
Which of the following statements about benzyl chloride is incorrect?
A. It is less reactive than alkyl halides.
B. It can be oxidised to benzaldehyde by boiling with copper nitrate solution.
C. It is a lachrymatory liquid and answers Beilstein’s test.
D. It gives a white precipitate with alcoholic silver nitrate.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Benzyl chloride is an alkyl halide with the chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl\]. It is not an aryl halide, and its carbocation is very stable.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Benzyl chloride (\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl\]) is an alkyl halide where chlorine is present on the side chain as a substituent. The chlorine atom is not directly attached to the benzene ring. Its structure is shown below:

Image: Structures of benzyl chloride and the benzyl group.
Let’s go through each statement and assess its accuracy.
Statement A
In benzyl chloride, the chlorine atom can leave as a chloride anion (\[C{l^ - }\]) leaving behind a benzyl carbocation as shown below:
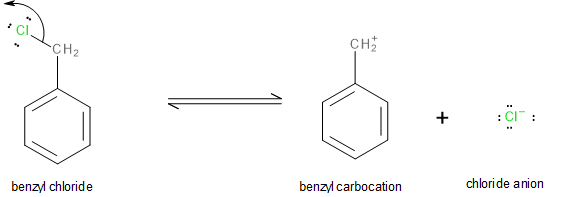
Image: Formation of benzyl carbocation.
The benzyl carbocation thus formed is a very stable intermediate. This is because it exhibits a very strong resonance (-R effect) which allows the excess positive charge to disperse all over the benzene ring as shown here:
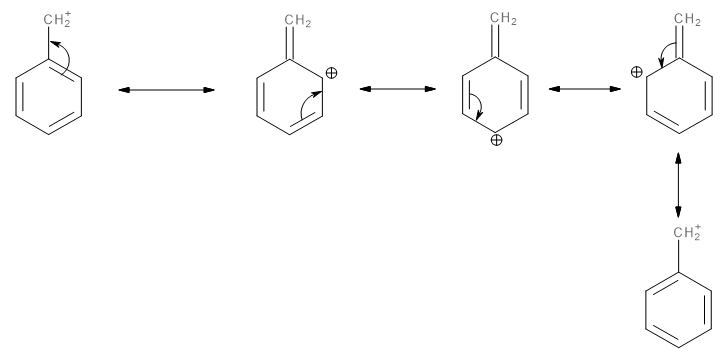
Image: Resonating structures of benzyl carbocation.
The high stability of the benzyl carbocation makes it prone to nucleophilic attacks. Thus, the reactivity of benzyl chloride towards\[{S_N}1\] reactions increases compared to alkyl halides since alkyl halides form alkyl carbocations which do not exhibit resonance and therefore, are less stable.
Thus, statement A is incorrect.
Statement B
This statement is correct since benzyl chloride can be oxidised into benzaldehyde by boiling with copper nitrate solution in the presence of carbon dioxide.
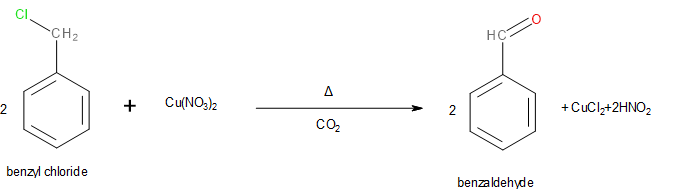
Image: Oxidation of benzyl chloride into benzaldehyde.
Statement C
This statement is also true. Benzyl chloride stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal glands in the eyes to produce tears. Benzyl chloride is an irritant as well and has been used for chemical warfare.
Beilstein’s test of benzyl chloride involves heating a copper wire on a flame first, dipping it into a benzyl chloride solution followed by heating it over a flame. Heating the copper wire on the flame first forms a coating \[CuO\]which reacts with the benzyl chloride solution form \[CuC{l_2}\].\[CuC{l_2}\]burns with a green flame.
Statement D
Benzyl chloride can easily dissociate into benzyl carbocation and a chloride anion which can then go on to react with alcoholic silver nitrate (\[AgN{O_3}\]) to form a white precipitate of silver chloride (\[AgCl\]). Thus, this statement is true as well.
Thus, option A is correct.
Note: In statement A, if the reactivity was explicitly mentioned to be towards a\[{S_N}2\]reaction, then statement A would have been incorrect since the benzene ring is quite bulky which will make the back-side attack of a nucleophile quite difficult. Benzyl chloride prefers to react the\[{S_N}1\]way.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Benzyl chloride (\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl\]) is an alkyl halide where chlorine is present on the side chain as a substituent. The chlorine atom is not directly attached to the benzene ring. Its structure is shown below:

Image: Structures of benzyl chloride and the benzyl group.
Let’s go through each statement and assess its accuracy.
Statement A
In benzyl chloride, the chlorine atom can leave as a chloride anion (\[C{l^ - }\]) leaving behind a benzyl carbocation as shown below:

Image: Formation of benzyl carbocation.
The benzyl carbocation thus formed is a very stable intermediate. This is because it exhibits a very strong resonance (-R effect) which allows the excess positive charge to disperse all over the benzene ring as shown here:

Image: Resonating structures of benzyl carbocation.
The high stability of the benzyl carbocation makes it prone to nucleophilic attacks. Thus, the reactivity of benzyl chloride towards\[{S_N}1\] reactions increases compared to alkyl halides since alkyl halides form alkyl carbocations which do not exhibit resonance and therefore, are less stable.
Thus, statement A is incorrect.
Statement B
This statement is correct since benzyl chloride can be oxidised into benzaldehyde by boiling with copper nitrate solution in the presence of carbon dioxide.

Image: Oxidation of benzyl chloride into benzaldehyde.
Statement C
This statement is also true. Benzyl chloride stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal glands in the eyes to produce tears. Benzyl chloride is an irritant as well and has been used for chemical warfare.
Beilstein’s test of benzyl chloride involves heating a copper wire on a flame first, dipping it into a benzyl chloride solution followed by heating it over a flame. Heating the copper wire on the flame first forms a coating \[CuO\]which reacts with the benzyl chloride solution form \[CuC{l_2}\].\[CuC{l_2}\]burns with a green flame.
Statement D
Benzyl chloride can easily dissociate into benzyl carbocation and a chloride anion which can then go on to react with alcoholic silver nitrate (\[AgN{O_3}\]) to form a white precipitate of silver chloride (\[AgCl\]). Thus, this statement is true as well.
Thus, option A is correct.
Note: In statement A, if the reactivity was explicitly mentioned to be towards a\[{S_N}2\]reaction, then statement A would have been incorrect since the benzene ring is quite bulky which will make the back-side attack of a nucleophile quite difficult. Benzyl chloride prefers to react the\[{S_N}1\]way.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




