
Which ray/radiation can be detected by GM-counter?
A) Alpha
B) Beta
C) Gamma
D) All
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Keep in mind that the GM counter is the Geiger-Muller counter which consists of a metallic tube that is filled with gas and a high voltage range of $100V$ is applied to this gas. This leads to the ionization of the gas.
Complete step by step solution:
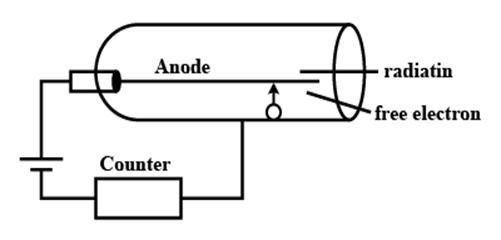
Let us first talk about the Geiger-Muller counter.
Geiger-Muller counter is a device used to detect various radiations and is also known as GM counter.
Geiger-Muller consists of a tube which is filled with gases like helium, neon, or argon at the lowest pressure.
In this process, a high voltage is applied to the tube and there will be the conduction of charge on the tube. Also, the gas in the tube will become conductive by the means of ionization when a particle or photon of incident radiation would ionize. It can be used to detect $\beta - rays$, and $\gamma - rays$. It cannot detect $\alpha - rays$, as $\alpha - rays$ cannot pass through an aluminium window.
Therefore, option (B) and (C) are the correct options.
Additional Information:
In the past, radioactive isotopes were used on humans in medical research work. For this, it became important to make sure that the amount of radioactive material used should be as little as possible. To achieve this, Geiger and Muller developed a ‘particle detector’ to measure ionizing radiation in 1928.
ADVANTAGES OF GM-COUNTER:
1) It can also detect cosmic rays.
2) It has high sensitivity.
3) As the pulse height is constant over a large range, so the power supply needs to be regulated.
4) As the output pulse is very high, therefore the amplification needed should be very subtle
DISADVANTAGES OF GM-COUNTER:
1) Due to a lack of differentiating abilities, energy cannot be measured by it.
2) It cannot detect uncharged particles.
3) It is less efficient as it has large paralysis time limits and large dead time.
4) Its lifetime is less as the quenching agent used in this counter often decomposes.
Note: Different particles will have different units, but the widely used unit is Counter per minute $(CPM)$. This unit is usually used for $\alpha $ particles and $\beta $ particles. The radiations are measured in $\mu Sv\,h{r^{ - 1}}$ which is microSieverts per hour and $mR\,h{r^{ - 1}}$ which is milli-Roentgens per hour.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first talk about the Geiger-Muller counter.
Geiger-Muller counter is a device used to detect various radiations and is also known as GM counter.
Geiger-Muller consists of a tube which is filled with gases like helium, neon, or argon at the lowest pressure.
In this process, a high voltage is applied to the tube and there will be the conduction of charge on the tube. Also, the gas in the tube will become conductive by the means of ionization when a particle or photon of incident radiation would ionize. It can be used to detect $\beta - rays$, and $\gamma - rays$. It cannot detect $\alpha - rays$, as $\alpha - rays$ cannot pass through an aluminium window.
Therefore, option (B) and (C) are the correct options.
Additional Information:
In the past, radioactive isotopes were used on humans in medical research work. For this, it became important to make sure that the amount of radioactive material used should be as little as possible. To achieve this, Geiger and Muller developed a ‘particle detector’ to measure ionizing radiation in 1928.
ADVANTAGES OF GM-COUNTER:
1) It can also detect cosmic rays.
2) It has high sensitivity.
3) As the pulse height is constant over a large range, so the power supply needs to be regulated.
4) As the output pulse is very high, therefore the amplification needed should be very subtle
DISADVANTAGES OF GM-COUNTER:
1) Due to a lack of differentiating abilities, energy cannot be measured by it.
2) It cannot detect uncharged particles.
3) It is less efficient as it has large paralysis time limits and large dead time.
4) Its lifetime is less as the quenching agent used in this counter often decomposes.
Note: Different particles will have different units, but the widely used unit is Counter per minute $(CPM)$. This unit is usually used for $\alpha $ particles and $\beta $ particles. The radiations are measured in $\mu Sv\,h{r^{ - 1}}$ which is microSieverts per hour and $mR\,h{r^{ - 1}}$ which is milli-Roentgens per hour.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




