
Which is poorest reducing agent
A. Nascent hydrogen
B. Atomic hydrogen
C. Dihydrogen
D. All have the same reducing strength
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A substance that donates electrons to the other substances in a redox reaction and oxidises itself to a higher valency state, is termed a reducing agent. To solve this problem, first, we have to understand which hydrogen is less reactive and more stable. Because that stable hydrogen has less tendency to lose electrons.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
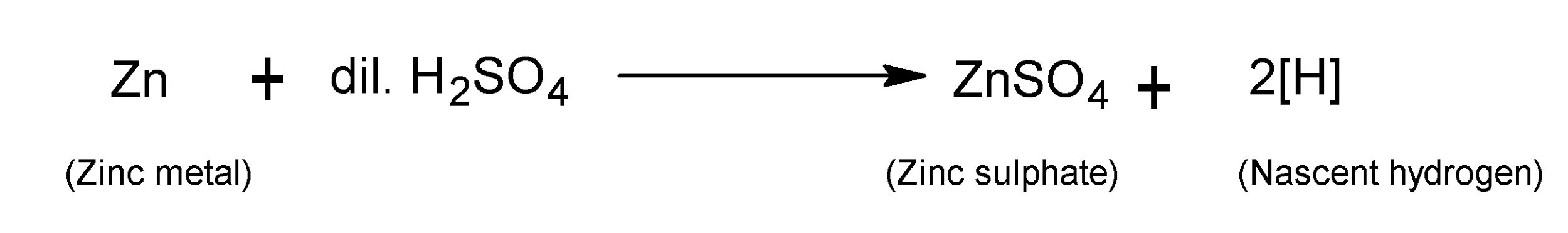
The hydrogen gas that is just liberated as a result of a chemical reaction is known as nascent hydrogen. Nascent hydrogen is produced when zinc is passed through dilute ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
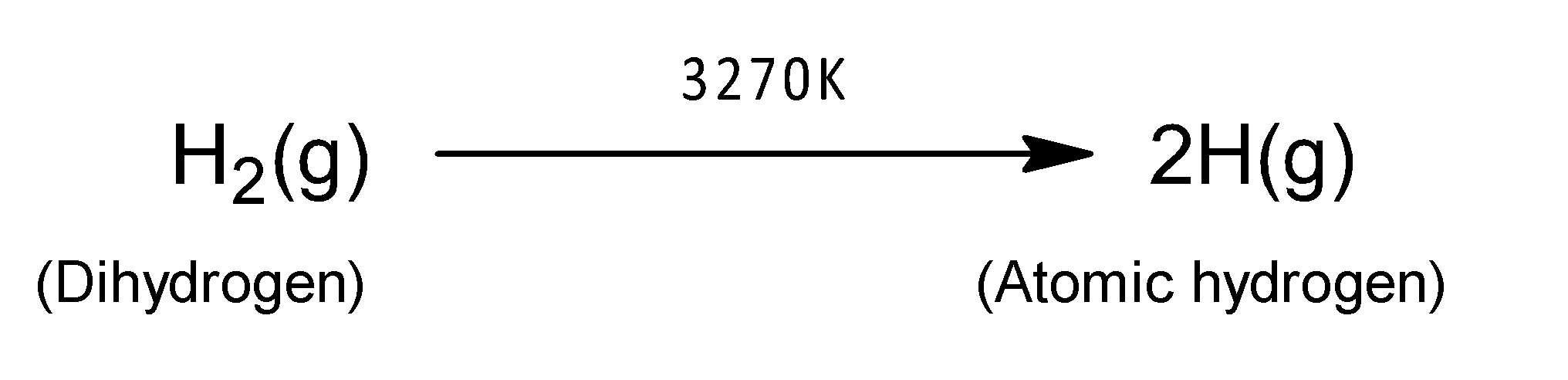
Atomic hydrogen can be formed by passing the electric discharge through molecular hydrogen at very low pressure. It has stronger reducing properties than newly formed nascent hydrogen. It can reduce metal salts like AgCl, CuO, etc. It is formed by hydrogen gas at atmospheric pressure through an electric arc between two tungsten rods at temperature $3270K$ and hydrogen absorbs energy, thereby dissociating into atoms of atomic hydrogen. This hydrogen acts as a very good reducing agent.
Dihydrogen is the weakest reducing agent among the atomic and nascent hydrogen. The reason for its poor reducing nature is that it is less reactive and more stable than other hydrogen.
The order of reducing the strength of hydrogens are :
Atomic hydrogen > Nascent hydrogen > Dihydrogen
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: All metals below the hydrogen in the electrochemical series will be reduced by hydrogen. Hydrogen can reduce oxides of Sn, Pb, Co, Fe, Ni, W, Mo, Cu, etc. All the metals above the hydrogen in this reactivity series will displace hydrogen from dilute acidic solutions.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The hydrogen gas that is just liberated as a result of a chemical reaction is known as nascent hydrogen. Nascent hydrogen is produced when zinc is passed through dilute ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.

Atomic hydrogen can be formed by passing the electric discharge through molecular hydrogen at very low pressure. It has stronger reducing properties than newly formed nascent hydrogen. It can reduce metal salts like AgCl, CuO, etc. It is formed by hydrogen gas at atmospheric pressure through an electric arc between two tungsten rods at temperature $3270K$ and hydrogen absorbs energy, thereby dissociating into atoms of atomic hydrogen. This hydrogen acts as a very good reducing agent.

Dihydrogen is the weakest reducing agent among the atomic and nascent hydrogen. The reason for its poor reducing nature is that it is less reactive and more stable than other hydrogen.
The order of reducing the strength of hydrogens are :
Atomic hydrogen > Nascent hydrogen > Dihydrogen
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: All metals below the hydrogen in the electrochemical series will be reduced by hydrogen. Hydrogen can reduce oxides of Sn, Pb, Co, Fe, Ni, W, Mo, Cu, etc. All the metals above the hydrogen in this reactivity series will displace hydrogen from dilute acidic solutions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




