
What is the type of deformation in plastic deformation?
A) Reversible
B) Permanent
C) Both
D) None
Answer
240k+ views
Hint:The deformation in the elastic region is reversible as the material goes back to its original shape and size on the removal of stress.
Complete step by step solution:
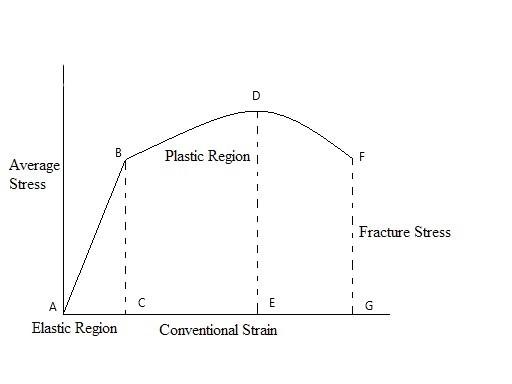
The above stress-strain curve is for a ductile material. In the given stress-strain curve, the part ABC represents the elastic region whereas the part BDFGEC represents the plastic region.
The point B is also known as the elastic limit or proportional limit. Point C on the x-axis represents the strain when stress corresponding to point B is applied on the material.
When stress greater than the elastic limit is applied, the material does not regain its original shape and size even after the removal of the applied stress. After the removal of stress greater than elastic limit, only elastic strain is recovered, the plastic strain remains. This strain that remains is known as a permanent set. It is not recoverable.
In brittle materials, the plastic region is smaller and the material cannot bear a stress much larger than the elastic limit of the material. However, the deformation in the plastic region of brittle materials is also non-recoverable.
Hence, plastic deformation in both brittle and ductile materials is permanent and irreversible.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer for this question.
Note: Deformation is the change in shape or size of an object. It is not the same as strain. Strain is change in dimension per unit dimension of the material or deformation per unit dimension. Deformation has the dimension of length whereas strain is dimensionless.
Complete step by step solution:

The above stress-strain curve is for a ductile material. In the given stress-strain curve, the part ABC represents the elastic region whereas the part BDFGEC represents the plastic region.
The point B is also known as the elastic limit or proportional limit. Point C on the x-axis represents the strain when stress corresponding to point B is applied on the material.
When stress greater than the elastic limit is applied, the material does not regain its original shape and size even after the removal of the applied stress. After the removal of stress greater than elastic limit, only elastic strain is recovered, the plastic strain remains. This strain that remains is known as a permanent set. It is not recoverable.
In brittle materials, the plastic region is smaller and the material cannot bear a stress much larger than the elastic limit of the material. However, the deformation in the plastic region of brittle materials is also non-recoverable.
Hence, plastic deformation in both brittle and ductile materials is permanent and irreversible.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer for this question.
Note: Deformation is the change in shape or size of an object. It is not the same as strain. Strain is change in dimension per unit dimension of the material or deformation per unit dimension. Deformation has the dimension of length whereas strain is dimensionless.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26




