
Urea is [CPMT $1984$]
A.Monoacidic base
B.Diacidic base
C.Neutral
D.Amphoteric
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Urea is an organic compound with chemical formula $CO{{(N{{H}_{2}})}_{2}}$. It is the major nitrogen-containing agent in mammalian urine. The chemical properties such as acidity, basicity, or amphoteric can be understood when urea is dissolved in an aqueous solution. From the ${{P}^{H}}$value, we can understand whether urea is neutral or not. When the solution ${{P}^{H}}=7$ is called neutral.
Complete answer:In urea two $-N{{H}_{2}}$ groups are attached by a carbonyl group ($C=O$). It is a white crystalline solid soluble in aqueous solution and alcoholic solution such as ethanol but insoluble in ether. Under investigation, it is found that the $C-N$bond length $1.37\overset{o}{\mathop{A}}\,$but in aliphatic amines the $C-N$bond length $1.47\overset{o}{\mathop{A}}\,$. The difference in bond length value indicates that urea has some double bond character. This can be explained by the following resonance structures:
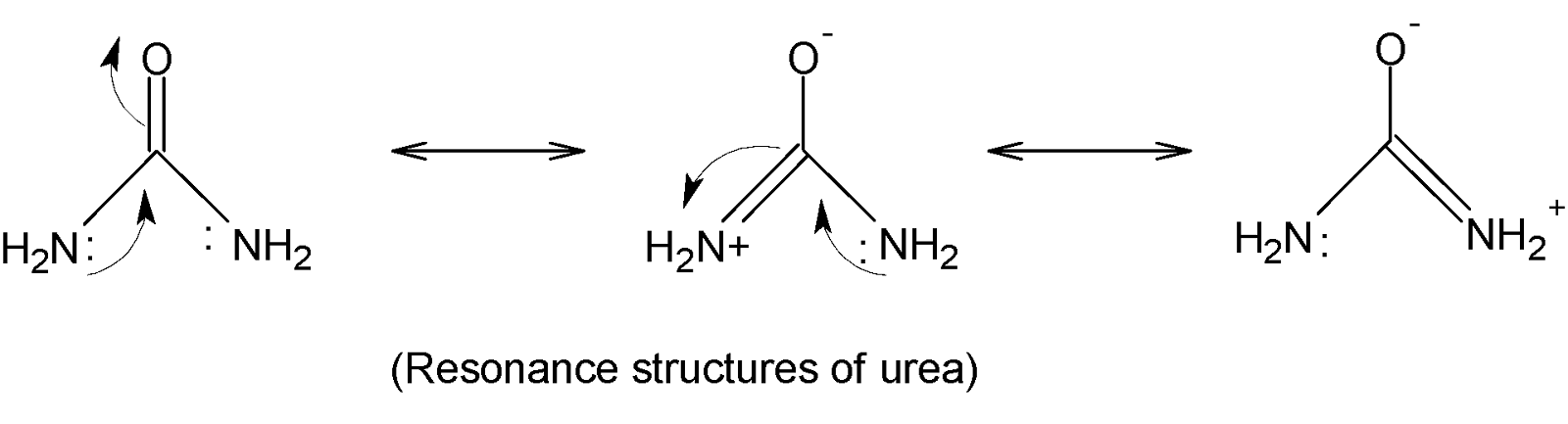
There are three resonance structures and both $C-N$bonds are identical and the negatively charged oxygen atom is capable of coordinating with one proton. Thus, urea acts as a monoacidic base.
This can be explained in another way when urea is dissolved in water, abstracts a proton from water, and leaves $H{{O}^{-}}$an ion in the solution. Thereby urea acts as a monoacidic base. A monoacidic base is a base that forms one $H{{O}^{-}}$ion when one molecule of it undergoes complete ionization. As it is a monobasic acid the
${{P}^{H}}$value is always greater than $7$, hence it is not a neutral compound.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Although urea is a monobasic acid, it is a weaker base than amines and a stronger base than amides The strong basicity of amines is due to the better availability of lone pairs on nitrogen for donation. In amide, the lower basicity is due to the poor availability of lone pair electrons as lone pairs on nitrogen participate in resonance.
Complete answer:In urea two $-N{{H}_{2}}$ groups are attached by a carbonyl group ($C=O$). It is a white crystalline solid soluble in aqueous solution and alcoholic solution such as ethanol but insoluble in ether. Under investigation, it is found that the $C-N$bond length $1.37\overset{o}{\mathop{A}}\,$but in aliphatic amines the $C-N$bond length $1.47\overset{o}{\mathop{A}}\,$. The difference in bond length value indicates that urea has some double bond character. This can be explained by the following resonance structures:

There are three resonance structures and both $C-N$bonds are identical and the negatively charged oxygen atom is capable of coordinating with one proton. Thus, urea acts as a monoacidic base.
This can be explained in another way when urea is dissolved in water, abstracts a proton from water, and leaves $H{{O}^{-}}$an ion in the solution. Thereby urea acts as a monoacidic base. A monoacidic base is a base that forms one $H{{O}^{-}}$ion when one molecule of it undergoes complete ionization. As it is a monobasic acid the
${{P}^{H}}$value is always greater than $7$, hence it is not a neutral compound.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Although urea is a monobasic acid, it is a weaker base than amines and a stronger base than amides The strong basicity of amines is due to the better availability of lone pairs on nitrogen for donation. In amide, the lower basicity is due to the poor availability of lone pair electrons as lone pairs on nitrogen participate in resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




