
What is the formula for sine waves?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:The sine wave is described as the waveform in which the amplitudes are always proportional to the displacement angle at every point. The sine or sinusoidal wave is a curve that describes the smooth repetitive oscillation.
Complete step by step solution:
A Sinusoidal wave is a form of the geometrical wave which oscillates up, down, right and left. It is used to reduce the complexity of the wave that is coming in the mathematical formulation. The basic formulation of the sine wave is written as;
\[y(t) = A\sin (2\pi ft + \varphi )\]
And it is also written it as;
\[y(t) = A\sin (\omega t + \varphi )\]
here, $\omega = 2\pi ft$
The sine wave is shown in the figure below,
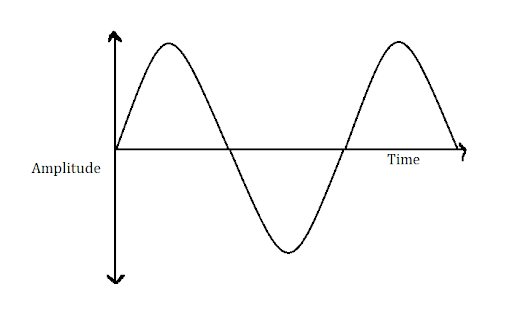
Image: Sinusoidal wave
In the mathematical expression we have the following representation which is defined as;
1. $A$ is defined as the amplitude of the sine wave. It is defined as the maximum displacement or distance covered by the sinusoidal wave when the body is vibrating.
2. $f$ is defined as the frequency. It is defined as the number of repeating events that can occur at a particular time.
3. $t$ is known as the time period of vibration.
4. $\varphi $ is known as a phase. It is defined as the relationship between the two sine waves.
5. $\omega $ is known as the angular frequency.
Hence formula of sine wave is \[y(t) = A\sin (\omega t + \varphi )\].
Note: There are three characteristics that separate the two or more sinusoid waves from each other. These characteristics are known as amplitude. Frequency and the phase. The application of the sine wave is that it is used in the transmission because it is a more efficient form of a wave as compared to the other waves.
Complete step by step solution:
A Sinusoidal wave is a form of the geometrical wave which oscillates up, down, right and left. It is used to reduce the complexity of the wave that is coming in the mathematical formulation. The basic formulation of the sine wave is written as;
\[y(t) = A\sin (2\pi ft + \varphi )\]
And it is also written it as;
\[y(t) = A\sin (\omega t + \varphi )\]
here, $\omega = 2\pi ft$
The sine wave is shown in the figure below,

Image: Sinusoidal wave
In the mathematical expression we have the following representation which is defined as;
1. $A$ is defined as the amplitude of the sine wave. It is defined as the maximum displacement or distance covered by the sinusoidal wave when the body is vibrating.
2. $f$ is defined as the frequency. It is defined as the number of repeating events that can occur at a particular time.
3. $t$ is known as the time period of vibration.
4. $\varphi $ is known as a phase. It is defined as the relationship between the two sine waves.
5. $\omega $ is known as the angular frequency.
Hence formula of sine wave is \[y(t) = A\sin (\omega t + \varphi )\].
Note: There are three characteristics that separate the two or more sinusoid waves from each other. These characteristics are known as amplitude. Frequency and the phase. The application of the sine wave is that it is used in the transmission because it is a more efficient form of a wave as compared to the other waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)




