
When\[C{H_3}C{H_2}CHC{l_2}\] is treated with $NaN{H_2}$ , the product formed is:
A.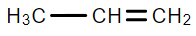
B.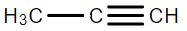
C.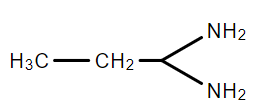
D.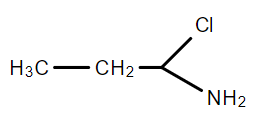
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question recall the methods for the preparation of alkyne from dihalides. Sodium amide is a strong reducing agent which removes the halide atoms and generates an alkyne.
Complete Step by step answer:
We know that Sodium amide ($NaN{H_2}$) is a strong base and is used for deprotonation of weak acids and also for elimination reactions. Treatment of either geminal dihalide (two halogens on one carbon) or vicinal dihalides (halogens on adjacent carbons) with two equivalents of $NaN{H_2}$ results in the formation of alkynes.
Understanding the mechanism of this reaction is important: First, there is deprotonation of functional groups which is what is known as initiation of an elimination reaction. In this case, halide atoms are removed to form the alkene. Specifically, this is an example of an E2 (elimination 2) reaction.
Since the alkene still has a halide attached, this too can be removed to generate a second double bond (π bond).
The mechanism of this reaction can be shown as:
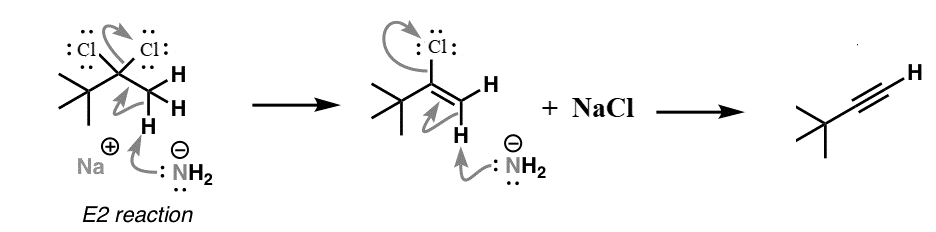
We can see from the above reaction that we receive an alkyne as the major product of the reaction.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note: We should keep in mind the formation of terminal alkynes by use of this reaction mechanism. The acidity of terminal alkynes plays an important role in major product determination when dihalides undergo base induced elimination reactions. High electronegativity of the triple bond in terminal alkynes makes the molecule acidic. Therefore, one of the base molecules will pull off the terminal hydrogen instead of one of the halides like we desire to happen in this reaction. This implies that we would need three bases for every terminal haloalkane instead of two to obtain an alkyne.
Complete Step by step answer:
We know that Sodium amide ($NaN{H_2}$) is a strong base and is used for deprotonation of weak acids and also for elimination reactions. Treatment of either geminal dihalide (two halogens on one carbon) or vicinal dihalides (halogens on adjacent carbons) with two equivalents of $NaN{H_2}$ results in the formation of alkynes.
Understanding the mechanism of this reaction is important: First, there is deprotonation of functional groups which is what is known as initiation of an elimination reaction. In this case, halide atoms are removed to form the alkene. Specifically, this is an example of an E2 (elimination 2) reaction.
Since the alkene still has a halide attached, this too can be removed to generate a second double bond (π bond).
The mechanism of this reaction can be shown as:

We can see from the above reaction that we receive an alkyne as the major product of the reaction.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note: We should keep in mind the formation of terminal alkynes by use of this reaction mechanism. The acidity of terminal alkynes plays an important role in major product determination when dihalides undergo base induced elimination reactions. High electronegativity of the triple bond in terminal alkynes makes the molecule acidic. Therefore, one of the base molecules will pull off the terminal hydrogen instead of one of the halides like we desire to happen in this reaction. This implies that we would need three bases for every terminal haloalkane instead of two to obtain an alkyne.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




