
Which of the following gem diols is stable?
A. \[\;C{H_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\]
B. \[\;CB{r_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\]
C. \[\;C{F_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\]
D. \[\;{C_6}{H_5} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - {C_6}{H_5}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxyl group is bound with a saturated carbon atom. Primary alcohol(ethanol) is used as a drug. Based on the number of \[ - OH\] groups there are two kinds of alcohol, one is gem diol and the other one is a vicinal diol.
Complete step by step answer:
When the two \[ - OH\] groups are attached at the same carbon of the organic compound then it is called gem diol. And when the \[ - OH\] groups are in two different but neighboring carbon then it is called vicinal diol.
The gem diols are less stable than vicinal diols
The stability of gem diols can be increased in the presence of the electron-withdrawing group at the alpha position. +I effect decreases the stability of the gem diol and increases the extent of dehydration as follows.
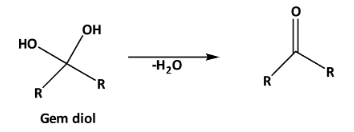
And -I effect increases the stability of gem diol. As well as the intramolecular hydrogen bonding also increases the stability of gem diol.
In the case of \[\;C{H_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\] the methyl group shows the positive inductive effect, as a result, the stability decreases, and dehydration of this gem diol takes place.
In the case of \[\;{C_6}{H_5} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - {C_6}{H_5}\] the two phenyl groups show a positive resonance effect, as a result, the stability decreases, and dehydration of this gem diol takes place.
In the case of \[\;CB{r_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\] the electronegativity of bromine is less, as a result, the stability decreases, and dehydration of this gem diol takes place.
But in case of \[\;C{F_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\] due to the highest electronegativity of fluorine this gem diol is stable.
Therefore, considering the stability factor of gem diol the most stable gem diol is \[\;C{F_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\].
The correct answer is C.
Note: The vicinal diols can be formed by oxidation of the double bonds. For example, when acidified \[\;KMn{O_4}\] reacts with cyclohexene oxidation of the double bonds takes place and vicinal diol is formed as follows,
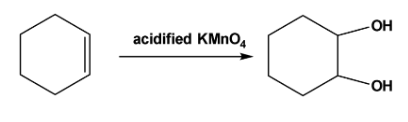
Complete step by step answer:
When the two \[ - OH\] groups are attached at the same carbon of the organic compound then it is called gem diol. And when the \[ - OH\] groups are in two different but neighboring carbon then it is called vicinal diol.
The gem diols are less stable than vicinal diols
The stability of gem diols can be increased in the presence of the electron-withdrawing group at the alpha position. +I effect decreases the stability of the gem diol and increases the extent of dehydration as follows.

And -I effect increases the stability of gem diol. As well as the intramolecular hydrogen bonding also increases the stability of gem diol.
In the case of \[\;C{H_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\] the methyl group shows the positive inductive effect, as a result, the stability decreases, and dehydration of this gem diol takes place.
In the case of \[\;{C_6}{H_5} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - {C_6}{H_5}\] the two phenyl groups show a positive resonance effect, as a result, the stability decreases, and dehydration of this gem diol takes place.
In the case of \[\;CB{r_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\] the electronegativity of bromine is less, as a result, the stability decreases, and dehydration of this gem diol takes place.
But in case of \[\;C{F_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\] due to the highest electronegativity of fluorine this gem diol is stable.
Therefore, considering the stability factor of gem diol the most stable gem diol is \[\;C{F_3} - C{\left( {OH} \right)_2} - H\].
The correct answer is C.
Note: The vicinal diols can be formed by oxidation of the double bonds. For example, when acidified \[\;KMn{O_4}\] reacts with cyclohexene oxidation of the double bonds takes place and vicinal diol is formed as follows,

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




