
Which of the following symbols is used for capacitance in circuits?
A)
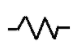
B)
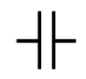
C)
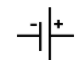
D)
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The symbol itself shows the meaning of what they are. When analysing the components deeply, the working principle and arrangements have similarities with the symbols which denote the component. Capacitors have two parallel plates arranged within it.
Complete step by step solution:
Let's discuss some components and how to denote all those in an electrical circuit with the help of a diagram:
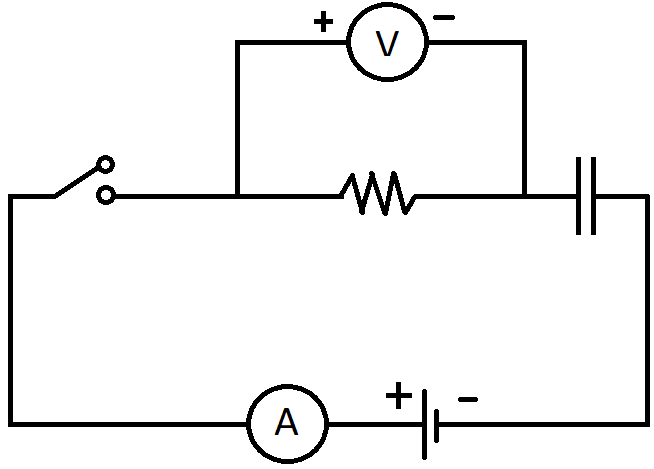
Capacitor: We all know about electric current, conductance, and resistance. But, the capacitance is another important part of understanding the concept of electricity. Capacitors are capable of storing electric charge. A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field.
In its simplest form, a capacitor consists of two conducting plates separated by an insulating material called the dielectric. The capacitance is directly proportional to the surface areas of the plates, and is inversely proportional to the separation between the plates.
Now we know that the capacitor is an arrangement of two parallel plates. And from that information we can understand how a capacitor is denoted or what the symbol of a capacitor is in an electric circuit.
We can see the capacitor denoted as two parallel line in the circuit
That is,
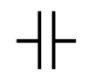
So, the final Answer is Option (B).
Note: The other three symbols are:
Resistor: We know, a resistor is a passive two terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. Ohm’s law states that current flowing through a material is directly proportional to voltage applied across that material and the proportionality constant is the resistance of the material at a constant temperature.
Resistor is denoted by the symbol:
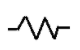
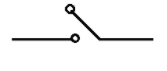
Electric Switch is denoted by the symbol:
DC supply is denoted by the symbol:
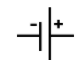
Complete step by step solution:
Let's discuss some components and how to denote all those in an electrical circuit with the help of a diagram:

Capacitor: We all know about electric current, conductance, and resistance. But, the capacitance is another important part of understanding the concept of electricity. Capacitors are capable of storing electric charge. A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field.
In its simplest form, a capacitor consists of two conducting plates separated by an insulating material called the dielectric. The capacitance is directly proportional to the surface areas of the plates, and is inversely proportional to the separation between the plates.
Now we know that the capacitor is an arrangement of two parallel plates. And from that information we can understand how a capacitor is denoted or what the symbol of a capacitor is in an electric circuit.
We can see the capacitor denoted as two parallel line in the circuit
That is,
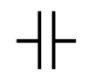
So, the final Answer is Option (B).
Note: The other three symbols are:
Resistor: We know, a resistor is a passive two terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. Ohm’s law states that current flowing through a material is directly proportional to voltage applied across that material and the proportionality constant is the resistance of the material at a constant temperature.
Resistor is denoted by the symbol:
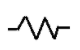
Electric Switch is denoted by the symbol:

DC supply is denoted by the symbol:
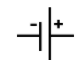
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




