two shadows, and there are two illuminated regions on the screen. However, as the slits are narrowed in width, the light diffracts into the geometrical shadow, and the light waves overlap on the screen. Diffraction is itself caused by the wave nature of light, being another example of an interference effect.
Formula Used: The formulae used in the solution are given here.
The path difference between two waves travelling at an angle $\theta $ is given by $\Delta x = d\cos \theta $ where $d$ is the distance between two slits.
For a small value of $\theta $, $\cos \theta = 1$, thus, $\Delta x = d$.
Complete Step by Step Solution: Young’s double-slit experiment uses two coherent sources of light placed at a small distance apart, usually, only a few orders of magnitude greater than the wavelength of light is used. Young’s double-slit experiment helped in understanding the wave theory of light. When light passes through narrow slits, it is diffracted into semi-circular waves.
As the screen is perpendicular to the plane containing the slits, therefore fringes obtained will be semi-circular.
The path difference between two waves travelling at an angle $\theta $ is given by $\Delta x = d\cos \theta $ where $d$ is the distance between two slits.
For a small value of $\theta $, $\cos \theta = 1$, thus, $\Delta x = d$.
When the two waves are in phase, i.e. the path difference is equal to an integral number of wavelengths, the summed amplitude, and therefore the summed intensity is maximum.
Given that, two coherent point sources (${S_1},{S_2}$) emitting light of wavelength $600nm$ are placed perpendicular to the screen in the $x - z$ plane. The screen is parallel to the $x - z$ plane (for $z > 0$) at a distance $D = 3m$, from the mid-point of ${S_1},{S_2}$. The distance between the sources $d = 0.6003mm$. The origin O is at the intersection of the screen and the line joining ${S_1},{S_2}$.
$\dfrac{d}{\lambda } = \dfrac{{0.6003 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{600 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}}} = \dfrac{{0.6003 \times {{10}^4}}}{6} = \dfrac{{6003}}{6} = 1000.5$
At O,
$\therefore $ Path difference $d = \left( {1000 + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\lambda $.
When they are in anti-phase, i.e. the path difference is equal to half a wavelength, one and a half wavelengths, etc., then the two waves cancel and the summed intensity is zero.
Hence, it is darker at O.
Hence, options A and B are the correct answers.
Note: The observation of interference effects definitively indicates the presence of overlapping waves. Thomas Young postulated that light is a wave and is subject to the superposition principle; his great experimental achievement was to demonstrate the constructive and destructive interference of light. In a modern version of Young’s experiment, differing in its essentials only in the source of light, a laser equally illuminates two parallel slits in an otherwise opaque surface. The light passing through the two slits is observed on a distant screen. When the widths of the slits are significantly greater than the wavelength of the light, the rules of geometrical optics hold—the light casts two shadows, and there are two illuminated regions on the screen. However, as the slits are narrowed in width, the light diffracts into the geometrical shadow, and the light waves overlap on the screen. Diffraction is itself caused by the wave nature of light, being another example of an interference effect.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




