
Which of the following figures is correct when a monochromatic light passes through a prism?
A)
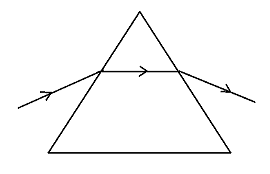
B)
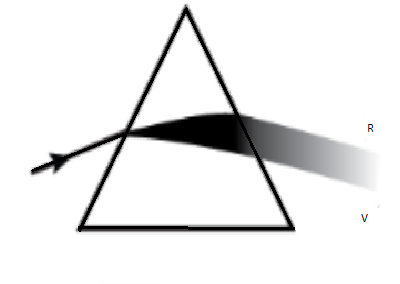
C)

D) None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Monochromatic light is a single colored light which is electromagnetic radiation derived from electromagnetic radiation from the atoms. Such lights have only one color and single wavelength. When white light passes through a prism it splits into its component colors. Monochromatic light has no such components.
Complete step by step solution:
Monochromatic lights are obtained when photons emission takes place. During this process the electromagnetic radiation leads to the production of monochromatic light. It is not made up of any components of visible light. When a monochromatic light is directed to pass through a substance or material, it induces transitions which are characteristic to the chemical properties of the constituent elements of such material.
When white light is made to pass through a prism it splits into its component colors. Since there are seven different colors of which visible light is made up of. Hence they split based on their wavelength. Similar thing happens when a monochromatic beam of light is made to pass through a prism. The monochromatic light will have some wavelength. The light will have some angle of deviation when it emerges out from the prism. Just like any single visible ray of light. The angle of deviation will depend on the wavelength of light.
From the above discussion, it is clear that monochromatic light when passed through prism will have some angle of deviation but it won’t split into any component of light. Also the light won't travel in a straight line when it emerges out of the prism.
Hence Option A is the correct option.
Note: It should be noted that monochromatic is single colored light ray.
Monochromatic light is one of the light as observed in the spectrum of visible light. As the spectrum of white light has some angle of deviation when it passes through prism, hence monochromatic light will also have some angle of deviation.
Complete step by step solution:
Monochromatic lights are obtained when photons emission takes place. During this process the electromagnetic radiation leads to the production of monochromatic light. It is not made up of any components of visible light. When a monochromatic light is directed to pass through a substance or material, it induces transitions which are characteristic to the chemical properties of the constituent elements of such material.
When white light is made to pass through a prism it splits into its component colors. Since there are seven different colors of which visible light is made up of. Hence they split based on their wavelength. Similar thing happens when a monochromatic beam of light is made to pass through a prism. The monochromatic light will have some wavelength. The light will have some angle of deviation when it emerges out from the prism. Just like any single visible ray of light. The angle of deviation will depend on the wavelength of light.
From the above discussion, it is clear that monochromatic light when passed through prism will have some angle of deviation but it won’t split into any component of light. Also the light won't travel in a straight line when it emerges out of the prism.
Hence Option A is the correct option.
Note: It should be noted that monochromatic is single colored light ray.
Monochromatic light is one of the light as observed in the spectrum of visible light. As the spectrum of white light has some angle of deviation when it passes through prism, hence monochromatic light will also have some angle of deviation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




