
Which of the following is the most stable
A. $1-butene$
B. $2-butene$
C. $1-pentene$
D. $2-pentene$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here we have four alkenes in the given options. The stability of alkenes depends on the number of alkyl substituents, conjugation, and many other factors. To solve this question first we will have to draw the structures of the given alkenes one by one for deciding their stability.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Alkenes are one kind of hydrocarbon containing the carbon-carbon double bond ($C=C$). There are many factors on which the stability of alkenes depends.
a. Alkenes with a higher number of alkyl substituents across the double bond are more stable. It is found that tetrasubstituted alkene is more stable than trisubstituted and monosubstituted alkene.
b. Alkenes with a greater number of hyperconjugation structures are considered to be more stable.
c. Alkenes with conjugation are more stable and have lower energy because of resonance between two double bonds.
d. Trans alkenes are found to be more stable than cis alkenes. As cis alkenes have higher steric hindrance.
Now we can decide the stability of the given alkenes depending upon written factors.
The structures of $1-butene$, $2-butene$,$1-pentene$and $2-pentene$are shown below:
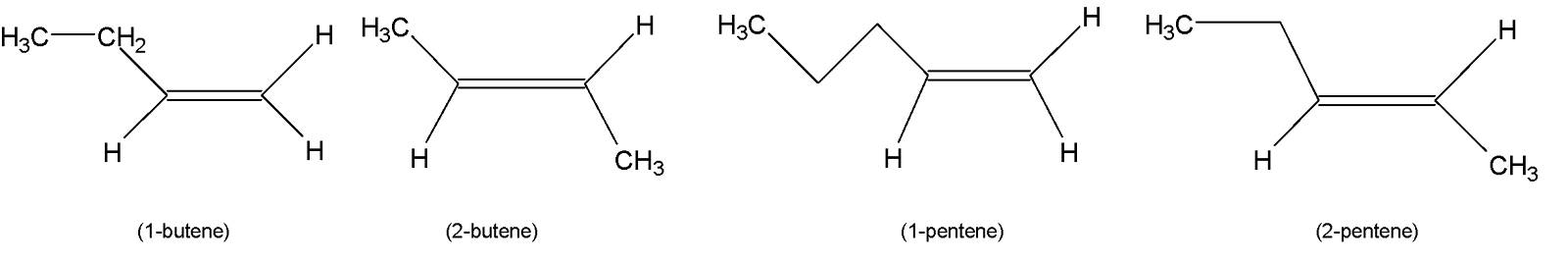
$1-butene$and $1-pentene$ are mono-substituted alkenes Whereas $2-butene$and $2-pentene$are disubstituted alkenes. Again disubstituted alkenes are more stable than mono-substituted alkenes. Now the two di-substituted alkenes $2-pentene$have a higher number of alkylated carbon atoms and are hence more stable than the other due to $(+R)$ the effect of the alkyl group.
Therefore $2-pentene$ is the most stable alkene among the four options.
Thus, option (D) correct.
Note: When two sets of electrons share a double bond is formed. There are four electrons that are shared between two atoms in a double bond. A double bond is formed by covalent bonds. Double bonds are more stable than single bonds and hence require higher energy to break the bonded atoms apart.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Alkenes are one kind of hydrocarbon containing the carbon-carbon double bond ($C=C$). There are many factors on which the stability of alkenes depends.
a. Alkenes with a higher number of alkyl substituents across the double bond are more stable. It is found that tetrasubstituted alkene is more stable than trisubstituted and monosubstituted alkene.
b. Alkenes with a greater number of hyperconjugation structures are considered to be more stable.
c. Alkenes with conjugation are more stable and have lower energy because of resonance between two double bonds.
d. Trans alkenes are found to be more stable than cis alkenes. As cis alkenes have higher steric hindrance.
Now we can decide the stability of the given alkenes depending upon written factors.
The structures of $1-butene$, $2-butene$,$1-pentene$and $2-pentene$are shown below:

$1-butene$and $1-pentene$ are mono-substituted alkenes Whereas $2-butene$and $2-pentene$are disubstituted alkenes. Again disubstituted alkenes are more stable than mono-substituted alkenes. Now the two di-substituted alkenes $2-pentene$have a higher number of alkylated carbon atoms and are hence more stable than the other due to $(+R)$ the effect of the alkyl group.
Therefore $2-pentene$ is the most stable alkene among the four options.
Thus, option (D) correct.
Note: When two sets of electrons share a double bond is formed. There are four electrons that are shared between two atoms in a double bond. A double bond is formed by covalent bonds. Double bonds are more stable than single bonds and hence require higher energy to break the bonded atoms apart.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




