
Using the truth table, examine whether the following statement pattern is tautology, contradiction and contingency.
$(p\wedge \sim q)\leftrightarrow (p\to q)$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Construct the truth table for $(p\wedge \sim q)\leftrightarrow (p\to q)$ and if all the propositions are true in every row then it is tautology, if all the propositions are false in every row then contradiction and if there is at least one row with true condition and one row with false condition, then it is contingency.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic- specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions and propositional calculus- which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is for each combination of values taken by their logical variables. A truth table can be used to show whether a propositional expression is true for all input values, that is logically valid.
Tautology: A tautology has a logical form that cannot possibly be false no matter what truth values are assigned to the sentence letters.
Contradiction: A tautology has a logical form that cannot possibly be true no matter what truth values are assigned to the sentence letters.
Contingency: A Contingency has a logical form that can be either true or false depending on what truth values are assigned to the sentence letters.
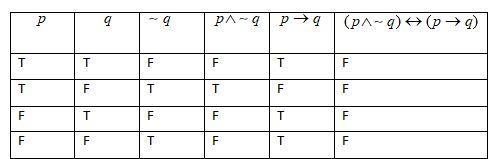
Note: $p\wedge q$ is true when both $p$ and $q$ are true. $p\to q$ is true when $q$ is true or both are false. $p\leftrightarrow q$ is true when both $p$ and $q$ are true or both are false. This is the rule used to draw the above truth table.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic- specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions and propositional calculus- which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is for each combination of values taken by their logical variables. A truth table can be used to show whether a propositional expression is true for all input values, that is logically valid.
Tautology: A tautology has a logical form that cannot possibly be false no matter what truth values are assigned to the sentence letters.
Contradiction: A tautology has a logical form that cannot possibly be true no matter what truth values are assigned to the sentence letters.
Contingency: A Contingency has a logical form that can be either true or false depending on what truth values are assigned to the sentence letters.

Note: $p\wedge q$ is true when both $p$ and $q$ are true. $p\to q$ is true when $q$ is true or both are false. $p\leftrightarrow q$ is true when both $p$ and $q$ are true or both are false. This is the rule used to draw the above truth table.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




