
Which of the following does not have a tetrahedral structure?
(A) \[{\text{SO}}_4^{ - 2}\]
(B) \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\]
(C) \[{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}\]
(D) \[{\text{SeO}}_4^{ - 2}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Based on the number of electron pairs that surround the central metal atom, in a molecule, VSEPR theory predicts the shape and geometry of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer: VSEPR theory states that electron pairs repel each other and hence atoms in a molecule will always arrange themselves in a manner such that there is minimum repulsion between their electron pairs. This arrangement directly affects the shape and geometry of the molecule. Based on this assumption, let us take a look at the shapes of the molecules mentioned above –
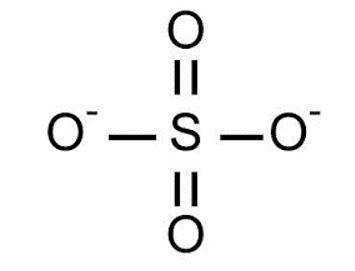
- \[{\text{SO}}_4^{ - 2}\]
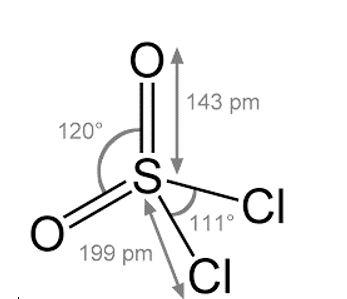
• \[{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}\]
• \[{\text{SeO}}_4^{ - 2}\]

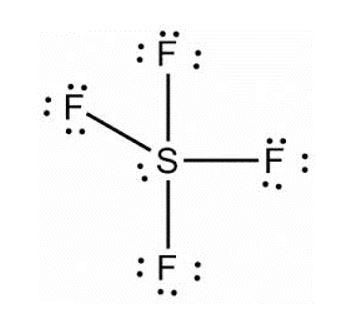
According to VSEPR theory, there are five groups in molecule i.e. one lone pair and 4 bonds around sulphur. This lone pair is present at one of the equatorial positions than the axial ones. Hence, the shape of the molecule is trigonal bipyramidal and not tetragonal.
molecule i.e. one lone pair and 4 bonds around sulphur. This lone pair is present at one of the equatorial positions than the axial ones. Hence, the shape of the molecule is trigonal bipyramidal and not tetragonal.
Hence, option B is correct.
Additional information: According to the VSEPR theory, the repulsion between two electrons is caused by the Pauli exclusion principle. Some important postulates of VSEPR theory are –
- The electron pairs orient themselves in a way that minimizes the electron-electron repulsion between them and maximizes the distance between them.
- If the central atom of the molecule is surrounded by bond pairs of electrons, then the molecule will be asymmetric in shape.
- If the central atom is surrounded by both lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons, the molecule will have a distorted shape.
Note: Out of the options mentioned above, all molecules except \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] have four groups that surround the central atom and hence all have tetrahedral shape.
Complete step by step answer: VSEPR theory states that electron pairs repel each other and hence atoms in a molecule will always arrange themselves in a manner such that there is minimum repulsion between their electron pairs. This arrangement directly affects the shape and geometry of the molecule. Based on this assumption, let us take a look at the shapes of the molecules mentioned above –
- \[{\text{SO}}_4^{ - 2}\]

- • \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\]



According to VSEPR theory, there are five groups in
 molecule i.e. one lone pair and 4 bonds around sulphur. This lone pair is present at one of the equatorial positions than the axial ones. Hence, the shape of the molecule is trigonal bipyramidal and not tetragonal.
molecule i.e. one lone pair and 4 bonds around sulphur. This lone pair is present at one of the equatorial positions than the axial ones. Hence, the shape of the molecule is trigonal bipyramidal and not tetragonal. Hence, option B is correct.
Additional information: According to the VSEPR theory, the repulsion between two electrons is caused by the Pauli exclusion principle. Some important postulates of VSEPR theory are –
- The electron pairs orient themselves in a way that minimizes the electron-electron repulsion between them and maximizes the distance between them.
- If the central atom of the molecule is surrounded by bond pairs of electrons, then the molecule will be asymmetric in shape.
- If the central atom is surrounded by both lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons, the molecule will have a distorted shape.
Note: Out of the options mentioned above, all molecules except \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] have four groups that surround the central atom and hence all have tetrahedral shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




