
Which of the following organic compound will give a mixture of \[1 - \]chloro butane and \[2 - \]chlorobutane on chlorination
A. 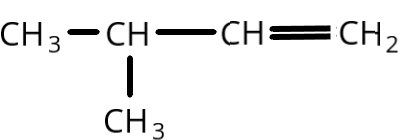
B. 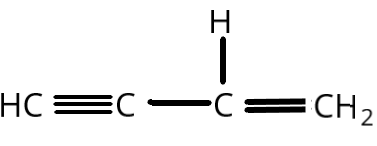
C. \[C{H_2} = CH - CH = C{H_2}\]
D. \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alkenes undergo chlorination reactions in which the chlorine atom added to the carbon atom which was earlier forms a double bond. Alkenes can be chlorinated using hydrogen chloride according to the Markovnikov addition rule to give a major product.
Complete Step-by-Step Explanation:
In order to know that alkanes get chlorinated when chlorine is added to them. Another name for it is hydrogen halogenation. Halogenation typically takes place in hot or sunny environments. An illustration of an addition reaction is hydrogen halogenation reaction. An electrophilic addition has occurred. In this location, hydrogen chloride oxidized to protons and chloride ions. A carbocation is created when the proton is bound to the alkene breaking the double bond. Rearrangements can then take place to create a more stable carbocation. The product is then attacked by chlorine.
An alkene with four carbons and a double bond at the first carbon can be chlorinated to produce the required products. Here, only the products \[1 - \]chlorobutane and \[2 - \]chlorobutane can occur if the double bond is present in the first carbon.
Therefore, the correct option is: (D) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\].
Option ‘D ’ is correct
Note: It should be noted that the electron donation makes the double bond(=) more reactive and abundant in the alkyl groups' electrons. In contrast, the double bond becomes less reactive and electron-deficient when electron-withdrawing groups, such as floro, nitro, are present.
Complete Step-by-Step Explanation:
In order to know that alkanes get chlorinated when chlorine is added to them. Another name for it is hydrogen halogenation. Halogenation typically takes place in hot or sunny environments. An illustration of an addition reaction is hydrogen halogenation reaction. An electrophilic addition has occurred. In this location, hydrogen chloride oxidized to protons and chloride ions. A carbocation is created when the proton is bound to the alkene breaking the double bond. Rearrangements can then take place to create a more stable carbocation. The product is then attacked by chlorine.
An alkene with four carbons and a double bond at the first carbon can be chlorinated to produce the required products. Here, only the products \[1 - \]chlorobutane and \[2 - \]chlorobutane can occur if the double bond is present in the first carbon.
Therefore, the correct option is: (D) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\].
Option ‘D ’ is correct
Note: It should be noted that the electron donation makes the double bond(=) more reactive and abundant in the alkyl groups' electrons. In contrast, the double bond becomes less reactive and electron-deficient when electron-withdrawing groups, such as floro, nitro, are present.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




