
Which Colour of light has the highest speed?
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint: Before starting this question, we should know about the “Dispersion of light”. Dispersion is the term used to describe the breaking of visible light into its individual colours. The alteration of the light ray's speed, which creates a different angle of departure for each wavelength, is what causes dispersion of light.
Complete answer:
Splitting of white light
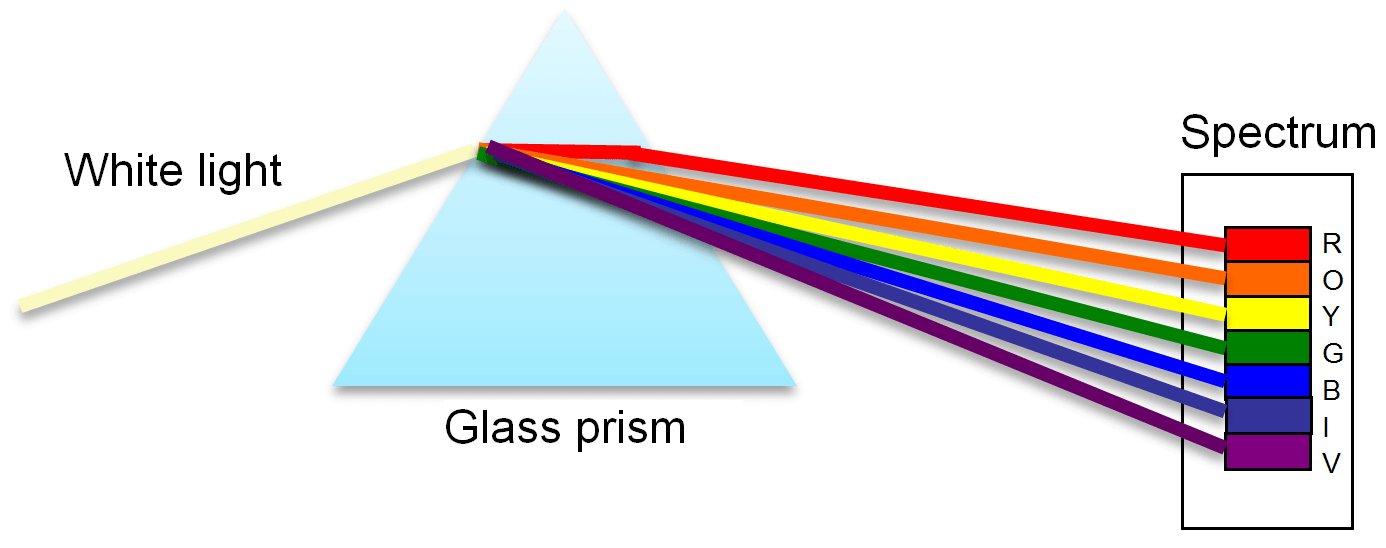
Seven of the colour ranges that make up white light are not visible in a distinct pattern. Dispersion is the term used to describe the division of white light into its individual colours. The seven colours of the rainbow may not always be visible. It is a result of colour overlapping. All seven of the colours that make up white light are divided apart by the degree of bending of the light's path, which is determined by the angle the incident beam of light makes with the surface and the difference in the refractive indices of the two media (Snell's law).
White light can be used to create the band of seven colours by employing a narrow light beam, glass prism, and lens configuration. It is known as the spectrum. Spectrums come in a variety of forms.
The speed of different colours of light varies. When light travels through a prism, it bends the light in diverse ways, causing it to spread out rather than combine. Red goes the fastest, so it is on top, and violet travels the slowest, so it is at the bottom.
Note:It is not required for the light source to always be white in order to obtain a spectrum. A band of three to four colours is also produced by composite light, which has a range of three to four colours. Black (or dark) denotes the absence of light rays, while white light is composed of the seven visible colours (VIBGYOR).
Complete answer:
Splitting of white light

Seven of the colour ranges that make up white light are not visible in a distinct pattern. Dispersion is the term used to describe the division of white light into its individual colours. The seven colours of the rainbow may not always be visible. It is a result of colour overlapping. All seven of the colours that make up white light are divided apart by the degree of bending of the light's path, which is determined by the angle the incident beam of light makes with the surface and the difference in the refractive indices of the two media (Snell's law).
White light can be used to create the band of seven colours by employing a narrow light beam, glass prism, and lens configuration. It is known as the spectrum. Spectrums come in a variety of forms.
The speed of different colours of light varies. When light travels through a prism, it bends the light in diverse ways, causing it to spread out rather than combine. Red goes the fastest, so it is on top, and violet travels the slowest, so it is at the bottom.
Note:It is not required for the light source to always be white in order to obtain a spectrum. A band of three to four colours is also produced by composite light, which has a range of three to four colours. Black (or dark) denotes the absence of light rays, while white light is composed of the seven visible colours (VIBGYOR).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




