
Which one is false in the following statements
A. Each carbon in ethylene is\[s{p^2}\] hybridization
B. Each carbon in acetylene is\[s{p^3}\] hybridization
C. Each carbon in benzene is\[s{p^2}\] hybridization
D. Each carbon in ethane is\[s{p^3}\] hybridization
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Molecules possess shapes.
The fundamental idea in molecular shapes is known as valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) which says that electron pairs repel each other and try to increase the distance from each other.
Complete step by step solution:Here we have to find out which of the given statements is true.
We have to find out the hybridization present in ethylene, acetylene, benzene, and ethane.
There are two types of electron groups: single, double, or triple, and lone electron pairs in the VSEPR model.
If we apply VSEPR to simple molecules, we have to first count the number of electron groups around the central atom. It must be remembered that multiple bonds are to be taken as one electron group.
The hybridization will be based on the number of electron groups.
A. Each carbon in ethylene is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization
Its chemical formula is \[{C_2}{H_4}\].
Its structure is \[{H_2}C = C{H_2}\].
Here the carbon atom is double-bonded to another carbon atom and also bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
So, we consider that there are three electron groups present in each carbon atom. Three orbitals are involved.
So, there is \[s{p^2}\]hybridization.
So, A is correct.
B. Each carbon in acetylene is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization
This is a chemical compound with the formula and structure\[H - C \equiv C - H\].
Let us consider the triple bond as a single electron group.
So, there are three electron groups present in each carbon atom.
So, there is sp hybridization.
So, B is incorrect.
C. Each carbon in benzene is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization
This is a chemical compound with the formula\[{C_6}{H_6}\].
Its structure is as follows:-
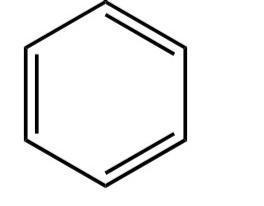
Image: Benzene
Let us consider the double bond as a single electron group.
So, there are three electron groups present in each carbon atom.
So, there is \[s{p^2}\]hybridization.
So, C is correct.
D. Each carbon in ethane is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization
Its chemical formula is \[{C_2}{H_6}\].
Its structure is \[{H_3}C - C{H_3}\].
Here the carbon atom is singly bonded to another carbon atom and also bonded to three other hydrogen atoms.
So, there are four electron groups present in each carbon atom.
So, there is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization.
So, D is correct.
Thus, the statement that each carbon in acetylene is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Note: The shape of\[N{H_3}\]is an instance of a molecule whose central atom carries four electron groups but only three of them are connected to hydrogen atoms. The remaining electron pair is a lone pair.
Due to the repulsion between the lone pair and bond pair, the shape of ammonia is trigonal pyramidal.
The fundamental idea in molecular shapes is known as valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) which says that electron pairs repel each other and try to increase the distance from each other.
Complete step by step solution:Here we have to find out which of the given statements is true.
We have to find out the hybridization present in ethylene, acetylene, benzene, and ethane.
There are two types of electron groups: single, double, or triple, and lone electron pairs in the VSEPR model.
If we apply VSEPR to simple molecules, we have to first count the number of electron groups around the central atom. It must be remembered that multiple bonds are to be taken as one electron group.
The hybridization will be based on the number of electron groups.
A. Each carbon in ethylene is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization
Its chemical formula is \[{C_2}{H_4}\].
Its structure is \[{H_2}C = C{H_2}\].
Here the carbon atom is double-bonded to another carbon atom and also bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
So, we consider that there are three electron groups present in each carbon atom. Three orbitals are involved.
So, there is \[s{p^2}\]hybridization.
So, A is correct.
B. Each carbon in acetylene is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization
This is a chemical compound with the formula and structure\[H - C \equiv C - H\].
Let us consider the triple bond as a single electron group.
So, there are three electron groups present in each carbon atom.
So, there is sp hybridization.
So, B is incorrect.
C. Each carbon in benzene is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization
This is a chemical compound with the formula\[{C_6}{H_6}\].
Its structure is as follows:-

Image: Benzene
Let us consider the double bond as a single electron group.
So, there are three electron groups present in each carbon atom.
So, there is \[s{p^2}\]hybridization.
So, C is correct.
D. Each carbon in ethane is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization
Its chemical formula is \[{C_2}{H_6}\].
Its structure is \[{H_3}C - C{H_3}\].
Here the carbon atom is singly bonded to another carbon atom and also bonded to three other hydrogen atoms.
So, there are four electron groups present in each carbon atom.
So, there is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization.
So, D is correct.
Thus, the statement that each carbon in acetylene is \[s{p^3}\] hybridization is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Note: The shape of\[N{H_3}\]is an instance of a molecule whose central atom carries four electron groups but only three of them are connected to hydrogen atoms. The remaining electron pair is a lone pair.
Due to the repulsion between the lone pair and bond pair, the shape of ammonia is trigonal pyramidal.
Recently Updated Pages
Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Admit Card Out, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




