
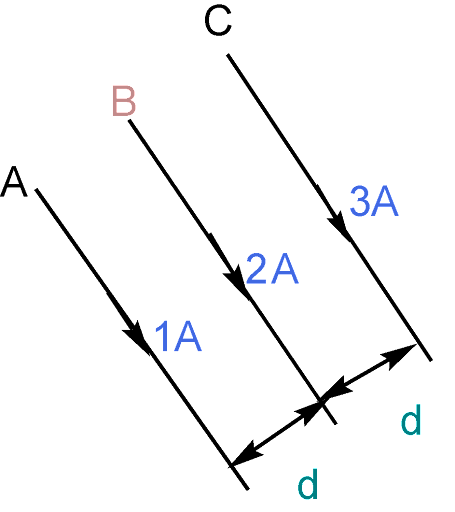
Three long straight wires A, B and C are carrying currents as shown in figure. Then the resultant force on B is directed:
A. perpendicular to the plane of the paper and outward
B. perpendicular to the plane of the paper and inward
C. towards A
D. towards C
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When three current carrying conductors are positioned in parallel to each other, all the conductors apply force on each other. When current is traveling in the same direction the conductors attract each other and when the current is traveling in opposite direction the conductors repel each other.
Formula used:
As there are three wires A, B, and C which are parallel to each other but we need to find the resultant force on B wire. So, for this, B wire experiences force due to wire A and C. So, we find two different cases. For each case, B wire is parallel to other wire and separated by a distance d. So, the force between two wires is defined as
$F=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
Where, $I_1$ and $I_2$ is current in wire 1 and wire 2 (wire A and B or wire C and B). the d is distance between two wires
Complete step by step solution:
When two current-carrying wires are positioned parallel to one another, the magnetic fields of the two wires will interact, creating a force that acts between the wires. Each wire is subject to an equal amount of force, but it is acting in opposing directions. This is accurate even if the conductors carry currents of various strengths.
First, express force between two parallel wires. The force between two parallel wires with currents ${{I}_{1}}$ and ${{I}_{2}}$ and spaced by a distance d is given by
$F=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
Therefore,
$F\propto {{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}$ and $F\propto \dfrac{1}{d}$
Find the more powerful force
Wire B is being drawn toward wire A and C by wire A and wire C.
In both situations, there is an equal distance between the wires.
${{I}_{A}}{{I}_{B}}=(IA)(2A)=3{{A}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{C}}{{I}_{B}}=(3A)(2A)=6{{A}^{2}}$
$\because F\propto {{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}$
$\therefore {{F}_{BC}}>{{F}_{AB}}$
Since, the wire is pulled in the direction of C.
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: It's important to keep in mind that the force acting on one wire is a result of the other wire's magnetic field. The majority of students frequently make errors when determining force on a specific wire by factoring in their own magnetic fields. The force attracts if the currents are flowing in the same direction, and repels if they are flowing in the opposite direction.
Formula used:
As there are three wires A, B, and C which are parallel to each other but we need to find the resultant force on B wire. So, for this, B wire experiences force due to wire A and C. So, we find two different cases. For each case, B wire is parallel to other wire and separated by a distance d. So, the force between two wires is defined as
$F=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
Where, $I_1$ and $I_2$ is current in wire 1 and wire 2 (wire A and B or wire C and B). the d is distance between two wires
Complete step by step solution:
When two current-carrying wires are positioned parallel to one another, the magnetic fields of the two wires will interact, creating a force that acts between the wires. Each wire is subject to an equal amount of force, but it is acting in opposing directions. This is accurate even if the conductors carry currents of various strengths.
First, express force between two parallel wires. The force between two parallel wires with currents ${{I}_{1}}$ and ${{I}_{2}}$ and spaced by a distance d is given by
$F=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}{2\pi d}$
Therefore,
$F\propto {{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}$ and $F\propto \dfrac{1}{d}$
Find the more powerful force
Wire B is being drawn toward wire A and C by wire A and wire C.
In both situations, there is an equal distance between the wires.
${{I}_{A}}{{I}_{B}}=(IA)(2A)=3{{A}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{C}}{{I}_{B}}=(3A)(2A)=6{{A}^{2}}$
$\because F\propto {{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}$
$\therefore {{F}_{BC}}>{{F}_{AB}}$
Since, the wire is pulled in the direction of C.
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: It's important to keep in mind that the force acting on one wire is a result of the other wire's magnetic field. The majority of students frequently make errors when determining force on a specific wire by factoring in their own magnetic fields. The force attracts if the currents are flowing in the same direction, and repels if they are flowing in the opposite direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




