
Vinyl chloride reacts with HCl to form major product of
(A) 1,3-dichloroethane
(B) 1,2-dichloroethane
(C) Tetrachloroethylene
(D) 1,1-dichloroethane
Answer
241.5k+ views
Hint: Vinyl chloride is a gas which has no colour. It is toxic and flammable in nature. It is also termed chloroethylene. Globally, it is one of the twenty most used petrochemicals.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's first understand the structure of Vinyl chloride. It is an alkene having one halogen group. The chemical structure of the compound vinyl chloride is,
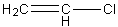
Image: Vinyl Chloride
Let's understand Markovnikov's addition reaction in detail. In Markovnikov's addition, when an alkene or alkyne undergoes a reaction with Hydrogen chloride, a proton gets attached to that C atom of double bond which has the largest count of Hydrogen atoms. And the halogen atom gets added to the other carbon atom present in the double bond.
Here, the reaction of Vinyl chloride with HCl follows Markovnikov's addition. So, the H atom of the HCl gets attached to that carbon atom of the vinyl chloride which has a larger number of H atoms. So, the reaction is,
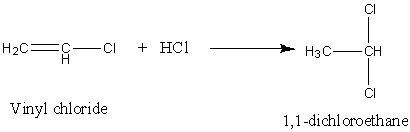
Image: Vinyl chloride undergoes reaction with HCl.
Therefore, the reaction of Vinyl Chloride and HCl gives 1,1-dichloroethane. Hence, option (D) is right.
Additional Information:
In anti-Markovnikov's addition, the addition of the proton to that C atom of the double bond occurs, where there are fewer Hydrogen atoms present. So, it is the opposite of Markovnikov's addition.
Note: Nowadays, exposure to vinyl chloride causes many health impacts. Normally, the exposure occurs because of polluted air and polluted water. Also, workers in the manufacturing industries of vinyl chloride are exposed to vinyl chloride due to inhalation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's first understand the structure of Vinyl chloride. It is an alkene having one halogen group. The chemical structure of the compound vinyl chloride is,
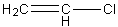
Image: Vinyl Chloride
Let's understand Markovnikov's addition reaction in detail. In Markovnikov's addition, when an alkene or alkyne undergoes a reaction with Hydrogen chloride, a proton gets attached to that C atom of double bond which has the largest count of Hydrogen atoms. And the halogen atom gets added to the other carbon atom present in the double bond.
Here, the reaction of Vinyl chloride with HCl follows Markovnikov's addition. So, the H atom of the HCl gets attached to that carbon atom of the vinyl chloride which has a larger number of H atoms. So, the reaction is,
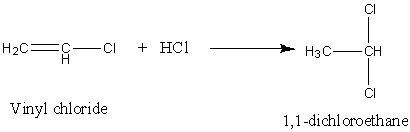
Image: Vinyl chloride undergoes reaction with HCl.
Therefore, the reaction of Vinyl Chloride and HCl gives 1,1-dichloroethane. Hence, option (D) is right.
Additional Information:
In anti-Markovnikov's addition, the addition of the proton to that C atom of the double bond occurs, where there are fewer Hydrogen atoms present. So, it is the opposite of Markovnikov's addition.
Note: Nowadays, exposure to vinyl chloride causes many health impacts. Normally, the exposure occurs because of polluted air and polluted water. Also, workers in the manufacturing industries of vinyl chloride are exposed to vinyl chloride due to inhalation.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




