
What is \[C\] Double Bond called?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Double bonds are created when two atoms trade two pairs of electrons. This type of relationship is stronger than a single bond but less stable since it is more reactive than a single bond. The double lines that make up the double bond sign stand in for a double bond between two atoms.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When two substances are linked by a bond and at least four of the connected electrons—rather than just two—are shared, a double bond frequently results. Two carbon monoxide atoms, one hydrogen atom, and one hydrogen atom make up the most common compound with a doubly bonded ingredient.
Alkenes include the double carbon-carbon bonds and are unsaturated hydrocarbons with \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}\] as the molecular formula. This formula for molecules is quite similar to that of cycloalkanes. Alkenes are named using the same general naming conventions as alkanes, with the suffix changing to "ene."
Double bonds in hydrocarbons are demonstrated by changing the suffix "ane" to "ene". Where there are many double bonds, the suffix is changed to add a prefix that specifies how many double bonds are present. In the same way, the suffix "yne" is used to describe triple bonds.
An alkene that has a single alkyl group that is attached to the \[s{p^2}\] the hybridised carbon atom of the double bond is mono-substituted. A terminal alkene is an alkene that has its double bond at the end of the carbon atom chain. Alkenes that contain two, three, or four alkyl groups attached to the double bond's carbon atoms are referred to as di-, tri-, and tetra-substituted, respectively.
For example, Ethene \[({C_2}{H_4})\]is the simplest alkene which is often called by the common name ethylene.
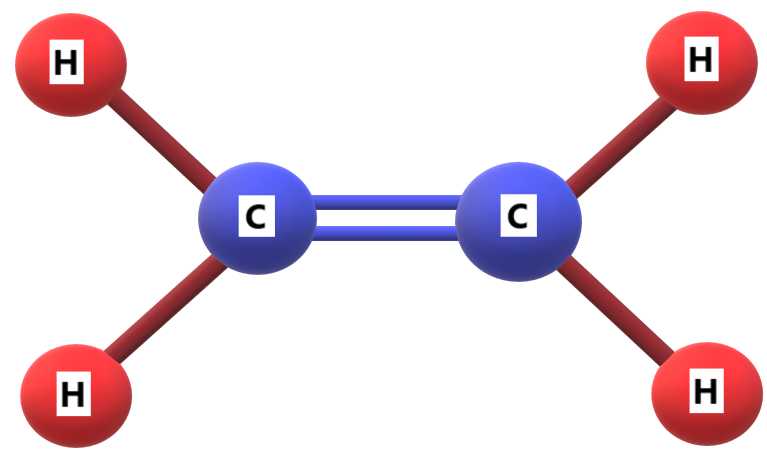
Therefore, \[C\]double bond is called alkenes.
Note: As we know that the alkyl groups bonded to the \[s{p^2}\] hybridised carbon atoms of alkenes affect the stability of the double bond. The chemical reactivity of alkenes also is often affected by the number of alkyl groups that bonded to the \[s{p^2}\] hybridised carbon atoms. Then the alkenes by the number of alkyl groups attached to the \[C = C\] structural unit.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When two substances are linked by a bond and at least four of the connected electrons—rather than just two—are shared, a double bond frequently results. Two carbon monoxide atoms, one hydrogen atom, and one hydrogen atom make up the most common compound with a doubly bonded ingredient.
Alkenes include the double carbon-carbon bonds and are unsaturated hydrocarbons with \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}\] as the molecular formula. This formula for molecules is quite similar to that of cycloalkanes. Alkenes are named using the same general naming conventions as alkanes, with the suffix changing to "ene."
Double bonds in hydrocarbons are demonstrated by changing the suffix "ane" to "ene". Where there are many double bonds, the suffix is changed to add a prefix that specifies how many double bonds are present. In the same way, the suffix "yne" is used to describe triple bonds.
An alkene that has a single alkyl group that is attached to the \[s{p^2}\] the hybridised carbon atom of the double bond is mono-substituted. A terminal alkene is an alkene that has its double bond at the end of the carbon atom chain. Alkenes that contain two, three, or four alkyl groups attached to the double bond's carbon atoms are referred to as di-, tri-, and tetra-substituted, respectively.
For example, Ethene \[({C_2}{H_4})\]is the simplest alkene which is often called by the common name ethylene.

Therefore, \[C\]double bond is called alkenes.
Note: As we know that the alkyl groups bonded to the \[s{p^2}\] hybridised carbon atoms of alkenes affect the stability of the double bond. The chemical reactivity of alkenes also is often affected by the number of alkyl groups that bonded to the \[s{p^2}\] hybridised carbon atoms. Then the alkenes by the number of alkyl groups attached to the \[C = C\] structural unit.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




